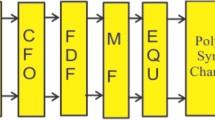
Abstract
Timing recovery in communication systems with linear modulations is usually performed with a non-data-aided feedback loop based on a fractional interpolator timing corrector and the Gardner’s timing error detector. The contribution of this paper is twofold. First, some design rules are given to predict the behaviour of the loop if pipeline is used. Second, it is shown that pipelining can be used to reduce power consumption in a timing feedback loop. A timing recovery loop has been implemented in an FPGA device and power consumption measures indicates that by including 16 extra registers in the loop the power consumption decreases a 63% and the synchronizer can process up to 66.5 MSPS.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
European Telecommunications Standards Institute. (1997). Digital video broadcasting (DVB): Framing structure, channel coding and modulation for 11/12 GHz satellite services. European standard (Telecommunications series), EN 300 421 V1.1.2.
Parhi, K. K. (1999). VLSI digital signal processing: design and implementation. New York: Wiley.
Gardner, F. M. (2005). Phaselock techniques. New York: Wiley.
Spagna, F. (2001) An improved delay compensation technique for digital clock recovery loops”. The 8th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS), vol. 3, pp. 1395–1398.
Bergmans, J. W. M. (1995). Effect of loop delay on stability of discrete-time PLL. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I, 42(4), 229–231, (April).
De Gloria, A., Grosso, D., Olivieri, M., & Restani, G. (1999). A novel stability analysis of a PLL for timing recovery in hard disk drives. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I, 46(8), 1026–1031, (August).
Meyr, H., Moeneclaey, M., & Fechtel, S. A. (1998). Digital communications receivers. synchronization, chanel estimation and signal processing. New York: Wiley.
Gardner, F. M. (1986). A BPSK/QPSK timing-error detector for sampled receivers. IEEE Transactions on Communications, COM-34(5), 423–429, (May).
Cardells, F., Valls J., Almenar, V. (2003). Symbol timing synchronization in FPGA-based software radios: Application to DVB-S. 13th International Conference on Field Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL 2003), Lisbon, Portugal, September.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by FEDER, the Spanish Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia, under Grant No. TEC2005-08406-C03-01 and Generatitat Valenciana, under Grant No. GV06/114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Torres, V., Pérez-Pascual, A., Sansaloni, T. et al. Design and FPGA-Implementation of a High Performance Timing Recovery Loop for Broadband Communications. J Sign Process Syst Sign Image Video Technol 56, 17–23 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-008-0252-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-008-0252-0