Abstract
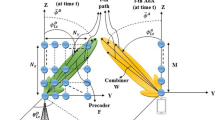
Many existing adaptive beamformers possess robustness against arbitrary array steering vector (ASV) mismatches within presumed uncertainty set. However, when the array facing a large steering direction error, their performance degrade significantly since the uncertainty in steering direction generally gives rise to an outstanding mismatch in ASV. In the applications of microphone array, large steering direction error is often unavoidable because of the motion of target speaker. Meanwhile, in addition to conventional adaptive beamformers, microphone array also requests a controlled frequency response to target signal. In this paper, we propose a new adaptive microphone array implemented in frequency domain with controlled mainlobe and frequency response. A compact ASV uncertainty set explicitly modelling steering direction error and the other arbitrary ASV errors is exploited to derive beamformer with robust constraints on array magnitude response. Numerical results show that the proposed microphone array not only produces large controlled robust response region and robust frequency response, but also achieves high performance in SINR enhancement.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The vector h(f) may also variate with the change of data block k. However, for simplicity, we assume it is fixed in this paper.
References
Affes, S., & Grenier, Y. (1997). A signal subspace tracking algorithm for microphone array processing of speech. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio Processing, 5(5), 425–437.
Applebaum, S. P., & Chapman, D. J. (1976). Adaptive arrays with main beam constraints. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 24(5), 650–662.
Bell, K. L., Ephraim, Y., & Van Trees, H. L. (2000). A Bayesian approach to robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 48(2), 386–398.
Brandstein, M., & Ward, D. (2001). Microphone arrays: Signal processing techniques and applications. New York: Springer.
Buckley, K. M. (1987). Spatial/spectral filtering with linearly constrained minimum variance beamformers. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing, ASSP-35(3), 249–266.
Buckley, K. M., & Griffiths, L. J. (1986). An adaptive generalized sidelobe canceller with derivative constraints. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, AP-34(3), 311–319.
Capon, J. (1969). High-resolution frequency wavenumber spectrum analysis. Proceedings of the IEEE, 57(8), 1408–1418.
Carlson, B. D. (1988). Covariance matrix estimation errors and diagonal loading in adaptive arrays. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 24, 397–401.
Chang, L., & Yeh, C. C. (1992). Performance of DMI and eigenspace-based beamformers. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 40, 1336–1347.
Chen, C. Y., & Vaidyanathan, P. P. (2007). Quadratically constrained beamforming robust against direction-of-arrival mismatch. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 55(8), 4139–4150.
Claesson, I., & Nordholm, S. (1992). A spatial filtering approach to robust adaptive beaming. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 40(9), 1093–1096.
Cox, H., Zeskind, R. M., & Owen, M. M. (1987). Robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing, ASSP-35(10), 1365–1376.
Er, M. H., & Cantoni, A. (1983). Derivative constraints for broad-band element space antenna array processors. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing, ASSP-31(6), 1378–1393.
Er, M. H., & Cantoni, A. (1986). A new set of linear constraints for broad-band time domain element space processor. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, AP-34(3), 320–329.
Er, M. H., & Cantoni, A. (1986). An unconstrained partitioned realization for derivative constrained broad-band antenna array processors. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, Signal Processing, 34(6), 1376–1379.
Feldman, D., & Griffiths, L. (1994). A projection approach for robust adaptive beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 42(4), 867–876.
Frost III, O. L. (1972). An algorithm for linearly constrained adaptive array processing. Proceedings of the IEEE, 60, 926–935.
Fudge, G. L. (1996). Spatial blocking filter derivative constraints for the generalized sidelobe canceller and MUSIC. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 44(1), 51–61.
Fudge, G. L., & Linebarger, D. A. (1994). A calibrated generalized sidelobe canceller for wideband beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 42(10), 2871 –2875.
Gannot, S., Burshtein, D., & Weinstein, E. (2001). Signal enhancement using beamforming and nonstationarity with applications to speech. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 49(8), 1614–1626.
Griffiths, L. J., & Jim, C. W. (1982). An alternative approach to linearly constrained adaptive beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, AP-30(1), 27–34.
Guerci, J. R. (2003). Space-time adaptive processing. Norwood: Artech House.
Jablon, N. K. (1986). Adaptive beamforming with the generalized sidelobe canceller in the presence of array imperfection. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 34(8), 996–1012.
Kim, J. W., & Un, C. K. (1993). A robust adaptive array based on signal subspace approach. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 41(1), 3166–3171.
Lee, C. C., & Lee, J. H. (1997). Eigenspace-based adaptive array beamforming with robust capabilities. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 45(12), 1711–1716.
Li, J., & Stoica, P. (Eds.) (2006). Robust adaptive beamforming. New York: Wiley.
Li, J., Stoica, P., & Wang, Z. (2003). On robust Capon beamforming and diagonal loading. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 51(7), 1702–1715.
Li, J., Stoica, P., & Wang, Z. (2004). Doubly constrained robust capon beamformer. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 52(9), 2407–2423.
Li, J., Xie, Y., Stoica, P., Zheng, X., & Ward, J. (2007). Beampattern synthesis via a matrix apporach for signal power estimation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 55(12), 5643–5657.
Lorenz, R. G., & Boyd, S. P. (2005). Robust minimum variance beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 53(5), 1684–1696.
Sayed, A. H., & Kailath, T. (2001). A survey of spectral factorization methods Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications, 8(6–7), 467–496. citeseer.ist.psu.edu/sayed01survey.html.
Shahbazpanahi, S., Gershman, A. B., Luo, Z. Q., & Wong, K. M. (2003). Robust adaptive beamforming for general-rank signal models. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 51(9), 2257–2269.
Takao, K., Fujita, M., & Nishi, T. (1976). An adaptive antenna array under directional constraint. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 24(5), 662–669.
Van Veen, B. D. (1991). Minimum variance beamforming with soft response constraints. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 39(9), 1964–1972.
Van Veen, B. D., & Buckley, K. M. (1988). Beamforming: A versatile approach to spatial filtering. IEEE ASSP Magazine, 5(2), 4–24.
Vorobyov, S. A., Gershman, A. B., & Luo, Z. Q. (2003). Robust adaptive beamforming using worst-case performance optimization: A solution to the signal mismatch problem. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 51(2), 313–324.
Vural, A. M. (1979). Effects of perturbation on the performance of optimum/adaptive arrays. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 15(1), 76–87.
Wu, S. Q., & Zhang, J. (1999). A new robust beamforming method with antenna calibration errors. In Proc. IEEE wireless commun. networking conf. (Vol. 2, pp. 869–872).
Youn, W. S., & Un, C. K. (1994). Robust adaptive beamforming based on the eigenstructure method. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 42(6), 1543–1547.
Yu, Z. L. (2006). New techniques for robust beamformer design. Ph.D. dissertation, School of Electric & Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore.
Yu, Z. L., Er, M. H., & Ser, W. (2008). Novel adaptive beamformer based on semidefinite programming (SDP) with constraints on magnitude response. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 56(5), 1297–1307.
Yu, Z. L., Ser, W., & Er, M. H. (2007). A novel robust adaptive beamformer based on linear optimization. In Proc. of ICICS (pp. 1–4). Singapore.
Yu, Z. L., Ser, W., & Er, M. H. (2008). A novel robust adaptive beamformer based on worst-case linear optimization. In Proc. ICIEA (pp. 2435–2438). Singapore.
Yu, Z. L., Ser, W., & Er, M. H. (2008). Robust response control for adaptive beamformers against arbitrary array imperfections. Signal Processing, 88(9), 2234–2245. doi:10.1016/j.sigpro.2008.03.009.
Yu, Z. L., Ser, W., Er, M. H., Gu, Z., & Li, Y. (2009). Robust adaptive beamformers based on worst-case optimization and constraints on magnitude response. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 57(7), 2615–2628.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge all the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments that helped to improve the quality of this paper. This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 60802068 and 60825306, Guangdong Natural Science Foundation under grants 8451064101000498.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Z.L., Gu, Z., Ser, W. et al. Robust Adaptive Microphone Array with Mainlobe and Response Ripple Control. J Sign Process Syst 63, 301–313 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-009-0424-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-009-0424-6