Abstract
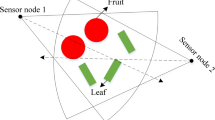
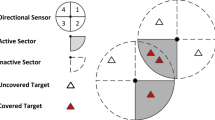
Wireless sensor network (WSN) is the key sensing resource for the internet of things (IoT) in vegetable greenhouse. The coverage control ensures that WSN can obtain enough effective information. However, the current coverage researches ignore the object size and lack of attention to the occlusion between targets. There are many leaves and fruits in vegetables, which can easily cause blind area and low utilization of directional sensors. Based on the geometric relationship between the directional sensors and targets, this paper studies a non-occlusion coverage scheme for the greenhouse IoT. Firstly, combined with the traditional coverage theory, a directional coverage model without occlusion is constructed by analysing the multivariate relationship between the sensor nodes and monitored targets. An objective function is then established to maximize the effective coverage. Based on the directional coverage model, this paper studies a hierarchical cooperative particle swarm optimization algorithm, which decomposes the global effective coverage problem into the utilization optimization of each sensor and finally get the orientation angle set. The experimental results show that the studied model and algorithm can avoid occlusion between covered objects while improving sensor utilization to a certain degree.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chi, T., & Chen, M. (2019). A frequency hopping method for spatial RFID/WiFi/Bluetooth scheduling in agricultural IoT. Wireless Networks,25(2), 805–817.
Mekonnen, Y., Namuduri, S., Burton, L., et al. (2019). Review—Machine learning techniques in wireless sensor network based precision agriculture. Journal of the Electrochemical Society,167(3), 037522.
Bako, B., & Božek, P. (2016). Trends in simulation and planning of manufacturing companies. In Proceeding of international conference on manufacturing engineering and materials (ICMEM) (Vol. 149, pp. 571–575).
Rubanga, D. P., Hatanaka, K., & Shimada, S. (2019). Development of a simplified smart agriculture system for small-scale greenhouse farming. Sensors and Materials,31(3), 831–843.
Zhang, R. B., Ren, Z. W., Sun, J., et al. (2017). Method for monitoring the cotton plant vigor based on the WSN technology. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,133, 68–79.
González-Amarillo, C. A., Corrales-Muñoz, J. C., Mendoza-Moreno, M. A., et al. (2018). An IoT-based traceability system for greenhouse seedling crops. IEEE Access,6, 67528–67535.
Shafi, U., Mumtaz, R., Garcia-Nieto, J., et al. (2019). Precision agriculture techniques and practices: from considerations to applications. Sensors,19(17), 3796.
Hanel, T., Jarmer, T., & Aschenbruck, N. (2019). Using distributed compressed sensing to derive continuous hyperspectral imaging from a wireless sensor network. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,166, 104974.
Oppenheim, D., Shani, G., Erlich, O., et al. (2019). Using deep learning for image-based potato tuber disease detection. Phytopathology,109(6), 1083–1087.
Kochhar, A., & Kumar, N. (2019). Wireless sensor networks for greenhouses: An end-to-end review. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,163, 104877.
Belfkih, A., Duvallet, C., & Sadeg, B. (2019). A survey on wireless sensor network databases. Wireless Networks,25(8), 4921–4946.
Kaushik, A., Indu, S., & Gupta, D. (2019). Grey wolf optimization based algorithm for optimum camera placement. Wireless Personal Communications,105(3), 1143–1167.
Zhao, J., Yoshida, R., Cheung, S. C. S., et al. (2013). Approximate techniques in solving optimal camera placement problems. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks,10, 10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/241913.
Al Hasan, M., Ramachandran, K. K., & Mitchell, J. E. (2008). Optimal placement of stereo sensors. Optimization Letters,2(1), 99–111.
Altahir, A. A., Asirvadam, V. S., Hamid, N. H., et al. (2017). Modeling multicamera coverage for placement optimization. IEEE Sensors Letters,1(6), 1–4.
Xiong, Y. H., Li, J., & Lu, M. J. (2019). Critical location spatial-temporal coverage optimization in visual sensor network. Sensors,19(19), 4106.
Peng, S., & Xiong, Y. (2019). An area coverage and energy consumption optimization approach based on improved adaptive particle swarm optimization for directional sensor networks. Sensors,19(5), 1192.
Fu, Y., Zhou, J., & Deng, L. (2014). Surveillance of a 2D plane area with 3D deployed cameras. Sensors,14(2), 1988–2011.
Panag, T. S., & Dhillon, J. S. (2019). Maximal coverage hybrid search algorithm for deployment in wireless sensor networks. Wireless Networks,25(2), 637–652.
Xenakis, A., Foukalas, F., & Stamoulis, G. (2017). Topology control with coverage and lifetime optimization of wireless sensor networks with unequal energy distribution. Computers and Electrical Engineering,64, 182–199.
Altahir, A. A., Asirvadam, V. S., Hamid, N. H., et al. (2017). Optimizing visual surveillance sensor coverage using dynamic programming. IEEE Sensors Journal,17(11), 3398–3405.
Altahir, A. A., Asirvadam, V. S., Hamid, N. H., et al. (2018). Optimizing visual sensor coverage overlaps for multiview surveillance systems. IEEE Sensors Journal,18(11), 4544–4552.
Tao, D., & Wu, T. Y. (2015). A survey on barrier coverage problem in directional sensor networks. IEEE Sensors Journal,15(2), 876–885.
Chang, C. Y., Hsiao, C. Y., & Chang, C. T. (2018). QoS guaranteed surveillance algorithms for directional wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Networks,81, 71–85.
Chang, J., Shen, X., Bai, W., et al. (2019). Hierarchy graph based barrier coverage strategy with a minimum number of sensors for underwater sensor networks. Sensors,19(11), 2546.
Rout, M., & Roy, R. (2016). Self-deployment of mobile sensors to achieve target coverage in the presence of obstacles. IEEE Sensors Journal,16(14), 1.
Yu, J., Wan, S., Cheng, X., et al. (2017). Coverage contribution area based k-coverage for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,66(9), 8510–8523.
Halder, S., & Ghosal, A. (2015). A location-wise predetermined deployment for optimizing lifetime in visual sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology,26(6), 1131–1145.
Wang, S., Yang, X., Wang, X., et al. (2019). A virtual force algorithm-levy-embedded grey wolf optimization algorithm for wireless sensor network coverage optimization. Sensors,19(12), 2735.
Sharmin, S., Nur, F. N., Razzasque, M. A., et al. (2017). Tradeoff between sensing quality and network lifetime for heterogeneous target coverage using directional sensor nodes. IEEE Access,5, 15490–15504.
Jun, S., Chang, T. W., Jeong, H., et al. (2017). Camera placement in smart cities for maximizing weighted coverage with budget limit. IEEE Sensors Journal,17(23), 7694–7703.
Cheng, B., Cui, L., Jia, W., et al. (2016). Multiple region of interest coverage in camera sensor networks for tele-intensive care units. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics,12(6), 2331–2341.
Tseng, Y. C., Chen, P. Y., & Chen, W. T. (2012). K-angle object coverage problem in a wireless sensor network. IEEE Sensors Journal,12(12), 3408–3416.
He, S. B., Shin, D. H., Zhang, J. S., et al. (2016). Full-view area coverage in camera sensor networks: Dimension reduction and near-optimal solutions. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology,65(9), 7448–7461.
Lin, Y. T., Saluja, K. K., & Megerian, S. (2011). Adaptive cost efficient deployment strategy for homogeneous wireless camera sensors. Ad Hoc Network,9(5), 713–726.
Karakaya, M., & Qi, H. (2011). Distributed target localization using a progressive certainty map in visual sensor networks. Ad Hoc Network,9(4), 576–590.
Yang, X. T., Wen, Y. Y., Yuan, D. N., et al. (2019). Coverage degree-coverage model in wireless visual sensor networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters,8(3), 817–820.
Karakaya, M., & Qi, H. R. (2012). Coverage estimation for crowded targets in visual sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks,8(3), 1–22.
Yap, F. G. H., & Yen, H. H. (2017). Novel visual sensor deployment algorithm in occluded wireless visual sensor networks. IEEE Systems Journal,11(4), 2512–2523.
Saeed, A., Abdelkader, A., Khan, M., et al. (2019). On realistic target coverage by autonomous drones. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks,15(3), 1–33.
Zhang, S. H., Li, X., He, H., et al. (2018). A next best view method based on self-occlusion information in depth images for moving object. Multimedia Tools and Applications,77(8), 9753–9777.
Zhang, S. H., Miao, Y. X., Li, X., et al. (2017). Determining next best view based on occlusion information in a single depth image of visual object. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems. https://doi.org/10.1177/1729881416685672.
Jun, S., Chang, T. W., & Yoon, H. J. (2012). Placing visual sensors using heuristic algorithms for bridge surveillance. Applied Sciences-Basel,8(1), 70.
Brown, T., Wang, Z., Shan, T., et al. (2017). Obstacle-aware wireless video sensor network deployment for 3D indoor monitoring. In Proceedings of globecom 2017—2017 IEEE global communications conference, Singapore, Singapore.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Grant Number 61871041, Technical System of National Bulk Vegetable Industry, Grant Number CARS-23-C06, and National Key Research and Development Program of China, Grant Number 2019YFD1101105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Li, Q., Zhu, H. et al. Directional sensor placement in vegetable greenhouse for maximizing target coverage without occlusion. Wireless Netw 26, 4677–4687 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02370-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-020-02370-8