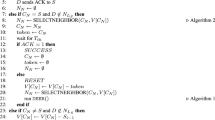Abstract
Energy-aware routing is important in multi-hop wireless networks that are powered by battery, e.g., wireless sensor networks. To maximize the network survivability, the energy efficiency of paths must be taken into account for route selection. Simple heuristics such as choosing paths with minimal energy consumption are ineffective, because the energy of the nodes on such paths may deplete quickly. The issue is particularly serious for the networks with regular traffic pattern as in monitoring sensor applications. Existing solutions to this issue typically adopt the multi-path routing approach, in which multiple paths are set up between source and destination and one (or all) of the paths is (are) used at a certain moment. However, this approach involves high overhead for establishment and management of multiple paths. In this paper, we present a static single-path routing scheme which uses one energy-efficient path for each communicating peer throughout the network lifetime, eliminating the overhead of multi-path routing. It is theoretically proved that our routing scheme achieves a constant factor approximate of the optimal solution. We compare the performance of the proposed scheme with that of multi-path routing via simulations. Despite the use of single static path, the proposed scheme outperforms existing multi-path routing schemes and produces performance close to the optimal multi-path solution, particularly in heavily loaded networks and multiple-gateway networks.












Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Note that the downstream only case or the upstream/downstream mixed case can be easily driven.
Among three formulation models presented in this paper, only the basic model can compute the route selection by one time execution of LP solver, and other two more sophisticated models require multiple executions of LP solvers. While the other two models may produce higher performance, we use only the basic model in the simulations as it is the most practical choice.
References
Zhao, F., & Guibas, L. (2004). Wireless sensor networks: An information processing approach. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers.
Cordeiro, C., & Agrawal, D. (2006). Ad Hoc & sensor networks: Theory and applications. Singapore: World Scientific.
Ganjali, Y., & Keshavarzian, A. (2004). Load balancing in ad hoc networks: Single-path routing vs. multi-path routing. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’04, Hong Kong.
Jones, C. E., Sivalingam, K. M., Agrawal, P., & Chen, J.-C. (2001). A survey of energy efficient network protocols for wireless networks. Wireless Networks, 7(4), 343–358.
Banerjee, S., & Misra, A. (2002). Minimum energy paths for reliable communication in multi-hop wireless networks. In Proceedings of ACM Mobihoc’02 (pp. 146–156).
Cruz, R. L., & Santhanam, A. (2003). Optimal routing, link scheduling, and power control in multi-hop wireless networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’03, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Bhatia, R., & Kodialam, M. (2004). On power efficient communication over multi-hop wireless networks: Joint routing, scheduling and power control. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’03, Hong Kong.
Kodialam, M., & Nandagopal, T. (2003). Characterizing the achievable rates in multihop wireless networks. In Proceedings of ACM Mobicom’03, San Diego, CA, USA (pp. 42–52).
Zhu, J., & Wang, X. (2005). PEER: A progressive energy efficient routing protocol for wireless ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’05, Miami, FL, USA (pp. 1887–1896).
Hsiao, P.-H., Hwang, A., Kung, H. T., & Vlah, D. (2001). Load balancing routing for wireless access networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’01, Anchorage, Alaska, USA (pp. 986–995).
Li, Q., Aslam, J., & Rus, D. (2001). Online power-aware routing in wireless ad-hoc networks. In Proceedings of ACM Mobicom’01, Rome, Italy (pp. 97–107).
Kar, K., Kodialam, M., Lakshman, T. V., & Tassiulas, L. (2003). Routing for network capacity maximization in energy-constrained ad-hoc networks. In Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM’03, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Popa, L., Rostamizadeh, A., Karp, R., Papadimitriou, C., & Stoica, I. (2007). Balancing traffic load in wireless networks with curveball routing. In Proceedings of ACM MobiHoc’07, Montreal, QC, Canada.
Chang, J. H., & Tassiulas, L. (2000). Energy conserving routing in wireless ad-hoc networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’0000, Tel-Aviv, Israel, March.
Srinivasan, V., Chiasserini, C.-F., Nuggehalli, P., & Rao, R. (2002). Optimal rate allocation and traffic splits for energy efficient routing in ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’02, New York, NY, USA (pp. 950–957).
Zussman, G., & Segall, A. (2003). Energy efficient routing in ad hoc disaster recovery networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’03, San Francisco, CA, USA.
Zhu, J., & Wang, X. (2005). PEER: A progressive energy efficient routing protocol for wireless ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM’05, Miami, FL, USA (pp. 1887–1896).
Slama, I., Jouaber, B., & Zeghlache, D. (2006). Routing for wireless sensor networks lifetime maximisation under energy constraints. In Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on Mobile technology, applications & systems Mobility’06, Bangkok, Thailand.
Ma, C., & Yang, Y. (2006). Battery-aware routing for streaming data transmissions in wireless sensor networks. Mobile Networks and Applications, 11(5), 757–767.
Chen, Y., & Nasser, N. (2006). Energy-balancing multipath routing protocol for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 3rd international conference on quality of service in heterogeneous wired/wireless networks QShine’06, Waterloo, ON, Canada.
Yu, M., Malvankar, A., & Foo, S. (2006). An energy-efficient path availability routing algorithm for mobile ad hoc sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE ICC’06, Istanbul, Turkey.
Luo, H., Luo, J., & Liu, Y. (2005). Energy efficient routing with adaptive data fusion in sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2005 joint workshop on foundations of mobile computing DIALM-POMC’05, Cologne, Germany.
Garey, M. R., & Johnson, D. S. (1979). Computers and intractability: A guide to the theory of NP-completeness. New York: Freeman Publication.
Dinitz, Y., Garg, N., & Goemans, M. X. (1998). On the single-source unsplittable flow problem. In IEEE symposium on foundations of computer science, FOCS’08 (pp. 290–299).
Kolliopoulos, S. G., & Stein, C. (1997). Improved approximation algorithms for unsplittable flow problems. In Proceedings of the 38th annual IEEE computer society conference on foundations of computer science, FOCS’97, Miami Beach, FL, USA, October (pp. 426–435).
Hua, C., & Peter Yum, T. S. (2008). Data aggregated maximum lifetime routing for wireless sensor networks. Elsevier Ad Hoc Networks, 6(3), 380–392.
Luo, J., & Hubaux, J. P. (2009). Joint sink mobility and routing to maximize the lifetime of wireless sensor networks: The case of constrained mobility. IEEE/ACM transactions on networking, issue 99, November (pp. 1–14).
Gatzianas, M., & Georgiadis, L. (2008). A distributed algorithm for maximum lifetime routing in sensor networks with mobile sink. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(3), 984–994.
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the IT R&D program of MKE/KEIT [KI002137, Ultra Small Cell Based Autonomic Wireless Network].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bejerano, Y., Lee, KT., Han, SJ. et al. Single-path routing for life time maximization in multi-hop wireless networks. Wireless Netw 17, 263–275 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-010-0278-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-010-0278-7