Abstract
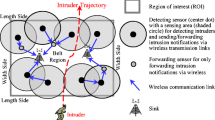
Barrier coverage constructs a sensing barrier for detecting intruders crossing a belt region. Recent studies mostly focus on efficient algorithms to guarantee barrier coverage, with little consideration on the collaboration between individual nodes. Observing that in many situations, sensors naturally fall into several clusters (or components), for example when the sensors are deployed uniformly at random with a relatively low density, or when random sensors go down as a result of energy exhaustion, we propose to use chain as a basic scheduling unit for sensing and communication. A chain is a set of sensors whose sensing areas overlap with each other, and it can be extracted from a cluster. We present a distributed algorithm, named BARRIER, to provide barrier coverage with a low communication overhead for the wireless sensor networks (WSNs). The algorithm is able to detect weak zones that are often found in an initial deployment of a WSN, and repair them by adding an appropriate number of sensors. Theoretic analysis and simulations show that, compared with a representative previous algorithm, BARRIER significantly reduces the communication overhead and reparation cost in terms of number of sensors.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balister, P., Bollobas, B., Sarkar, A., & Kumar, S. (2007). Reliable density estimates for achieving coverage and connectivity in thin strips of finite length. In Proceedings of ACM MobiCom, pp. 75–86.
Balister, P., Zheng, Z., Kumar, S., & Sinha, P. (2009). Trap coverage allowing coverage holes of bounded diameter in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 136–144.
Chen, A., Kumar, S., & Lai, T.H. (2007). Designing localized algorithms for barrier coverage. In Proceedings of ACM MobiCom, pp. 63–74.
Chen, A., Lai, T.H., Xuan, D. (2008). Measuring and guaranteeing quality barrier-coverage in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of ACM MobiHoc, pp. 421–430.
Chen, A., Lai, T. H., & Xuan, D. (2010). Measuring and guaranteeing quality of barrier coverage for general belts with wireless sensors. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 6(1), 2:1–2:31.
Du, J., Wang, K., Liu, H., & Guo, D. (2013). Maximizing the lifetime of k-discrete barrier coverage using mobile sensors. IEEE Sensors Journal, 13(12), 4690–4701.
Gong, X., Zhang, J., Cochran, D., & Xing, K. (to appear) Optimal placement for barrier coverage in bistatic radar sensor networks. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking. doi:10.1109/TNET.2014.2360849.
Kong, L., Zhu, Y., Wu, M.Y., & Shu, W. (2012). Mobile barrier coverage for dynamic objects in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE MASS, pp. 29–37.
Kumar, S., Lai, T.H., Posner, M.E., & Sinha, P. (2005). Barrier coverage with wireless sensors. In Proceedings of ACM MobiCom, pp. 284–298.
Kumar, S., Lai, T.H., Posner, M.E., & Sinha, P. (2007). Optimal sleep-wakeup algorithms for barriers of wireless sensors. In Proceedings of BROADNETS, pp. 327–336.
Liu, B., Dousse, O., Wang, J., & Saipulla, A. (2008). Strong barrier coverage of wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of ACM MobiHoc, pp. 411–420.
M Cardei, M.T., & Wu, W. (2005). Energy-efficient target coverage in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 261–266.
Ma, H., Yang, M., Li, D., Hong, Y., & Chen, W. (2012). Minimum camera barrier coverage in wireless camera sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 217–225.
Saipulla, A., Westphal, C., Liu, B., & Wang, J. (2009). Barrier coverage of line-based deployed wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 127–135.
Tao, D., & Wu, T. Y. (2015). A survey on barrier coverage problem in directional sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(2), 876–885.
Wang, W., Srinivasan, V., Chua, K.C., & Wang, B. (2007). Energy-efficient coverage for target detection in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IPSN, pp. 313–322.
Wang, Z., Liao, J., Cao, Q., Qi, H., & Wang, Z. (2014). Achieving k-barrier coverage in hybrid directional sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 13(7), 1443–1455.
Yang, G., & Qiao, D. (2009). Barrier information coverage with wireless sensors. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 918–926.
Yang, G., & Qiao, D. (2010). Multi-round sensor deployment for guaranteed barrier coverage. In Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, pp. 1–9.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grants 61271226, 61272410, 61202460 and 61471408; by the National High Technology Research and Development Program (“863” Program) of China under Grants 2014AA01A701 and 2015AA011303; by the National Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province under Grant 2014CFA040; by the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation under Grants 2014M560608; and by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities under Grant 2015QN073.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, T., Lin, H., Wang, C. et al. Chain-based barrier coverage in WSNs: toward identifying and repairing weak zones. Wireless Netw 22, 523–536 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-0988-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-0988-y