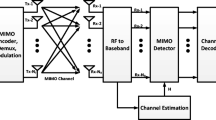
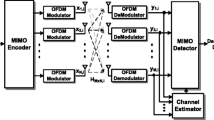
Abstract
Lattice Reduction aided MIMO detectors have been demonstrated to offer a promising gain by providing near-optimal performance. This paper presents a C-programmable ASIP baseband processor, for near-optimal MIMO detection targeting a 4×4 LTE system. The detector supports multiple MIMO detection modes, with both hard and soft output. In order to improve implementation efficiency, the previously reported MIMO detection algorithm Multi-Tree Selective Spanning Detector (MTSS) is modified to use orthogonal real-valued decomposition (ORVD). Afterwards, a low-complexity log-likelihood-ratio (LLR) improvement technique called counter-ML bit-flipping algorithm is proposed. The proposed LLR generation algorithm has been designed to take advantage of MTSS, by maximizing the reuse of computations. Performance of the proposed solution can be tuned ranging from SIC to near-ML to near-MAP. The baseband processor is designed using 40 nm process technology with an equivalent gate-count (GE) of 68.41 kGE. Operating at 600 MHz for a 4×4 QAM-64 LTE system, the processor delivers peak-throughputs of 3.6 Gbps and 2.05 Gbps in case of hard and soft output MIMO detection, with 13.03 mW and 22.99 mW respective power consumption. The corresponding energy efficiency is 3.61 pJ/bit and 11.17 pJ/bit. In terms of energy efficiency, the proposed reconfigurable solution is comparable to recently reported ASIC MIMO detectors, while providing multiple-modes of operation and the flexilibility of C-programming.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
3gpp lte-a http://www.3gpp.org/technologies/keywords-acronyms/97-lte-advanced.
Target tool suite website http://www.retarget.com.
Ahmad, U, Li, M, Appeltans, R, Nguyen, D, Amin, A, Dejonghe, A, Van der Perre, L, Lauwereins, R, Pollin, S (2013). Exploration of lattice reduction aided soft-output mimo detection on a dlp/ilp baseband processor. Signal Processing, IEEE Transactions on, PP(1–1). doi:10.1109/TSP.2013.2279773.
Azzam, L, & Ayanoglu, E (2007). Reduced complexity sphere decoding for square qam via a new lattice representation. In: Global Telecommunications Conference, 2007. GLOBECOM ’07. IEEE, pp. 4242–4246.
Chen, S, Zhang, T, Xin, Y (2007). Relaxed k-best mimo signal detector design and VLSI implementation. Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, IEEE Transactions on, 15(3), 328–337. doi:10.1109/TVLSI.2007.893621.
Chu, X, & McAllister, J (2012). Software-defined sphere decoding for FPGA-based MIMO detection. Signal Processing, IEEE Transactions on, 60(11), 6017–6026. doi:10.1109/TSP.2012.2210951.
Gan, YH, Ling, C, Mow, WH (2009). Complex lattice reduction algorithm for low-complexity full-diversity MIMO detection. Signal Processing, IEEE Transactions on, 57(7), 2701–2710. doi:10.1109/TSP.2009.2016267.
Hochwald, B, & Ten Brink, S (2003). Achieving near-capacity on a multiple-antenna channel. Communications, IEEE Transactions on, 51(3), 389–399. doi:10.1109/TCOMM.2003.809789.
Lenstra, AK, Lenstra, HW, Lovasz, JL (1982). Factoring polynomials with rational coefficients. In: Mathematische Annalen, vol. 261, p. 515534.
Li, M, Bougard, B, Lopez, E, Bourdoux, A, Novo, D, Van Der Perre, L, Catthoor, F (2008). Selective spanning with fast enumeration: A near maximum-likelihood MIMO detector designed for parallel programmable baseband architectures. In: Communications, 2008. ICC ’08. IEEE International Conference on, pp. 737–741.
Li, M, Novo, D, Bougard, B, Naessens, F, Van der Perre, L, Catthoor, F (2008). An implementation friendly low complexity multiplierless llr generator for soft mimo sphere decoders. In: Signal Processing Systems, 2008. SiPS 2008. IEEE Workshop on, pp. 118–123.
Li, Q, Li, G, Lee, W, il Lee, M, Mazzarese, D, Clerckx, B, Li, Z (2010). Mimo techniques in wimax and lte: a feature overview. IEEE, Communications Magazine, 48(5), 86–92. doi:10.1109/MCOM.2010.5458368.
Liu, L, Lofgren, J, Nilsson, P (2012). Area-efficient configurable high-throughput signal detector supporting multiple MIMO modes. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 59(9), 2085 –2096. doi:10.1109/TCSI.2012.2185297.
Liu, L, Ye, F, Ma, X, Zhang, T, Ren, J (2010). A 1.1-Gb/s 115-pJ/bit configurable MIMO detector using 0.13- μm CMOS technology. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 57(9), 701–705. doi:10.1109/TCSII.2010.2058494.
Ma, X, & Zhang, W (2008). Performance analysis for MIMO systems with lattice-reduction aided linear equalization. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 56(2), 309–318. doi:10.1109/TCOMM.2008.060372.
Mahdavi, M, & Shabany, M (2012). Novel MIMO detection algorithm for high-order constellations in the complex domain. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, PP(99), 1. doi:10.1109/TVLSI.2012.2196296.
Mondal, S, Eltawil, A, Shen, CA, Salama, K (2010). Design and implementation of a sort-free K-Best sphere decoder. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 18(10), 1497 –1501. doi:10.1109/TVLSI.2009.2025168.
Patel, D, Smolyakov, V, Shabany, M, Gulak, P (2010). VLSI implementation of a WiMAX/LTE compliant low-complexity high-throughput soft-output K-Best MIMO detector. In: Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Symposium on, pp. 593 –596.
Ramacher, U (2007). Software-Defined Radio prospects for multistandard mobile phones. Computer, 40(10), 62–69. doi:10.1109/MC.2007.362.
Shabany, M, & Gulak, P (2012). A 675 Mbps, 4x4 64-QAM K-Best MIMO detector in 0.13 μm CMOS. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 20(1), 135–147. doi:10.1109/TVLSI.2010.2090367.
Shen, CA, Eltawil, A, Salama, K, Mondal, S (2012). A best-first soft/hard decision tree searching MIMO decoder for a 4×4 64-qam system. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) Systems, 20(8), 1537–1541. doi:10.1109/TVLSI.2011.2159821.
Wu andbben, D, Seethaler, D, Jalde andn, J, Matz, G (2011). Lattice reduction. Signal Processing Magazine. IEEE, 28(3), 70–91. doi:10.1109/MSP.2010.938758.
Wubben, D, Bohnke, R, Kuhn, V, Kammeyer, KD (2004). MMSE-based lattice-reduction for near-ML detection of MIMO systems. In: Smart Antennas, 2004. ITG Workshop on, pp. 106–113.
Yao, H, & Wornell, G (2002). Lattice-reduction-aided detectors for MIMO communication systems. In: Global Telecommunications Conference, 2002. GLOBECOM ’02. IEEE, vol. 1, pp. 424–428 vol. 1.
Zhang, W, & Ma, X (2010). Low-complexity soft-output decoding with lattice-reduction-aided detectors. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 58(9), 2621–2629. doi:10.1109/TCOMM.2010.080310.070641.
Zheng, C, McAllister, J, Wu, Y (2011). A kernel interleaved scheduling method for streaming applications on soft-core vector processors. In: Embedded Computer Systems (SAMOS), 2011 International Conference on, pp. 278–285.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, U., Li, M., Amin, A. et al. An Energy-Efficient Reconfigurable ASIP Supporting Multi-mode MIMO Detection. J Sign Process Syst 85, 5–21 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-015-0972-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-015-0972-x