Abstract
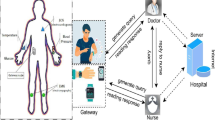
With the rapid development of group-oriented services, there are more and more multi-group communications in which users may join multiple group communications simultaneously. For example, in a wireless body area network (WBAN), medical personnels get together to hold a consultation for the patient and multiple consultation groups co-existed at the same time. A doctor may join more than one consultation groups simultaneously. Most existing group key establishment schemes establish a single group key for a single group. Applying a conventional group key establishment scheme in a straightforward manner (that is, running many times) can provide group-key-oriented multi-group key establishments. Since most group key establishment schemes suffer from larger rekeying overheads if users depart or join the network frequently, it is obvious that these schemes are not suitable for multiple groups co-existing applications such as WBAN. In this paper, we define a new type of user-oriented multi-group key establishments using secret sharing (UMKESS) for secure communications in WBAN. Since health data are private and sensitive information, efficient and secure data transmission in cloud-assisted WBANs is needed. In our proposed UMKESS, each user keeps only one share and uses the share to join multiple groups simultaneously, that is, or achieve multiple things at one stroke. Furthermore, the key generation center can manage user departing or joining dynamically with no rekeying overhead. The security strength of UMKESS is discussed in detail. In comparing to the latest group-key-oriented multi-group key establishment using secret sharing, UMKESS significantly improves the effectiveness of the multi-group communications and it is desirable for WBAN.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rafaeli, S., & Hutchison, D. (2003). A survey of key management for secure group communication. ACM Computing Surveys,35(3), 309–329.
Wong, C. K., Gouda, M. G., & Lam, S. S. (1998). Secure group communications using key graphs. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review,28, 68–79.
Sun, Y., & Liu, K. J. R. (2007). Hierarchical group access control for secure multicast communications. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking,15(6), 1514–1526.
Sherman, A. T., McGrew, D. A. (2003). Key establishment in large dynamic groups using one-way function trees. IEEE transactions on Software Engineering, 29(5), 444–458.
Park, M. H., Park, Y. H., Jeong, H. Y., et al. (2013). Key management for multiple multicast groups in wireless networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing,12(9), 1712–1723.
Laih, C., Lee, J., & Harn, L. (1989). A new threshold scheme and its application in designing the conference key distribution cryptosystem. Information Processing Letters,32, 95–99.
Blakley, G.R. (1979). Safeguarding cryptographic keys. In Proceedings of American Federation Of Information Processing Societies (AFIPS’79) Nat’l Computer Conference (Vol. 48, pp. 313–317).
Shamir, A. (1979). How to share a secret. Communications of the ACM,24(11), 612–613.
Harn, L. (2013). Group authentication. IEEE Transactions on Computers,62(9), 1893–1898.
Harn, L. (1995). Efficient sharing (broadcasting) of multiple secrets. IEE Proceedings-Computers and Digital Techniques,142(3), 237–240.
Harn, L. (1995). Comment on” Multistage secret sharing based on one-way function”. Electronics Letters,31(4), 262.
Hsu, C., Zeng, B., Cui, G., et al. (2014). A new secure authenticated group key transfer protocol. Wireless personal communications, 74(2), 457–467.
Berkovits, S. (1991). How to broadcast a secret. In Proceedings of Eurocrypt’91 Workshop Advances in Cryptology (pp. 536–541).
Li, C.H., & Pieprzyk J. (1999). Conference key agreement from secret sharing. In Proceeding of Fourth Australasian Conference Information Security and Privacy (ACISP’99) (pp. 64–76).
Saze, G. (2003). Generation of key predistribution schemes using secret sharing schemes. Discrete Applied Mathematics,128, 239–249.
Harn, L., & Lin, C. (2010). Authenticated group key transfer protocol based on secret sharing. IEEE Transactions on Computers,59(6), 842–846.
Hsu, C., Harn, L., Yi, M., et al. (2017). Computation-efficient key establishment in wireless group communications. Wireless Networks,23(1), 289–297.
Yining, L., Wei, G., Chun-I, F, Liang, C. & Chi, C. A practical privacy-preserving data aggregation (3PDA) scheme for smart grid. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics. https://doi.org/10.1109/tii2018.2809672.
Liu, Y., Zhong, Q., Chang, L., Xia, Z., He, D., & Cheng, C. (2017). A secure data backup scheme using multi-factor authentication. IET Information Security,11(5), 250–255.
Harn, L., & Hsu, C. F. (2017). A novel design of membership authentication and group key establishment protocol. Security and Communication Networks. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8547876.
Harn, L., & Hsu, C. F. (2017). A practical hybrid group key establishment for secure group communications. The Computer Journal,60(11), 1582–1589.
IEEE Standard 802.16-2004 (2004). Part 16: Air interface for fixed broadband wireless access systems, IEEE.
Wu, Q., Qin, B., Zhang, L., et al. (2011). Bridging broadcast encryption and group key agreement. Advances in Cryptology–ASIACRYPT 2011 (pp. 143–160). Berlin: Springer.
Stinson, D. R. (1997). On some methods for unconditionally secure key distribution and broadcast encryption. Designs, Codes and Cryptography,12, 215–243.
Stinson, D. R., & van Trung, T. (1998). Some new results on key distribution patterns and broadcast encryption. Designs, Codes and Cryptography,14, 261–279.
Waldvogel, M., Caronni, G., Sun, D., Weiler, N., & Plattner, B. (1999). The versakey framework: versatile group key management. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications,7(8), 1614–1631.
Wallner, D.M., Harder, E.J, & Agee R.C (1998) Key management for multicast: issues and architectures, IETF internet draft.
Wong, C.K., Gouda, M., & Lam, S.S. (1998). Secure group communications using key graphs. In Proceeding of the ACM SIGCOMM’98.
Mittra, S. (1997). Iolus: A framework for scalable secure multicasting. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM’97 (pp. 277–288).
Hsu, C., Cheng, Q., Tang, X., & Zeng, B. (2011). An ideal multi-secret sharing scheme based on MSP. Information Sciences,181(7), 1403–1409.
Karnin, E. D., Greene, J. W., & Hellman, M. E. (1983). On secret sharing systems. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory,29(1), 35–41.
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants nos. 61772224 and 61662016), the Nature Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2017A030310049), the Science and Technology Program of Guangzhou City (No. 201707010052), and the Opening Project of Guangdong Key Laboratory of Big Data Analysis and Processing (No. 2017011), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (SCUT). Bing Zeng is responsible for all correspondences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hsu, CF., Harn, L. & Zeng, B. UMKESS: user-oriented multi-group key establishments using secret sharing. Wireless Netw 26, 421–430 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1825-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1825-x