Abstract
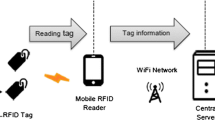
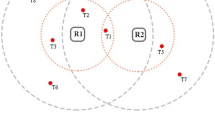
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is known as a universal technology and has been in the center of attention in the past few years. Readers and tags constitute the main parts of an RFID system. Similar to other wireless devices, RFID readers are confronted with the critical problem of collision. This is because in some applications, numerous readers are spread out densely and are attempting to attain the same tags simultaneously. Collisions are classified to reader-to-reader and reader-to-tag collisions. Both of these collisions may decrease the system’s throughput and performance, or even result in the consumption of a considerable amount of energy. Many various anti-collision protocols have been proposed to avoid these collisions, but there are only a few researches concerning their energy efficiency. While this paper will look at the main reader anti-collision protocols, it will also demonstrate the evaluation results of their energy efficiency via experimental simulations in similar circumstances. The obtained results can help in choosing the most efficient anti-collision protocol in applications like using mobile readers or combining RFIDs with WSN networks which have energy-consuming constraints.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yu, J., Lee, W., & Du, D.-Z. (2011). Reducing reader collision for mobile RFID. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 57(2), 574–582.
Bolic, M., Simplot-Ryl, D., & Stojmenovic, I. (Eds.). (2010). RFID systems: Research trends and challenges. Hoboken: Wiley.
Roussos, G. (2008). Networked RFID: systems, software and services. Berlin: Springer.
Joshi, G. P., & Kim, S. W. (2008). Survey, nomenclature and comparison of reader anti-collision protocols in RFID. IETE Technical Review, 25(5), 234–243.
Mitrokotsa, A., & Douligeris, C. (2009). Integrated RFID and sensor networks: Architectures and applications. RFID and Sensor Networks: Architectures, Protocols, Security and Integrations, 512, 511–535.
Liu, H., Bolic, M., Nayak, A., & Stojmenovic, I. (2008). Taxonomy and challenges of the integration of RFID and wireless sensor networks. IEEE Network, 22(6), 26–35.
Meguerditchian, C., Safa, H., & El-Hajj, W. (2011). New reader anti-collision algorithm for dense rfid environments. In 18th International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems (ICECS) (pp. 85–88). IEEE.
Ko, D., Kim, B., & An, S. (2010). Research on anti-reader collision protocols for integrated RFID-WSNs. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems (TIIS), 4(5), 776–796.
Li, Z., He, C., & Tan, H.-Z. (2011). Survey of the advances in reader anti-collision algorithms for RFID systems. In Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Chinese (pp. 3771–3776). IEEE.
Galiotto, C., Cetin. K., Frattasi, S., Marchetti, N., Prasad, N. R., & Prasad, R. (2011). High fairness reader anti-collision protocol in passive RFID systems. In International Conference on RFID on (pp. 113–120). IEEE.
Golsorkhtabaramiri, M., Hosseinzadeh, M., Reshadi, M., & Rahmani, M. A. (2015). A reader anti-collision protocol for RFID-enhanced wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 81(2), 893–905.
Heikalabad, S. R., Navin, A. H., Mirnia, M., Ebadi, S., & Golesorkhtabar, M. (2010). EBDHR: Energy balancing and dynamic hierarchical routing algorithm for wireless sensor networks. IEICE Electronics Express, 7(15), 1112–1118.
Golsorkhtabaramiri, M., & Hosseinzadeh, M. (2013). A novel stable cluster-based protocol for heterogeneous RFID enhanced wireless sensor networks. QScience Connect, 35, 1–12.
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., & Pavon-Marino, P. (2013). A centralized and aligned scheduler for passive RFID dense reader environments working under EPCglobal standard. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 34, 172–185.
Hsu, C.-H., Chen, S.-C., Yu, C.-H., & Park, J. H. (2009). Alleviating reader collision problem in mobile RFID networks. Personal and Ubiquitous Computing, 13(7), 489–497.
Ferrero, R., Gandino, F., Montrucchio, B., & Rebaudengo, M. (2014). Improving colorwave with the probabilistic approach for reader-to-reader anti-collision TDMA protocols. Wireless Networks, 20(3), 397–409.
Finkenzeller, K. (2003). RFID handbook: Fundamentals and applications in contactless smart cards and identification, R. Waddington (2nd ed.). Hoboken: Wiley.
ETSI, EN (2017). 302 208-1 version 1.4.1 2011. http://www.etsi.org. March 2017.
Maina, J. Y., Mickle, M. H., Lovell, M. R., & Schaefer, L. A. (2007). Application of CDMA for anti-collision and increased read efficiency of multiple RFID tags. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 26(1), 37–43.
Alrezaamiri, H., Golsorkhtabaramiri, M., Farmanbar, M., & Naeemaeiaali, H. (2015). A high throughput CDMA-based reader collision avoidance protocol for RFID networks (HRCP). Journal of Advances in Computer Research, 6(1), 1–8.
Qiao, J., Wang, W., Zhang, Y., & Niu, S. (2012). Code division cooperative identification reader anti-collision protocol in smart RFID systems. In 19th International Conference Telecommunications (ICT) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Gandino, F., Ferrero, R., Montrucchio, B., & Rebaudengo, M. (2013). DCNS: An adaptable high throughput RFID reader-to-reader anticollision protocol. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 24(5), 893–905.
Gandino, F., Ferrero, R., Montrucchio, B., & Rebaudengo, M. (2011). Probabilistic DCS: An RFID reader-to-reader anti-collision protocol. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 34(3), 821–832.
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., & Pavón-Mariño, P. (2013). A maximum likelihood-based distributed protocol for passive RFID dense reader environments. The Journal of Supercomputing, 64(2), 456–476.
Waldrop, J, Engels, D. W., & Sarma S. E. (2003). Colorwave: An anticollision algorithm for the reader collision problem. In International Conference Communications (ICC) (Vol. 2, pp. 1206–1210). IEEE.
Birari, S. M., & Iyer, S. (2005). PULSE: A MAC protocol for RFID networks. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 3823, 1036–1046.
Eom, J.-B., Yim, S.-B., & Lee, T.-J. (2009). An efficient reader anticollision algorithm in dense RFID networks with mobile RFID readers. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 56(7), 2326–2336.
Ferrero, R., Gandino, F., Montrucchio, B., & Rebaudengo, M. (2012). A fair and high throughput reader-to-reader anticollision protocol in dense RFID networks. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 8(3), 697–706.
EPC Radio-Frequency Identify Protocols Class-1 Generation-2 UHF RFID EPCGlobal (2017) [Online]. Available http://www.gs1.org.
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., Ferrero, R., Gandino, F., Pavon-Marino, P., & Rebaudengo, M. (2013). A geometric distribution reader anti-collision protocol for RFID dense reader environments. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 10(2), 296–306.
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., & Mariño P. P. (2013). Using non-uniform probability distribution p* to improve identification performance in dense RFID reader environments. In Seventh International Conference Innovative Mobile and Internet Services in Ubiquitous Computing (IMIS) (pp. 468–471). IEEE.
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., Vales-Alonso, J., Angerer, C., & Rupp, M. A comparative study of RFID schedulers in dense reader environments. In International Conference Industrial Technology (ICIT) (pp. 1373–1378). IEEE.
Golsorkhtabaramiri, M., & Issazadehkojidi, N. (2017). A distance based RFID reader collision avoidance protocol for dense reader environments. Wireless Personal Communications, 95(2), 1781–1798.
Rezaie, H., & Golsorkhtabaramiri, M. (2017). A fair reader collision avoidance protocol for RFID dense reader environments. Wireless Networks. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-017-1447-8.
Ferrero, R., Gandino, F., Zhang, L., Montrucchio, B., Rebaudengo, M. (2013). Simulating reader-to-reader interference in RFID systems. In 27th International Conference Advanced Information Networking and Applications Workshops (WAINA) (pp. 1063–1069). IEEE.
SkyeTek. (2018). SkyemoduleM1-Mini, Datasheet. Available (2018) [Online]. Available: http://www.skyetek.com/docs/mn/m1minidatasheet.pdf.
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., & Vales-Alonso, J. (2011). On the optimal frame-length configuration on real passive RFID systems. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 34(3), 864–876.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Golsorkhtabaramiri, M., Issazadehkojidi, N., Pouresfehani, N. et al. Comparison of energy consumption for reader anti-collision protocols in dense RFID networks. Wireless Netw 25, 2393–2406 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1670-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1670-y