Abstract
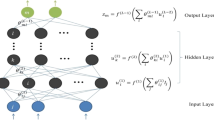
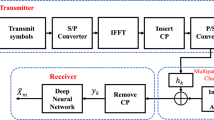
One of the major drawback in multi-carrier signals is large envelope fluctuations i.e., high peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR). The objective of this paper is to propose neural network based active gradient project sequence, a computationally efficient hybrid method to reduce PAPR in multiple-input multiple-output orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system without sacrificing BER performance. In this paper, a neural network based trained module of approximate gradient project scheme (AGP-NN) is combined in parallel with partial transmit sequence method. The Levenberg–Marquardt training algorithm is used to train neural network based AGP module. The simulation results show that the proposed technique not only outperforms other conventional techniques but also offers less computational complexity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu, Y., & Zou, W. Y. (1995). Orthogonal frequency division multiplexing: A multicarrier modulation scheme. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 41(3), 392–399.
Soo, Y., Kim, J., Yang, W. Y., & Kang, C. G. (2010). MIMO-OFDM wireless communications with matlab. Hoboken: Wiley.
Yang, K., & Chang, S. (2003). Peak-to-average power control in OFDM using standard arrays of linear block codes. IEEE Communication Letters, 7(4), 174–176.
Li, C. M., & Cheng, Y. Y. (2013). A low complexity partition dummy sequence insertion PAPR reduction method for the OFDM system. Wireless Personal Communications, 68(3), 949–961.
Armstrong, J. (2002). Peak-to-average power reduction for OFDM by repeated clipping and frequency domain filtering. IEEE Electronics Letter, 38(8), 246–247.
Cimini Jr, L. J., & Sollenberger, N. R. (2000). Peak-to-average power ratio reduction of an OFDM signal using partial transmit sequences. IEEE Communication Letter, 4(3), 86–88.
Bäuml, R. W., Fischer, R. F. H., & Huber, J. B. (1996). Reducing the peak-to-average power ratio of multicarrier modulation by selected mapping. IEEE Electronics Letters, 32(22), 2056–2057.
Chen, J. C., & Li, C. P. (2010). Tone reservation using near-optimal peak reduction tone set selection algorithm for PAPR reduction in OFDM systems. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 17(11), 933–936.
Pachori, K., & Mishra, A. (2015). PAPR Reduction in MIMO-OFDM by using active partial sequence. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing. doi:10.1007/s00034-015-0039-z.
Mishra, A., Saxena, R., & Patidar, M. (2015). AGP-NCS scheme for PAPR reduction. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-015-2275-8.
Duanmu, C., & Chen, H. (2014). Reduction of the PAPR in OFDM systems by intelligently applying both PTS and SLM algorithms. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-013-1325-3.
Pachori, K., & Mishra, A. (2015). An efficient combinational approach for PAPR reduction in MIMO-OFDM system. Wireless Networks. doi:10.1007/s11276-015-0974-4.
Mishra, A., Saxena, R., & Patidar, M. (2014). OFDM link with a better performance using artificial neural network. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-013-1593-y.
Jabrane, Y., Jimenez, V. P. G., Armeda, A. G., Said, B. E., & Ouahman, A. A. (2010). Reduction of power envelope fluctuations in OFDM signals by using neural networks. IEEE Communication Letters, 14(7), 599–601.
Jimenez, V. P. G., Jabrane, Y., Armeda, A. G., Said, B. E., & Ouahman, A. A. (2011). Reduction of envelope fluctuations of multi-carrier modulations using adaptive neural fuzzy inference systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 59(1), 19–25.
Wong, T. K., Wang, B., & Chen, J. C. (2011). OFDM PAPR reduction by switching null subcarriers and data subcarriers. IEEE Electronics Letters, 47(1), 62–63.
Jiang, T., & Wu, Y. W. (2008). An overview: Peak to average power ratio reduction techniques for OFDM signals. IEEE Transactions on Broadcasting, 54(2), 257–268.
Jones, D. (1999). Peak power reduction in OFDM and DMT via active constellation extension. Proceedings of Asliomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, 2, 1076–1079.
Hagan, M. T., Demuth, H. B., & Beale, M. (2011). Neural network design (4th ed.). New Delhi: Cengage Learning India Pvt. Ltd.
Alamouti, S. M. (1998). A simple transmit diversity technique for wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 16, 1451–1458.
Krongold, B. S., & Jones, D. L. (2003). PAR reduction in OFDM via active constellation extension. IEEE Transaction on Broadcasting, 49(3), 258–268.
Tellambura, C. (2001). Improved phase factor computation for the PAR reduction of an OFDM signal using PTS. IEEE Commununication Letters, 5(4), 135–137.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pachori, K., Mishra, A. A hybrid envelope fluctuations reduction approach using multilayer neural network for MIMO-OFDM signals. Wireless Netw 22, 2705–2712 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-1126-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-015-1126-6