Abstract
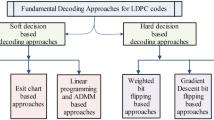
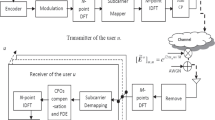
In this article we analyze a novel idea to increase the applicability of Bit Interleaved Coded Modulation with Iterative Decoding (BICM-ID) to legacy waveforms. One essential design parameter of BICM-ID receivers with respect to the error correcting capabilities is the symbol mapping of the digital modulation scheme. A so-called Semi-Set Partitioning (SSP) symbol mapping is well known to provide higher stepwise gains in robustness in every iteration than a Gray encoded symbol mapping. The novel approach is based on the idea to make in a first step of BICM-ID the deliberately false assumption that a well performing symbol mapping has been used at the transmitter, even though in reality a less powerful symbol mapping was applied. In a second step, the mismatch in both symbol mappings is compensated by an innovative Transformation of Extrinsic Information (TEI). After having reviewed the innovative TEI idea in more detail, we will discuss the fundamentals of the required signal processing. In addition, as a novelty of this article we will analyze three different ways to implement the TEI approach. Several simulation results will be shown which demonstrate the theoretically achievable performance gains.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leduc, J., Adrat, M., Antweiler, M., & Elders-Boll, H. (2010). Legacy waveforms on software defined radios: benefits of advanced digital signal processing (Proc. of NATO RTO information systems technology panel symposium (IST - 092 / RSY - 022)). Poland: Breslau.
Li, X., & Ritcey, J. A. (1997). Bit interleaved coded modulation with iterative decoding. IEEE Communication Letters, 1(6), 169–171.
Li, X., Chindapol, A., & Ritcey, J. A. (2002). Bit-interleaved coded modulation with iterative decoding and 8-PSK signaling. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 50(8), 1250–1257.
Adrat, M., Osten, T., Tschauner, M., Antweiler, M., Lewandowsky, J. (2014). Novel Transformations of Extrinsic Information applied to Innovative BICM-ID Receivers: Fundamentals and Limits. Proc. of SDR15-WInnComm-Europe, Rome (Italy).
Hagenauer, J., Offer, E., & Papke, L. (1996). Iterative decoding of binary block and convolutional codes. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 429–445.
Clevorn, T., & Vary, P. (2005). The box-minus operator and its application to Low-complexity belief propagation decoding. Proceedings of IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), 1, 687–691.
ten Brink, S. (2001). Convergence behavior of iteratively decoded parallel concatenated codes. IEEE Transaction on Communications, 1727–1737.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adrat, M., Lewandowsky, J., Tschauner, M. et al. Analysis of BICM-ID Receivers Exploiting Transformations of Extrinsic Information. J Sign Process Syst 83, 83–92 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-015-1046-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-015-1046-9