Abstract
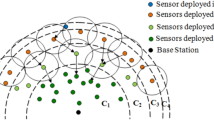
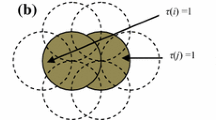
Wireless sensor networks are equipped with sensor nodes having limited battery as energy source. These sensor nodes have to maintain the desirable coverage of the network to ensure the periodical communication of the sensed data to the base station. Therefore, lifetime of sensor nodes and the energy efficient network coverage are the two major issues that needs to be addressed. Effective placement of wireless sensor nodes is of paramount importance as the lifetime of the network depends upon it. In this work, a corona based energy balanced node deployment scheme for sensors with a limited sensing range is proposed in which the nodes are distributed in accordance with a probability density function (PDF). Optimal number of nodes in each corona is determined using the proposed PDF. Performance of the scheme is evaluated in terms of coverage, energy balance and network lifetime through simulation. The intrinsic characteristic of the proposed PDF has been derived. It is noticed that the node distribution through the proposed scheme not only provides better coverage in each layer but also minimizes both the energy-hole and the coverage-hole problems in the deployment field while maintaining longevity of the sensor network.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biagetti, G., Crippa, P., Falaschetti, L., Orcioni, S., & Turchetti, C. (2016). Wireless surface electromyograph and electrocardiograph system on 802.15.4. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 62(3), 258–266.
Mishra, R., Kumar, P., Chaudhury, S., & Indu, S. (2013).Monitoring a large surveillance space through distributed facematching. In 2013 fourth national conference on computer vision, pattern recognition, image processing and graphics(NCVPRIPG) (pp. 1–5). December 2013.
Mathew, J., Hauser, C., Stoll, P., Kenel, C., Polyzos, D., Havermann, D., et al. (2017). Integrating fiber fabry-perot cavity sensor into 3-d printed metal components for extreme high-temperature monitoring applications. IEEE Sensors Journal, 17(13), 4107–4114.
Tanenbaum, A. S., Gamage, C., & Crispo, B. (2006). Taking sensor networks from the lab to the jungle. Computer, 39(8), 98–100.
Meng, S., Kashyap, S. R., Venkatramani, C., & Liu, L. (2012). Resource-aware application state monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 23(12), 2315–2329.
Dempsey, T., Sahin, G., Morton, Y. T., & Hopper, C. M. (2009). Intelligent sensing and classification in ad hoc networks: A case study. IEEE Aerospace and Electronic Systems Magazine, 24(8), 23–30.
Lin, S. C., Alshehri, A. A., Wang, P., & Akyildiz, I. F. (2017). Magnetic induction-based localization in randomly deployed wireless underground sensor networks. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 4(5), 1454–1465.
Joshi, Y. K., & Younis, M. (2016). Restoring connectivity in a resource constrained WSN. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 66, 151–165.
Chatterjee, P., & Das, N. (2014). Coverage constrained non-uniform node deployment in wireless sensor networks for load balancing. In 2014 applications and innovations in mobile computing (AIMoC) (pp. 126–132). February 2014.
Zhu, Chuan, Zheng, Chunlin, Shu, Lei, & Han, Guangjie. (2012). Review: A survey on coverage and connectivity issues in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 35(2), 619–632.
Anastasi, Giuseppe, Conti, Marco, Di Francesco, Mario, & Passarella, Andrea. (2009). Energy conservation in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Ad Hoc Networks, 7(3), 537–568.
Liu, A., Jin, X., Cui, G., & Chen, Z. (2013). Deployment guidelines for achieving maximum lifetime and avoiding energy holes in sensor network. Information Sciences, 230, 197–226. (Mobile and Internet Services in Ubiquitous and Pervasive Computing Environments.).
Yuan, J., Ling, Q., Yan, J., Zhang, W., & Gu, H. (2011). A novel non-uniform node distribution strategy for wireless sensor networks. In 2011 Chinese control and decision conference (CCDC) (pp. 3737–3741). May 2011.
Dietrich, I., & Dressler, F. (2009). On the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 5(1), 5:1–5:39.
Yetgin, H., Cheung, K. T. K., El-Hajjar, M., & Hanzo, L. H. (2017). A survey of network lifetime maximization techniques in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Communications Surveys Tutorials, 19(2), 828–854. (Secondquarter 2017).
Wu, X., Chen, G., & Das, S. K. (2008). Avoiding energy holes in wireless sensor networks with nonuniform node distribution. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 19(5), 710–720.
Lian, J., Naik, K., & Agnew, G. B. (2006). Data capacity improvement of wireless sensor networks using non-uniform sensor distribution. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2(2), 121–145.
Mishra, R., Jha, V., Tripathi, R. K., & Sharma, A. K. (2017). Energy efficient approach in wireless sensor networks using game theoretic approach and ant colony optimization. Wireless Personal Communications, 95(3), 3333–3355.
Amini, N., Fazeli, M., Miremadi, S. G.,&Manzuri, M. T. (2007). Distance-based segmentation: An energy-efficient clustering hierarchy for wireless microsensor networks. In Fifth annual conference on communication networks and services research (CNSR’07) (pp. 18–25). May 2007.
Rahman, A. U., Alharby, A., Hasbullah, H., & Almuzaini, K. (2016). Corona based deployment strategies in wireless sensor network. Journal of Network and Computer applications, 64(C), 176–193.
Ishizuka, M., & Aida, M. (2004). Performance study of node placement in sensor networks. In 24th international conference on distributed computing systems workshops, 2004. Proceedings (pp. 598–603). March 2004.
Rahman, I. A. A. U., Al-Shomrani, M. M., & Hasbullah, H. (2015). Two echelon architecture using relay node placement in wireless sensor network. Journal of Applied Sciences, 5, 214–222.
Ammari, H. M., & Das, S. (2010). A study of k-coverage and measures of connectivity in 3D wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 59(2), 243–257.
Gupta, H. P., & Rao, S. V. (2016). Demand-based coverage and connectivity-preserving routing in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Systems Journal, 10(4), 1380–1389.
Zaidi, S. A. R., Hafeez, M., Khayam, S. A., Mclernon, D. C., Ghogho, M., & Kim, K. (2009). On minimum cost coverage in wireless sensor networks. In 2009 43rd annual conference on information sciences and systems, (pp. 213–218). March 2009.
Halder, S., Ghosal, A., Chaudhuri, A., & DasBit, S. (2011). A probability density function for energy-balanced lifetime-enhancing node deployment in WSN (pp. 472–487). Berlin: Springer.
Halder, S., & DasBit, S. (2014). Design of a probability density function targeting energy-efficient node deployment in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 11(2), 204–219.
Halder, S., & Ghosal, A. (2014). Is sensordeployment using Gaussian distribution energy balanced? In2014 IEEE 11th consumer communications and networking conference (CCNC) (pp. 721–728). January 2014.
Bhardwaj, M., Garnett, T., & Chandrakasan, A. P. (2001).Upper bounds on the lifetime of sensor networks. In ICC2001. IEEE international conference on communications. Conference record (Cat. No. 01CH37240) (Vol. 3, pp. 785–790).
Mhatre, V., & Rosenberg, C. (2004). Design guidelines for wireless sensor networks: Communication, clustering and aggregation. Ad Hoc Networks, 2(1), 45–63.
Efthymiou, C., Nikoletseas, S., & Rolim, J. (2004). Energy balanced data propagation in wireless sensor networks. In 18th international parallel and distributed processing symposium, 2004. Proceedings. (p. 225). April 2004.
Liao, Wen-Hwa, Kuai, Ssu-Chi, & Lin, Mon-Shin. (2015). An energy-efficient sensor deployment scheme for wireless sensor networks using ant colony optimization algorithm. Wireless Personal Communications, 82(4), 2135–2153.
Liu, X. (2015). An optimal-distance-based transmission strategy for lifetime maximization of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal, 15(6), 3484–3491.
Ramos, H. S., Boukerche, A., Oliveira, A. L., Frery, A. C., Oliveira, E. M., & Loureiro, A. A. (2016). On the deployment of large-scale wireless sensor networks considering the energy hole problem. Computer Networks, 110, 154–167.
Ferng, H. W., Hadiputro, M., & Kurniawan, A. (2011). Design of novel node distribution strategies in corona-based wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 10(9), 1297–1311.
Younis, M., Senturk, I. F., Akkaya, K., Lee, S., & Senel, F. (2014). Topology management techniques for tolerating node failures in wireless sensor networks: A survey. Computer Networks, 58, 254–283.
Han, X., Cao, X., Lloyd, E. L., & Shen, C. C. (2010). Fault-tolerant relay node placement in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 9(5), 643–656.
Lee, S., & Younis, M. (2010). Recovery from multiple simultaneous failures in wireless sensor networks using minimum Steiner tree. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 70(5), 525–536.
Tamboli, N., & Younis, M. (2009). Coverage-aware connectivity restoration in mobile sensor networks. In 2009 IEEE international conference on communications (pp. 1–5). June 2009.
Wu, D., Li, R., & Bao, L. (2008). A holistic routing protocol design in underground wireless sensor networks. In 2008 The 4th international conference on mobile ad-hoc and sensor networks (pp. 187–194). December 2008.
Luo, J., Di, W., Pan, C., & Zha, J. (2015). Optimal energy strategy for node selection and data relay in WSN-based IoT. Mobile Networks and Applications, 20(2), 169–180.
Jha, V., Verma, S., Prakash, N., & Gupta, G. (2018). Corona based optimal node deployment distribution in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 102, 325–354.
Heinzelman, W. R., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000). Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd annual Hawaii international conference on system sciences (Vol. 2, pp. 10). January 2000.
Mishra, R., Jha, V., Tripathi, R. K., & Sharma, A. K. (2018). Design of probability density function targeting energy efficient network for coalition based wsns. Wireless Personal Communications, 99(2), 651–680.
Bhattacharjee, M., & Gupta, S. (2014). Determining redundant nodes in a location unaware wireless sensor network. In 2014 IEEE international conference on advanced communications, control and computing technologies (pp. 858–862) May 2014.
Li, J., & Mohapatra, P. (2007). Analytical modeling and mitigation techniques for the energy hole problem in sensor networks. Pervasive and Mobile Computing, 3(3), 233–254.
Xian, Q., & Long, Y. (2016). An enhanced greedy perimeter stateless routing algorithm for wireless sensor network. In 2016 IEEE international conference of online analysis and computing science (ICOACS) (pp. 181–184). May 2016.
Bernard, M., Kondak, K., Maza, I., & Ollero, A. (2011). Autonomous transportation and deployment with aerial robots for search and rescue missions. Journal of Field Robotics, 28(6), 914–931.
Song, W. Z., Huang, R., Xu, M., Shirazi, B., & LaHusen, R. (2010). Design and deployment of sensor network for real-time high-fidelity volcano monitoring. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 21(11), 1658–1674.
Mathisen, S. H., Grindheim, V., & Johansen, T. A. (2017). Approach methods for autonomous precision aerial drop from a small unmanned aerial vehicle. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 50(1), 3566–3573. (20th IFACWorld Congress).
Kyriakopoulos, C. A., Papadimitriou, G. I., Nicopolitidis, P., & Varvarigos, E. (2016). Energy-efficient lightpath establishment in backbone optical networks based on ant colony optimization. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 34(23), 5534–5541.
Dorigo, M., & Stützle, T. (2004). Ant colony optimization. Scituate: Bradford Company.
Voulkidis, A. C., Anastasopoulos, M. P., & Cottis, P. G. (2013). Energy efficiency in wireless sensor networks: A game-theoretic approach based on coalition formation. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 9(4), 43:1–43:27.
Huang, C.-F., & Tseng, Y.-C. (2005). The coverage problem in a wireless sensor network. Mobile Networks and Applications, 10(4), 519–528.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Summary of notations used in the paper is given below (Table 3):
The proof of Theorem 1 is as given below:
Let \(p_i\) denote the probability of a point (x, y) lying between the annulus i and \((i-1)\). From the proposed probability density function, the probability \(p_i\) is given by
Here, \(\iint f(x,y) dx dy\) is the domain area. The considered domain area is circular and is given as
By the fundamental law of probability,
Substituting Eq. (48) in Eq. (47),
Simplifying the above equation using the fundamental law of probability we get,
The proof of Theorem 2 is as given below:
The probability of discrete random variable X and Y for any value within a range i is given as
The probability of the variable X and Y between domain area \(A_i\) and \(A_\eta\) such that \(\eta > i\) is given as
Substituting value of \(A_i\) and \(A_{\eta }\) in the above equation we get
Simplifying the above equation we get
The CDF of X and Y using Eqs. (50) and (53) is obtained as
The proof of the Theorem 3 as as given below:
Expectations of two random variables X and Y is given as
Here, \(E_i [XY]\) is the expectation of X and Y in domain i. Now,
Simplifying the above equation we get,
Substituting the above equation in Eq. (54), we get
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mishra, R., Jha, V., Tripathi, R.K. et al. Corona based node distribution scheme targeting energy balancing in wireless sensor networks for the sensors having limited sensing range. Wireless Netw 26, 879–896 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1834-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-018-1834-9