Abstract
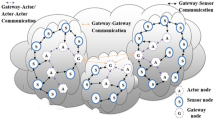
Wireless sensor and actor networks (WSAN) are captivating significant attention because of their suitability for safety–critical applications. Efficient actor placement in such applications is extremely desirable to perform effective and timely action across the deployment region. Nonetheless, harsh application environment inherently favors random placement of actors that leads to high concentration deployment and strangles coverage. Moreover, most of the published schemes lack rigorous validation and entirely rely on informal techniques (e.g., simulation) for evaluating nonfunctional properties of algorithms. This paper presents a localized movement control actor relocation (MCAR) algorithm that strives to improve connected coverage while minimizing movement overhead. MCAR pursues post-deployment actor repositioning in such a way that actors repel each other for better coverage while staying connected. We employ complementary formal and informal techniques for MCAR verification and validation. We model WSAN as a dynamic graph and transform MCAR to corresponding formal specification using Z notation. The resulting specification is analyzed and validated using Z eves tool. We simulate the specification to quantitatively demonstrate the efficiency of MCAR. Simulation results confirm the efficiency of MCAR in terms of movement overhead and connected coverage compared to contemporary schemes. The results show that MCAR can reduce distance movement up to 32 % while improving coverage up to 29 % compared to published schemes.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akyildiz, I. F., & Kasimoglu, I. H. (2004). Wireless sensor and actor networks: Research challenges. Journal Ad Hoc Networks, 2(4), 351–367.
Zeng, Y., Li, D., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2013). Real-time data report and task execution in wireless sensor and actuator networks using self-aware mobile actuators. Computer Communications, 36(9), 988–997.
Yao,Y., Cao, Q., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2013). EDAL: An energy-efficient, delay-aware, and lifetime-balancing data collection protocol for wireless sensor networks. In 10th IEEE international conference on mobile ad-hoc and sensor systems (MASS) (pp. 182–190), Hangzhou, China.
Batalin, M. A., & Sukhatme, G. S. (2005). The analysis of an efficient algorithm for robot coverage and exploration based on sensor network deployment. In Presented at the proceedings of the 2005 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation (ICRA 2005), Barcelona, Spain.
Akkaya, K., & Younis, M. (2007). C2AP: Coverage-aware and connectivity-constrained actor positioning in wireless sensor and actor networks. In Presented at the IEEE international performance computing, and communications conference (IPCCC′ 07), 2007, New Orleans, LA.
Akkaya, K., & Janapala, S. (2008). Maximizing connected coverage via controlled actor relocation in wireless sensor and actor networks. Journal Computer Networks, 52(14), 2779–2796.
Imran, M., Younis, M., Md Said, A., & Hasbullah, H. (2010). Volunteer-instigated connectivity restoration algorithm for wireless sensor and actor networks. In The proceedings of the 2010 IEEE international conference on wireless communications, networking and information security (WCNIS) (pp. 679–683), Beijing, China.
Tamboli, N., & Younis, M. (2010). Coverage-aware connectivity restoration in mobile sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 33(4), 363–374.
Imran, M., Younis, M., Haider, N., & Alnuem, M. A. (2012). Resource efficient connectivity restoration algorithm for mobile sensor/actor networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2012, 347.
Younis, M., Senturk, I. F., Akkaya, K., Lee, S., & Senel, F. (2014). Topology management techniques for tolerating node failures in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 58(1), 254–283.
Spivey, J. M. (1989). The Z notation: A reference manual. Englewood: Prentice-Hall Inc.
Wang, X., Xing, G., Zhang, Y., Lu, C., Pless, R., & Gill, C. (2003). Integrated coverage and connectivity configuration in wireless sensor networks. In Presented at the proceedings of the 1st international conference on embedded networked sensor systems, Los Angeles, California, USA, 2003.
Ghosh, A., & Das, S. K. (2008). Coverage and connectivity issues in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Journal of Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 4, 303–334.
Zhu, C., Zheng, C., Shu, L., & Han, G. (2012). A survey on coverage and connectivity issues in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 35, 619–632.
Younis, M., & Akkaya, K. (2008). Strategies and techniques for node placement in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Journal Ad Hoc Networks, 6(4), 621–655.
Batalin, M. A., & Sukhatme, G. S. (2002). Spreading out: A local approach to multi-robot coverage. In presented at the international symposium on distributed autonomous robotic systems, Fukuoka, Japan, 2002.
Heo, N., & Varshney, P. K. (2003). A distributed self spreading algorithm for mobile wireless sensor networks. In Presented at the IEEE wireless communications and networking (WCNC’ 03), 2003, New Orleans, LA, USA.
Wang, G., Cao, G., & Porta, T. L. (2004). Movement-assisted sensor deployment. In Presented at the 23rd international annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies (INFOCOM’04), Hong Kong.
Wang, G., Cao, G., Porta, T. L., & Zhang, W. (2005). Sensor relocation in mobile sensor networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE 24th annual joint conference of the IEEE computer and communications societies (INFOCOM 2005) (pp. 2302–2312), Miami, FL, USA 2005.
Li, M., Li, Z., & Vasilakos, A. V. (2013). A Survey on topology control in wireless sensor networks: Taxonomy, comparative study, and open issues. Proceedings of the IEEE, 101(12), 2538–2557.
Akkaya, K., & Younis, M. (2006). COLA: A coverage and latency aware actor placement for wireless sensor and actor networks. In Presented at the IEEE 64th vehicular technology conference (VTC-2006), 2006, Montreal, Canada.
Imran, M., Said, A. M., Younis, M., & Hasbullah, H. (2013). Application-centric recovery algorithm for wireless sensor and actor networks. International Journal of Communication Networks and Distributed Systems, 10(4), 379–401.
Imran, M., Haider, N., & Alnuem, M. A. (2012). Efficient movement control actor relocation for honing connected coverage in wireless sensor and actor networks. In The proceedings of the 37th IEEE annual international conference on local computer networks ( pp. 710–717), Florida, USA.
Alnuem, M., Zafar, N. A., Imran, M., Fayed, M., & Ullah, S. (2014). Formal specification and validation of a localized algorithm for segregation of critical/noncritical nodes in MAHSNs. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2014, 14. doi:10.1155/2014/140973.
Viana, A. C., Maag, S., & Zaidi, F. (2011). One step forward: Linking wireless self-organizing network validation techniques with formal testing approaches. ACM Computing Surveys, 43(2), 1–36.
Kurkowski, S., Camp, T., & Colagrosso, M. (2005). MANET simulation studies: the incredibles. SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 9, 50–61.
Andel, T. R., & Yasinsac, A. (2006). On the credibility of manet simulations. Computer, 39, 48–54.
Zafar, N. A. (2006). Modeling and formal specification of automated train control system using Z notation. In Multitopic conference, 2006. INMIC ‘06. IEEE (pp. 438–443).
Yousaf, S., Zafar, N. A., & Khan, S. A. (2010). Formal analysis of departure procedure of air traffic control system. In 2010 2nd international conference on software technology and engineering (ICSTE), 2010 (pp. V2-301–V2-305).
Fehnker, A., Fruth, M., & Mciver, A. K. (2009). Graphical modelling for simulation and formal analysis of wireless network protocols. In B. Michael, J. Cliff, R. Alexander, & T. Elena (Eds.), Methods, models and tools for fault tolerance (pp. 1–24). Berlin: Springer.
Maag, S., Grepet, C., & Cavalli, A. (2008). A formal validation methodology for MANET routing protocols based on nodes’ self similarity. Computer Communications, 31, 827–841.
Ölveczky, P. C., & Thorvaldsen, S. (2009). Formal modeling, performance estimation, and model checking of wireless sensor network algorithms in Real-Time Maude. Theoretical Computer Science, 410, 254–280.
Imran, M., & Zafar, N. A. (2012). Formal specification and validation of a hybrid connectivity restoration algorithm for wireless sensor and actor networks. Sensors, 12(9), 11754–11781.
Efrat, S. H.-P., & Mitchell, J. S. B. (2005). Approximation algorithms for two optimal location problems in sensor networks. In 2nd international conference on broadband networks (pp. 714–723), Boston, USA.
Funke, S. (2005). Topological hole detection in wireless sensor networks and its applications. In Presented at the proceedings of the 2005 joint workshop on foundations of mobile computing, Cologne, Germany.
Wang, Y., Gao, J., & Mitchell, J. S. B. (2006). Boundary recognition in sensor networks by topological methods. In Presented at the proceedings of the 12th annual international conference on mobile computing and networking, Los Angeles, CA, USA.
Saaltink, M. (1997). The Z/EVES system. In Presented at the proceedings of the 10th international conference of Z users on the Z formal specification notation.
Jorgic, M., Stojmenovic, I., Hauspie, M., & Simplot-Ryl, D. (2004). Localized algorithms for detection of critical nodes and links for connectivity in ad hoc networks. In The proceedings of the 3rd annual ifip mediterranean ad hoc networking workshop (pp. 360–371), Bodrum, Turkey.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Center of College of Computer and Information Sciences, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, through the Research Project No. RC131026.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Imran, M., Zafar, N.A., Alnuem, M.A. et al. Formal verification and validation of a movement control actor relocation algorithm for safety–critical applications. Wireless Netw 22, 247–265 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-0962-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-0962-8