Abstract
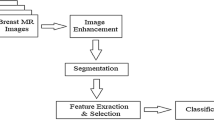
Breast cancer is one of the most significant medical problems of our time. Determining the appropriate methodologies for its early detection is still an open research problem in the scientific community. This research proposes a novel framework for automatically identifying and classifying breast cancer using MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) images. The proposed approach utilizes automatic segmentation methods to detect suspicious areas in MRI images, features new feature extraction, and utilizes a variety of classification methods to create an automatic decision-making system that is able to classify the MRI images as benign or malign cancers. This research used MRI images of 56 patients from the medical imaging department of King Abdullah Medical City (KAMC), Saudi Arabia to assess the performance of the proposed framework. Our framework was able to achieve a classification accuracy of over 98% for its optimal configuration (SVM -linear kernel), while demonstrating excellent false-positive and false negative rates, sensitivity and specificity (0%,15%, 97%, 100% respectively).









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Health Quality Ontario. (2007). Screening Mammography for Women Aged 40 to 49 Years at Average Risk for Breast Cancer: An Evidence-Based Analysis. Ontario Health Technology Assessment Series, 7(1), 1–32.
Moein, S. (Ed.). (2014). Medical diagnosis using artificial neural networks. Hershey, Pennsylvania: IGI Global.
Taylor, R. H., Menciassi, A., Fichtinger, G., & Dario, P. (2008). Medical robotics and computer-integrated surgery. Springer handbook of robotics (pp. 1199–1222). Springer.
Graber, M., Gordon, R., & Franklin, N. (2002). Reducing diagnostic errors in medicine: What’s the goal? Academic Medicine, 77(10), 981–992.
Jordanov, M., Bregman, J., Montgomery, K., & Heidel, M. (2015). Curbside radiology consults: How does the time allotted for review, level of training, and subspecialization affect interpretation accuracy? Clinical Imaging, 39(3), 497–503.
Woods, K., Bowyer, K. W., & Sallam, M. Y. (2002). Evaluating detection algorithms. In R. N. Strickland (Ed.), Image-processing techniques for tumor detection. New York: CRC Press.
Fraser, K. C., Meltzer, J. A., Graham, N. L., Leonard, C., Hirst, G., Black, S. E., & Rochon, E. (2014). Automated classification of primary progressive aphasia subtypes from narrative speech transcripts. Cortex, 55, 43–60.
Chand, S. (2020). A comparative study of breast cancer tumor classification by classical machine learning methods and deep learning method. Machine Vision and Applications, 31(6), 1–10.
Ibraheem, A. M., Rahouma, K. H., & Hamed, H. F. (2019). Automatic mri breast tumor detection using discrete wavelet transform and support vector machines. In 2019 Novel Intelligent and Leading Emerging Sciences Conference (NILES). IEEE, 1, 88–91.
Bakkouri, I., & Afdel, K. (2017). Breast tumor classification based on deep convolutional neural networks. In 2017 International Conference on Advanced Technologies for Signal and Image Processing (ATSIP). IEEE, 1–6.
Nejad, E. M., Affendey, L. S., Latip, R. B., & Bin Ishak, I. (2017). Classification of histopathology images of breast into benign and malignant using a single-layer convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Imaging, Signal Processing and Communication (pp. 50–53).
Maniak, T., Iqbal, R., & Doctor, F. (2020). Hierarchical spatial-temporal state machine for vehicle instrument cluster manufacturing. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, IEE press. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2020.3018054
Mahmud, S., Iqbal, R., & Doctor, F. (2016). Cloud enabled data analytics and visualization framework for health-shocks prediction. Journal of Future Generation of Computer Systems, Elsevier, 65, 169–181.
Iqbal, R., Doctor, F., More, B., Mahmud, S., & Yousuf, U. (2020). Big data analytics: Computational intelligence techniques and application. Journal of Technological Forecasting & Social Change, 153, 119253 ISSN 0040–1625. Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2018.03.024.
Assiri, A. S., Nazir, S., & Velastin, S. A. (2020). Breast tumor classification using an ensemble machine learning method. Journal of Imaging, 6(6), 39.
Vijayarajeswari, R., Parthasarathy, P., Vivekanandan, S., & Basha, A. A. (2019). Classification of mammogram for early detection of breast cancer using SVM classifier and Hough transform. Measurement, 146, 800–805.
Singh, V. K., Rashwan, H. A., Romani, S., Akram, F., Pandey, N., Sarker, M. M. K., & Torrents-Barrena, J. (2020). Breast tumor segmentation and shape classification in mammograms using generative adversarial and convolutional neural network. Expert Systems with Applications, 139, 112855.
Janghel, R. R., Shukla, A., Tiwari, R., & Kala, R. (2010) Breast cancer diagnosis using artificial neural network models. In Information sciences and interaction sciences (ICIS), 2010 3rd International Conference, Chicago, IL. 89–94.
Timp, S., Varela, C., & Karssemeijer, N. (2010). Computer-aided diagnosis with temporal analysis to improve radiologists’ interpretation of mammographic mass lesions. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 14(3), 803–808.
Cascio, D., Magro, R., Fauci, F., Iacomi, M., & Raso, G. (2012). Automatic detection of lung nodules in CT datasets based on stable 3D mass–spring models. Computers in Biology and Medicine., 42(11), 1098–1109.
Islam, M. M., Sattar, M. A., Amin, M. F., Yao, X., & Murase, K. (2009) A new adaptive merging and growing algorithm for designing artificial neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part B (Cybernetics), 39(3), 705–722.
Dominguez, A. R., & Nandi, A. K. (2008). Detection of masses in mammograms via statistically based enhancement, multilevel-thresholding segmentation, and region selection. Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics., 32(4), 304–315.
El-Naqa, I., Yang, Y., Wernick, M. N., Galatsanos, N. P., & Nishikawa, R. M. (2002). A support vector machine approach for detection of microcalcifications. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging., 21(12), 1552–1563.
Campanini, R., Dongiovanni, D., Iampieri, E., Lanconelli, N., Masotti, M., Palermo, G., & Roffilli, M. (2004). A novel featureless approach to mass detection in digital mammograms based on support vector machines. Physics in Medicine and Biology., 49(6), 961.
Zhang, P., Verma, B., & Kumar, K. (2004). A neural-genetic algorithm for feature selection and breast abnormality classification in digital mammography. Neural Networks, 3, 2303–2308.
Kinoshita, S. K., de Azevedo-Marques, P. M., Pereira, R. R., Jr., Rodrigues, J. A. H., & Rangayyan, R. M. (2007). Content-based retrieval of mammograms using visual features related to breast density patterns. Journal of Digital Imaging, 20(2), 172–190.
Lu, Z., & Ye, J. (2017). Cosine measures of neutrosophic cubic sets for multiple attribute decision-making. Symmetry, 9(7), 121.
Shen, S., Huang, L., Zhou, H., Yu, S., Fan, E., & Cao, Q. (2018). Multistage signaling game-based optimal detection strategies for suppressing malware diffusion in fog-cloud-based IoT networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 5(2), 1043–1054.
Xia, F., & Huang, S. (2020). Application research of color design and collocation in image processing. Computer Systems Science and Engineering, 35(2), 91–98.
Ye, J., & Fu, J. (2016). Multi-period medical diagnosis method using a single valued neutrosophic similarity measure based on tangent function. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 123, 142–149.
Ying, C., Huang, Z., & Ying, C. (2018). Accelerating the image processing by the optimization strategy for deep learning algorithm DBN. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2018(1), 1–8.
Cui, W. H., & Ye, J. (2019). Logarithmic similarity measure of dynamic neutrosophic cubic sets and its application in medical diagnosis. Computers in Industry, 111, 198–206.
Fu, J., Ye, J., & Cui, W. (2018). An evaluation method of risk grades for prostate cancer using similarity measure of cubic hesitant fuzzy sets. Journal of biomedical informatics, 87, 131–137.
Tang, S., & Yu, F. (2021). Construction and verification of retinal vessel segmentation algorithm for color fundus image under BP neural network model. The Journal of Supercomputing, 77(4), 3870–3884.
Alshanbari, H., Amain, S., Shuttelworth, J., Slman, K., & Muslam, S. (2015). Automatic segmentation in breast cancer using watershed algorithm. International Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Science, 2(2), 1–6.
Pang, S., Fan, M., Wang, X., Wang, J., Song, T., Wang, X., & Cheng, X. (2020). VGG16-T: A novel deep convolutional neural network with boosting to identify pathological type of lung cancer in early stage by CT images. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 13(1), 771–780.
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the medical imaging department of King Abdullah Medical City (KAMC), Saudi Arabia for the provision of MRI images for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amin, S.A., Al Shanabari, H., Iqbal, R. et al. An Intelligent Framework for Automatic Breast Cancer Classification Using Novel Feature Extraction and Machine Learning Techniques. J Sign Process Syst 95, 293–303 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-022-01753-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11265-022-01753-8