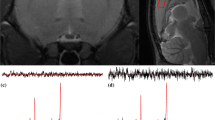
Abstract
When acquired at short echo-time, the proton MRS signals contain contributions from metabolites and water, and a large baseline (‘background’) component. The background contributions in proton short echo-time MRS signals make accurate and reliable quantification difficult. The purpose of the present study was to compare the influence of the background-accommodation strategy on the metabolite concentration estimates at 7 T using QUEST. Two strategies were investigated to accommodate the background, (1) the measured background signal was incorporated in the metabolite basis-set; and (2) the background signal was estimated and subtracted from the in vivo signal using Subtract-QUEST. The influence of the background-accommodation strategy was addressed with the aid of Monte Carlo and in vivo studies. For the signals considered in this study, statistically significant differences between the in vivo concentration estimates using the two approaches were observed for three metabolites namely Cho, NAA, and Tau. The observed underestimation of the ‘background’ estimates using Subtract-QUEST led to an overestimation of these metabolite estimates. Consequently, we can conclude that, including the ‘background’ signal in the metabolite basis-set would lead to more accurate quantifications at higher magnetic field strengths when the differences between the apparent relaxation times of the ‘background’ and the metabolite signals are reduced. However, the use of the Subtract-QUEST method is the method of choice when measurement time is critical especially for diseased animals.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Young, K., Govindaraju, V., Soher, B. J., & Maudsley, A. A. (1998). Automated spectral analysis II: Application of wavelet shrinkage for characterization of non-parameterized signals. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 40, 816–821.
Ratiney, H., Srinivasan, R., Henry, R. G., Okuda, D., Nelson, S. J., & Pelletier, D. (2007). Early and progressive disease marker in MS; Results from a large cross-sectional spectroscopic imaging study at 3 T. In American Academy of Neurology 59th Annual Meeting, Boston, USA, May, pp P02.041.
Hofmann, L., Slotboom, J., Boesch, C., & Kreis, R. (2001). Characterization of the macromolecular baseline in localized 1H-MR spectra of human brain. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 39, 855–863.
Hofmann, L., Slotboom, J., Jung, B., Maloca, P., Boesch, C., & Kreis, R. (2002). Quantitative 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy of human brain: Influence of composition and parametrization of the basis-set in linear combination model-fitting. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 48, 440–453.
Seeger, U., Mader, I., Nagele, T., Grodd, W., Lutz, O., & Klose, U. (2001). Reliable detection of macromolecules in single volume 1H NMR spectra of the human brain. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 45, 948–954.
Seeger, U., Klose, U., Mader, I., Grodd, W., & Nagele, T. (2003). Parameterized evaluation of macromolecules and lipids in proton MR spectroscopy of brain diseases. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 49, 19–28.
Tkac, I., Rao, R., Georgieff, M. K., & Gruetter, R. (2003). Developmental and regional changes in the neurochemical profile of the rat brain determined by in vivo 1H NMR spectroscopy. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 50, 24–32.
Cudalbu, C., Bucur, A., Graveron-Demilly, D., Beuf, O., & Cavassila, S. (2007). Comparison of two strategies of background-accommodation: Influence on the metabolite concentration estimation from in vivo Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy data. Conference of Proceedings IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 2007, 2077–2080.
Kassem, M. N. E., & Bartha, R. (2003). Quantitative proton short-echo-time LASER spectroscopy of normal human white matter and hippocampus at 4 T incorporating macromolecule subtraction. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 49, 918–927.
Rabeson, H., Ratiney, H., Cudalbu, C., Cavassila, S., Capobianco, E., de Beer, R., van Ormondt, D., & Graveron-Demilly, D. (2006). Signal disentanglement in in vivo MR spectroscopy: By semi-parametric processing or by measurement? In Proc. ProRISC, IEEE Benelux, Veldhoven, The Netherlands, pp. 176–183.
Gottschalk, M., Lamalle, L., & Segebarth, C. (2007). Short-TE localized 1H MRS of the human brain at 3 T: Quantification of the metabolite signals using two approaches to account for macromolecular signal contributions. NMR in Biomedicine DOI 10.1002/nbm.1219 (Oct 23)
Provencher, S. W. (1993). Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 30, 672–679.
Provencher, S. W. (2001). Automatic quantitation of localized in vivo 1H spectra with LCModel. NMR in Biomedicine, 14, 260–264.
Soher, B. J., Young, K., & Maudsley, A. A. (2001). Representation of strong baseline contributions in 1H MR spectra. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 45, 966–972.
Schubert, F., Seifert, F., Elster, C., Link, A., Walzel, M., Mientusand, S., et al. (2002). Serial 1H-MRS in relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis: Effects of interferon-beta therapy on absolute metabolite concentrations. MAGMA, 14, 213–222.
Lemmerling, P., Vanhamme, L., in, , t Zandt, H. J. A., Van Huffel, S., & Van Hecke, P. (2002). Time-domain quantification of short-echo-time in-vivo proton MRS. MAGMA, 15, 178–179.
Weiland, E., Roell, S. A., Leibfritz, D., & Krueger, G. (2003). Time-domain fitting of 1H-MR spectra of the human brain: A model-free integration of the macromolecular baseline. In ISMRM, Toronto, pp. 1160.
Coenradie, Y., de Beer, R., van Ormondt, D., Cavassila, S., Ratiney, H., & Graveron-Demilly, D. (2002). Background-signal parametrization in vivo MR spectroscopy. MAGMA, 15, 369.
Coenradie, Y., de Beer, R., van Ormondt, D., Ratiney, H., Cavassila, S., & Graveron-Demilly, D. (2002). Background-signal parametrization in vivo MR spectroscopy. In: Proceedings of ProRISC, IEEE Benelux, Veldhoven, The Netherlands, pp. 248–254.
Stanley, J. A., & Pettegrew, J. W. (2001). Postprocessing method to segregate and quantify the broad components underlying the phosphodiester spectral region of in vivo 31P brain spectra. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 45, 390–396.
Cavassila, S., van Ormondt, D., & Graveron-Demilly, D. (2002). Cramer–Rao bound analysis of spectroscopic signal processing methods.. In H. Yan (Ed.), Signal processing for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy (pp. 613–640). New York: Marcel Dekker chap 21.
Ratiney, H., Coenradie, Y., Cavassila, S., van Ormondt, D., & Graveron-Demilly, D. (2004). Time-domain quantitation of 1H short echo-time signals: Background accommodation. MAGMA, 16, 284–296.
Poullet, J. B., Sima, D. M., Van Huffel, S., & Van Hecke, P. (2007). Frequency-selective quantitation of short-echo time 1H magnetic resonance spectra. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 186, 293–304.
Cudalbu, C., Cavassila, S., Ratiney, H., Grenier, D., Briguet, A., & Graveron-Demilly, D. (2006). Estimation of metabolite concentrations of healthy mouse brain by magnetic resonance spectroscopy at 7 Tesla. Comptes Rendus Chimie, 9, 534–538.
Cudalbu, C., Cavassila, S., Ratiney, H., Beuf, O., van Ormondt, D., & Graveron-Demilly, D. (2005). Metabolite concentration estimates in the rat brain by magnetic resonance spectroscopy using QUEST and two approaches to invoke prior knowledge. In Proc. ProRISC, IEEE Benelux, Veldhoven, The Netherlands, pp. 609–614.
Cudalbu, C., Cavassila, S., Rabeson, H., van Ormondt, D., & Graveron-Demilly D. (2007). Influence of measured and simulated basis-sets on the metabolite concentration estimates. NMR in Biomedicine DOI 10.1002/nbm.1234. (Dec 17)
Cudalbu, C., Cavassila, S., Ratiney, H., Beuf, O., Briguet, A., & Graveron-Demilly, D. (2005). Metabolite concentrations of healthy mouse brain by Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy at 7 Tesla. In Proc. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, IEEE EMB Shanghai, pp. 1392–1395.
Tkac, I., Starcuk, Z., Choi, I. Y., & Gruetter, R. (1999). In vivo 1H NMR spectroscopy of rat brain at 1 ms echo time. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 41, 649–656.
Gruetter, R. (1993). Automatic, localized in vivo adjustment of all first- and second-order shim coils. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 29, 804–811.
Pfeuffer, J., Tkac, I., Provencher, S., & Gruetter, R. (1999). Toward an in vivo neurochemical profile: Quantification of 18 metabolites in short echo-time 1H spectra of the rat brain. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 141, 104–120.
Berhar, K. L., & Ogino, T. (1993). Characterization of macromolecule resonances in the H NMR spectrum of rat brain. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 30, 38–44.
Pijnappel, W. W. F., van den Boogaart, A., de Beer, R., & van Ormondt, D. (1992). SVD-based quantification of magnetic resonance signals. Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 97, 122–134.
Naressi, A., Couturier, C., Devos, J. M., Janssen, M., Mangeat, C., de Beer, R., et al. (2001). Java-based graphical user interface for the MRUI quantitation. MAGMA, 12, 141–152.
Cavassila, S., Deval, S., Huegen, C., van Ormondt, D., & Graveron-Demilly, D. (2001). Cramer–Rao bounds: An evaluation tool for quantitation. NMR in Biomedicine, 14, 278–283.
Cavassila, S., Deval, S., Huegen, C., van Ormondt, D., & Graveron-Demilly, D. (1999). The beneficial influence of prior knowledge on the quantitation of in vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy signals. Investigative Radiology, 34, 242–246.
Otazo, R., Mueller, B., Ugurbil, K., Wald, L., & Posse, S. (2006). Signal-to-noise ratio and spectral linewidth improvements between 1.5 and 7 Tesla in proton echo-planar spectroscopic imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 56, 1200–1210.
de Graaf, R. A., Brown, P. B., McIntyre, S., Nixon, T. W., Behar, K. L., & Rothman, D. L. (2006). High magnetic field water and metabolite proton T1 and T2 relaxation in rat brain in vivo. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 56, 386–394.
Acknowledgment
The experiments were performed by the authors at the ANIMAGE platform, Lyon, France. The development of the inversion recovery sequence was based on the PRESS sequence provided by BRUKER BioSpin MRI Ettlingen, Germany. The authors thank Dr. D Wecker and Dr. F Hennel from Bruker Biospin for support with method modifications.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cudalbu, C., Beuf, O. & Cavassila, S. In Vivo Short Echo Time Localized 1H MRS of the Rat Brain at 7 T: Influence of Two Strategies of Background-accommodation on the Metabolite Concentration Estimation using QUEST. J Sign Process Syst Sign Image Video Technol 55, 25–34 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-008-0187-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-008-0187-5