Abstract
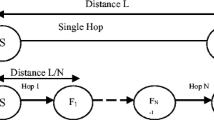
Wireless NanoSensor Networks (WNSNs) will allow novel intelligent nanomaterial-based sensors, or nanosensors, to detect new types of events at the nanoscale in a distributed fashion over extended areas. Two main characteristics are expected to guide the design of WNSNs architectures and protocols, namely, their Terahertz Band wireless communication and their nanoscale energy harvesting process. In this paper, a routing framework for WNSNs is proposed to optimize the use of the harvested energy to guarantee the perpetual operation of the WNSN while, at the same time, increasing the overall network throughput. The proposed routing framework, which is based on a previously proposed medium access control protocol for the joint throughput and lifetime optimization in WNSNs, uses a hierarchical cluster-based architecture that offloads the network operation complexity from the individual nanosensors towards the cluster heads, or nano-controllers. This framework is based on the evaluation of the probability of saving energy through a multi-hop transmission, the tuning of the transmission power of each nanosensor for throughput and hop distance optimization, and the selection of the next hop nanosensor on the basis of their available energy and current load. The performance of this framework is also numerically evaluated in terms of energy, capacity, and delay, and compared to that of the single-hop communication for the same WNSN scenario. The results show how the energy per bit consumption and the achievable throughput can be jointly maximized by exploiting the peculiarities of this networking paradigm.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I. F., & Jornet, J. M. (2010). Electromagnetic wireless nanosensor networks. Nano Communication Networks (Elsevier) Journal, 1(1), 3–19.
Box, F. (1986). Utilization of atmospheric transmission losses for interference-resistant communications. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 34(10), 1009–1015.
Cottone, F., Vocca, H., & Gammaitoni, L. (2009). Nonlinear energy harvesting. Physical Review Letters, 102(8), 080601. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.080601.
Deligeorgis, G., Coccetti, F., Konstantinidis, G., & Plana, R. (2012). Radio frequency signal detection by ballistic transport in y-shaped graphene nanoribbons. Applied Physics Letters, 101(1), 013502.
Drexler, K. E. (1986). Molecular engineering: Assemblers and future space hardware. Paper AAS-86-415, presented at Aerospace XXI, the 33rd annual meeting of the American Astronautical Society, Boulder, CO, 26–29 Oct 1986.
Drexler, E. (1992). Nanosystems: Molecular machinery, manufacturing, and computation. NY: Wiley.
Gammaitoni, L., Neri, I., & Vocca, H. (2009). Nonlinear oscillators for vibration energy harvesting. Applied Physical Letters, 94, 164102. doi:10.1063/1.3120279.
Jornet, J. M., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2011). Channel modeling and capacity analysis of electromagnetic wireless nanonetworks in the terahertz band. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 10(10), 3211–3221.
Jornet, J. M., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2012). Joint energy harvesting and communication analysis for perpetual wireless nanosensor networks in the terahertz band. IEEE Transactions on Nanotechnology, 11(3), 570–580.
Jornet, J. M., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2013). Graphene-based plasmonic nano-antenna for terahertz band communication in nanonetworks. To appear in IEEE JSAC, Special Issue on Emerging Technologies for Communications.
Otsuji, T., Boubanga Tombet, S., Satou, A., Ryzhii, M., & Ryzhii, V. (2013). Terahertz-wave generation using graphene—toward new types of terahertz lasers. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, 19(1), 8,400,209.
Papoulis, A., & Pillai, S. U. (2002). Probability, random variables and stochastic processes. McGraw-Hill.
Piesiewicz, R., Kleine-Ostmann, T., Krumbholz, N., Mittleman, D., Koch, m., Schoebel, J., & Kurner, T. (2007). Short-range ultra-broadband terahertz communications: Concepts and perspectives. IEEE Antennas and Propagation Magazine, 49(6), 24–39.
Ponomarenko, L. A., Schedin, F., Katsnelson, M. I., Yang, R., Hill, E. W., Novoselov, K. S., & Geim, A. K. (2008). Chaotic Dirac billiard in graphene quantum dots. Science, 320(5874), 356–358.
Sensale-Rodriguez, B., Yan, R., Kelly, M. M., Fang, T., Tahy, K., Hwang, W. S., Jena, D., Liu, L., & Xing, H. G. (2012). Broadband graphene terahertz modulators enabled by intraband transitions. Nature Communications, 3, 780.
Tamagnone, M., Gomez-Diaz, J. S., Mosig, J. R., & Perruisseau-Carrier, J. (2012). Reconfigurable terahertz plasmonic antenna concept using a graphene stack. Applied Physics Letters, 101(21), 214102.
Vicarelli, L., Vitiello, M.S., Coquillat, D., Lombardo, A., Ferrari, A.C., Knap, W., Polini, M., Pellegrini, V., & Tredicucci, A. (2012). Graphene field-effect transistors as room-temperature terahertz detectors. Nature Materials, 11, 865–871.
Wang, P., Jornet, J. M., Malik, M. A., Akkari, N., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2013). Energy and spectrum-aware MAC protocol for perpetual wireless nanosensor networks in the terahertz band. Ad Hoc Networks (Elsevier) Journal. (to appear)
Wang, Z. L. (2008). Towards self-powered nanosystems: From nanogenerators to nanopiezotronics. Advanced Functional Materials, 18(22), 3553–3567.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Pu Wang and Dr. M. G. Abbas Malik for their invaluable support in the preparation of this paper. The material presented in this paper is based upon work funded by King Abdulaziz University, under Grant No. (11-15-1432/HiCi). The authors, therefore, acknowledge technical and financial support of KAU.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pierobon, M., Jornet, J.M., Akkari, N. et al. A routing framework for energy harvesting wireless nanosensor networks in the Terahertz Band. Wireless Netw 20, 1169–1183 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-013-0665-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-013-0665-y