Abstract
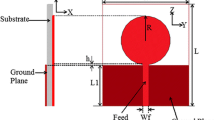
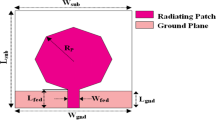
Circular monopole antenna for ultra-wide band applications with notch band transition from WLAN to WiMAX is presented. The proposed antenna rejects WiMAX band (3.3–3.8 GHz). Antennas utilises modified mushroom-type electromagnetic band gap (EBG) structures to achieve band-notched designs. The proposed inductance enhanced modified EBG structures are 34 % compact than the conventional mushroom EBG structures. The band notched antenna designs using EBG structures have advantages like notch-frequency tuning, antenna design independent approach and omnidirectional radiation pattern. The step wise effect of inductance enhancement and tuning of notch from WLAN band (5–6 GHz) to WiMAX band is shown. Effect of variation of EBG structure parameters on which notched frequency depends is investigated. The proposed antenna has been fabricated on low cost FR4 substrate with overall dimensions as (42 × 50 × 1.6) mm3. Measured results are in good agreement with simulated ones.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Federal Communications Commission. (2002). Revision of part 15 of the commission’s rules regarding ultra-wideband transmission systems. Tech. rep. ET-Docket 98-153, FCC02-48, Federal Communications Commission (FCC), Washington, DC, USA.
Liang, J., Chiau, C. C., Chen, X., & Parini, C. G. (2004). Printed circular disc monopole antenna for ultra-wideband applications. Electronics Letters, 40(20), 1246–1248.
Cho, Y. J., Kim, K. H., Choi, D. H., Lee, S. S., & Park, S. O. (2006). A miniature UWB planar monopole antenna with 5-GHz band-rejection filter and the time-domain characteristics. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 54(5), 1453–1460.
Lee, W. S., Kim, D. Z., Kim, K. J., & Yu, J. W. (2006). Wideband planar monopole antennas with dual band-notched characteristics. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(6), 2800–2806.
Chung, K., Kim, J., & Choi, J. (2005). Wideband microstrip-FED monopole antenna having frequency band-notch function. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 15(11), 766–768.
Kim, Y., & Kwon, D. H. (2004). CPW-FED planar ultra-wideband antenna having a frequency band notch function. Electronics Letters, 40(7), 403–405.
Abbosh, A. M., Bialkowski, M. E., Mazierska, J., & Jacob, M. V. (2006). A planar UWB antenna with signal rejection capability in the 4–6 GHz band. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 16(5), 278–280.
Hu, S., Chen, H., Law, C. L., Shen, Z., Zui, L., Zhang, W., et al. (2007). Backscattering cross section of ultrawideband antennas. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 6, 70–73.
Lui, W. J., Cheng, C. H., Cheng, Y., & Zhu, H. (2005). Frequency notched ultra-wideband microstrip slot antenna with fractal tuning stub. Electronics Letters, 41(6), 294–296.
Abbosh, A. M., & Bialkowski, M. E. (2009). Design of UWB planar band-notched antenna using parasitic elements. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 57(3), 796–799.
Kim, K. H., & Park, S. O. (2006). Analysis of the small band-rejected antenna with the parasitic strip for UWB. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 54(6), 1688–1692.
Qu, S. W., Li, J. L., & Xue, Q. (2006). A band-notched ultra-wideband printed monopole antenna. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 5, 495–498.
Ryu, K. S., & Kishk, A. A. (2009). UWB antenna with single or dual band notches for lower WLAN band and upper WLAN band. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 57(12), 3942–3950.
Zhu, F., Gao, S., Ho, A. T. S., Al Hameed, A., See, C. H., Brown, T. W. C., et al. (2013). Multiple band-notched UWB antenna with band-rejected elements integrated in the feed line. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 61(5), 3952–3960.
Foudazi, A., Hassani, H. R., & Ali Nezhad, S. M. (2012). Small UWB planar monopole antenna with added GPS/GSM/WLAN bands. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 60(6), 2987–2992.
Tang, M. C., Xiao, S., Deng, T., Wang, D., Guan, J., Wang, B., et al. (2011). Compact UWB antenna with multiple band-notches for WiMAX and WLAN. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 59(4), 1372–1376.
Deng, J. Y., Yin, Y. Z., Zhou, S. G., & Liu, Q. Z. (2008). Compact ultra-wideband antenna with tri-band notched characteristics. Electronics Letters, 44(21), 1231–1233.
Trang, N. D., Lee, D. H., & Park, H. C. (2011). Design and analysis of compact printed triple band-notched UWB antenna. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 10, 403–406.
Yazdi, M., & Komjani, N. (2011). Design of a band-notched UWB monopole antenna by means of an EBG structure. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 10, 170–173.
Peng, L., & Ruan, C. (2011). UWB band-notched monopole antenna design using electromagnetic-bandgap structures. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 59, 1074–1081.
Zheng, Q. R., Fu, Y. Q., & Yuan, N. C. (2008). A novel compact spiral electromagnetic band-gap (EBG) structure. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 56(6), 1656–1660.
Wang, C.-L., Shiue, G. H., Guo, W.-D., & Wu, R.-B. (2006). A systematic design to suppress wideband ground bounce noise in high-speed circuits by electromagnetic-bandgap-enhanced split powers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(12), 4209–4217.
Xie, H.-H., Jiao, Y.-C., Song, K., & Yang, B. (2010). Miniature electromagnetic band-gap structure using spiral ground plane. Progress in Electromagnetics Research Letters, 17, 163–170.
Simovski, C. R., Maagt, P., & Melchakova, I. (2005). High-impedance surfaces having stable resonance with respect to polarization and incidence angle. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 53(3), 908–914.
McVay, J., & Engheta, N. (2004). High impedance metamaterial surfaces using Hilbert-curve inclusions. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters, 14(3), 130–132.
Vardaxoglou, J. C., Gousetis, G., & Feresidis, A. P. (2007). Miniaturisation schemes for metallodielectric electromagnetic bandgap structures. IET Microwaves, Antennas and Propagation, 1(1), 234–239.
Yang, F., & Rahmat-Samii, Y. (2004). Polarization dependent electromagnetic band gap (PDEBG) structures: designs and applications. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 41(6), 439–444.
Sievenpiper, D. F., Schaffner, J. H., Song, H. J., Loo, R. Y., & Tangonan, G. (2003). Two-dimensional beam steering using an electrically tunable impedance surface. EEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 51(10), 2713–2722.
Boutayeb, H., & Denidni, T. A. (2006). Technique for reducing the power supply in reconfigurable cylindrical electromagnetic bandgap structures. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 5(1), 424–425.
Ge, Y., & Esselle, K. P. (2007). GA/FDTD technique for the design and optimisation of periodic metamaterials. IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, 1(1), 158–164.
Dai, M., & Sung, C. W. (2013). Achieving high diversity and multiplexing gains in the asynchronous parallel relay network. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 24(2), 232–243.
Arslan, H., Chen, Z. N., & Di Benedetto, M.-G. (2006). Ultra-wideband wireless communication. Hoboken: Wiley.
Oppermann, I., Hamalainen, M., & Linatti, J. (2004). UWB theory and applications. Hoboken: Wiley.
Yang, F., & Rahmat-Samii, Y. (2004). Electromagnetic band gap structures in antenna engineering. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Sievenpiper, D. (1999). High-impedance electromagnetic surfaces. Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Electrical Engineering University of California, Los Angeles.
Jaglan, N., & Gupta, S. D. (2015). Design and analysis of performance enhanced microstrip patch antenna with EBG substrate. International Journal of Microwave and Optical Technology (IJMOT), 10(2), 79–88.
Jaglan, N., & Gupta, S. D. (2015). Reflection phase characteristics of EBG structures and Wlan band notched circular monopole antenna design. International Journal of Communications Antenna and Propagation (IRECAP), 5(4), 233–240.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaglan, N., Gupta, S.D., Kanaujia, B.K. et al. Band notched UWB circular monopole antenna with inductance enhanced modified mushroom EBG structures. Wireless Netw 24, 383–393 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1343-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-016-1343-7