Abstract
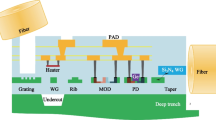
In this paper, we propose a reconfigurable load balanced symmetric TDM switch fabric. We fold this two-stage switch to reduce 50% hardware complexity, and then implement a 3.65 mm × 3.57 mm prototype switch fabric IC, including a digital 8 × 8 switch core, eight 16B20B CODECs, eight SERDES ports, eight CML I/O interfaces and a PLL, in 0.18 μm CMOS technology. The digital 8 × 8 switch core has reconfigurable connection patterns for the ease of scaling up to an N×N switch (N is power of 4). We propose the 16B20B CODEC scheme to reduce the switch core clock rate by half. In the SERDES, we employ the half-rate scheme and then use static CMOS gates for the low power consumption. We develop a low power, area-efficient and wide-band CML I/O interface with our patented PMOS active load inductive-peaking scheme for high-speed data transmission. With the 16B20B CODEC, the half-rate, and the PMOS active load schemes, almost 50% of the power is saved as compared with the design of the 8B10B CODEC, the full-rate and on-chip inductors CML schemes. Our measurement shows that an 8 × 8 switch fabric IC can achieve 20 Gbps switching rate and consumes only about 690 mW power. A terabit switch fabric can then be constructed by cascading the designed switch ICs.























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karol, M. J., Hluchyj, M. G., & Morgan, S. P. (1987). Input versus output queueing on a space-division packet switch. IEEE Trans Commun, 35, 1347–1356.
Anderson, T., Owicki, S., Saxe, J., & Thacker, C. (1993). High-speed switch scheduling for local-area networks. ACM Transactions on Computer Systems, 11, 319–352.
Tamir, Y., & Chi, H. C. (1993). Symmetric crossbar arbiters for VLSI communication switches. IEEE Trans Parallel Distrib Syst, 4, 13–27.
McKeown, N. (1995). Scheduling algorithms for input-queued cell switches. PhD Thesis. University of California at Berkeley.
McKeown, N., Anantharam, V., & Walrand, J. (1999). Achieving 100% throughput in an input-queued switch. IEEE Trans Commun, 47, 1260–1267.
Mekkittikul, A., & McKeown, N. (1998). A practical scheduling algorithm to achieve 100% throughput in input-queued switches. Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, 2, 792–799.
Dai, J., & Prabhakar, B. (2000). The throughput of data switches with and without speedup. Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, 2, 556–564.
Li, Y., Panwar, S., & Chao, H. J. (2001). On the performance of a dual round-robin switch. Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, 3, 1688–1697.
Chang, C. S., Lee, D. S., & Shih, Y. J. (2004). Mailbox switch: a scalable two-stage switch architecture for conflict resolution of ordered packets. Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, 3, 1995–2006.
Chang, C. S., Lee, D. S., & Jou, Y. S. (2002). Load balanced Birkhoff-von Neumann switches, part I: one-stage buffering. Comput Commun, 25, 611–622.
Shen, Y., Jiang, S., Panwar, S. S., & Chao, H. J. (2005). Byte-focal: a practical load balanced switch. IEEE High Performance Switching and Routing, (pp. 6–12).
Jaramillo, J. J., Milan, F., & Srikant, R. (2006). Padded frames: A novel algorithm for stable scheduling in load-balanced switches. Proceedings of CISS.
Keslassy, I., & McKeown, N. (2002). Maintaining packet order in two-stage switches. Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, 2, 1032–1041.
Keslassy, I., Chuang, S. T., Yu, K., Miller, D., Horowitz, M., Solgaard, O., et al. (2003). Scaling internet routers using Optics. Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM.
Yu, C. L., Chang, C. S., & Lee, D. S. (2007). CR switch: a load-balanced switch with contention and reservation. accepted by IEEE INFOCOM.
Gripp, J., Simsarian, J. E., Bernasconi, P., Le Grange, J. D., Zhang, L., Buhl, L., et al. (2005). Load-balanced optical packet router based on 40 Gb/s wavelength converters and time buffers. Proceedings of IEEE European Conference on Optical Communication.
Chiu, C. T., Chang, C. C., Chen, S. M., Tzeng, H. C., Du, M. C., Hsu, Y. H., et al. (2005). A 20 Gbps scalable load-balanced TDM switch with CODEC for high speed networking applications. IEEE System-on-Chip for Real-Time Applications, (pp. 508–513).
Widmer, A. X., & Franaszek, P. A. (1983). A DC-balanced, partitioned- block, 8B/10B transmission code. IBM J Res Dev, 27(5), 440.
Guo, Y., Zhang, Z., Hu, W., & Yang, L. (2002). “CMOS multiplexer and demultiplexer for gigabit Ethernet. IEEE International Conference on Communications, Circuits and Systems and West Sino Expositions, 1, 819–823.
Lu, J. H., Lei, T., Chen, H. T., Xie, T. T., Chen, Z. H., & Wang, Z. G. (2001). Design techniques of CMOS SCL circuits for Gb/s applications. 4th International Conference on ASIC, (pp. 559–562).
Lu, H. W., & Su, C. C. (2004). A 5 Gbps CMOS LVDS transmitter with multi-phase tree-type multiplexer. IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Advanced System Integrated Circuits, (pp. 228–231).
Larsson, P. (1999). A 2-1600-MHz CMOS clock recovery PLL with low-Vdd capability. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 34, 1951–1960.
Manteatis, J. G. (1996). Low-jitter process-independent DLL and PLL based on self-biased techniques. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 31, 1723–1732.
Lin, T. H., & Chi, C. C. (2006). A 70–490 MHz 50% duty-cycle correction circuit in 0.35-μm CMOS. in Proc. IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conf., (pp. 91–94).
Lin, T. H., Chi, C. C., Chiu, W. H., & Huang, Y. H. (2010). A Synchronous 50% Duty-Cycle Clock Generator in 0.35-μm CMOS. IEEE Trans. on VLSI (accepted).
Razavi, B. (2001). Design of analog CMOS integrated circuits. Mc. Graw Hill.
Chiu, C. T., Wu, J. M., Hsu, S. H., Kao, M. S., Jen, C. H., & Hsu, Y. S. (2005). A 10 Gb/s wide-Band current-mode logic I/O interface for high-speed interconnect in 0.18 μm CMOS technology. IEEE International SOC Conference, (pp. 257–260).
Cherry, E. M., & Hooper, D. E. (1963). The design of wide-band transistor feedback amplifier. Proceedings of IEE, 110(2), 375–389.
Tomita, Y., Kibune, M., Ogawa, J., & Walker, W. W. (2004). A 10 Gb/s receiver with equalizer and on-chip ISI monitor in 0.11 μm CMOS. VLSI Circuits. Digest of Technical Papers.
Coban, A. L., Koroglu, M. H., & Ahmed, K. A. (2005). A 2.5-3.125 Gb/s quad transceiver with second order analog DLL based CDRs. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 40, 1940–1947.
Kim, J., Yang, J., Byun, S., Jun, H., Park, J., Conroy, C. S. G., et al. (2005). A four-channel 3.125 Gb/s/ch CMOS serial-link transceiver with a mixed-mode adaptive equalizer. IEEE J Solid-State Circuits, 40, 462–471.
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to acknowledge the support of this work by National Science Council (Taiwan) (NSC-96-2752-E-007-002-PAE), and the chip fabrication support of National Chip Implementation Center (Taiwan) and Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC). We also like to thank President W.T. Chen, Prof. C.S. Chang and Prof. D.S. Lee for support of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This research is supported by the National Science Council, Taiwan, R.O.C., under the Program for Promoting Academic Excellence of Universities NSC 96-2752-E-007-002-PAE.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chiu, CT., Hsu, YH., Wu, JM. et al. An 8 × 8 20 Gbps Reconfigurable Load Balanced TDM Switch IC for High-Speed Networking. J Sign Process Syst 66, 57–73 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-010-0518-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-010-0518-1