Abstract
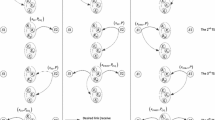
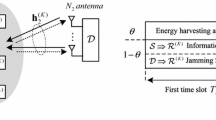
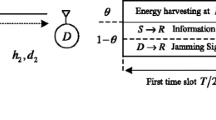
This paper considers secure two-way relay communications in the presence of an eavesdropper. Two users without a direct link between them communicate via an energy harvesting two-way relay. A friendly jammer is employed to reduce information leakage to the eavesdropper. The relay relies on the signals received to harvest energy and forward signals to the users. The power splitting factor and transmit power at the users and jammer are jointly optimized using geometric programming to maximize the secrecy capacity of the system. The imperfect cancellation of the jamming signal is interpreted as noise at the users which decreases the secrecy capacity. Further, it is shown that the secrecy capacity with a jammer is greater than without a jammer. The effect of the relay, jammer, and eavesdropper locations on the performance is studied. It is shown that the secrecy capacity is greater when the relay is equidistant from the users. In addition, having the jammer closer to the eavesdropper results in a higher secrecy capacity.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varshney, L. R. (2008). Transporting information and energy simultaneously. In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on information theory (pp. 1612–1616), Toronto, ON.
Grover, P., & Sahai, A. (2010). Shannon meets Tesla: Wireless information and power transfer. In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on information theory (pp. 2363–2367), Austin, TX.
Hossain, M. A., Noor, R. M., Yau, K. A., Ahmedy, I., & Anjum, S. S. (2019). A survey on simultaneous wireless information and power transfer with cooperative relay and future challenges. IEEE Access, 7, 19166–19198.
Liu, L., Zhang, R., & Chua, K.-C. (2013). Wireless information transfer with opportunistic energy harvesting. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(1), 288–300.
Zhou, X., Zhang, R., & Ho, C. K. (2013). Wireless information and power transfer: Architecture design and rate-energy tradeoff. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 61(11), 4754–4767.
Nasir, A. A., Zhou, X., Durrani, S., & Kennedy, R. A. (2013). Relaying protocols for wireless energy harvesting and information processing. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 12(7), 3622–3636.
Ju, M., Kang, K., Hwang, K., & Jeong, C. (2015). Maximum transmission rate of PSR/TSR protocols in wireless energy harvesting DF-based relay networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 33(12), 2701–2717.
Di, X., Xiong, K., Fan, P., & Yang, H. (2017). Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer in cooperative relay networks with rateless codes. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66(4), 2981–2996.
Atapattu, S., & Evans, J. (2016). Optimal energy harvesting protocols for wireless relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 15(8), 5789–5803.
Huang, S., Yao, Y., & Feng, Z. (2018). Simultaneous wireless information and power transfer for relay assisted energy harvesting network. Wireless Networks, 24(2), 453–462.
Ye, Y., Li, Y., Wang, D., Zhou, F., Hu, R. Q., & Zhang, H. (2018). Optimal transmission schemes for DF relaying networks using SWIPT. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(8), 7062–7072.
Jiang, D., Zheng, H., Tang, D., & Tang, Y. (2015). Relay selection and power allocation for cognitive energy harvesting two-way relaying networks. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on electronics information and emergency communication (pp. 163–166), Beijing, China.
Zhou, L., & Chao, H.-C. (2011). Multimedia traffic security architecture for the internet of things. IEEE Network, 25(3), 35–40.
Leung-Yan-Cheong, S. K., & Hellman, M. E. (1978). The Gaussian wire-tap channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 24(4), 451–456.
Delfs, H., & Knebl, H. (2007). Introduction to cryptography: Principles and applications (2nd ed.). Springer.
Hong, Y.-P., Lan, P., & Kuo, C.-J. (2013). Enhancing physical-layer secrecy in multiantenna wireless systems: An overview of signal processing approaches. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 30(5), 29–40.
Barros, J., & Rodrigues, M. R. D. (2006). Secrecy capacity of wireless channels. In Proceedings of IEEE international symposium on information theory (pp. 356–360), Seattle, WA.
Wyner, A. D. (1975). The wire-tap channel. Bell System Technical Journal, 54(8), 1355–1387.
Oohama, Y. (2001). Coding for relay channels with confidential messages. In Proceedings of IEEE information theory workshop (pp. 87–89), Cairns, Australia.
Son, P. N., & Kong, H. Y. (2015). Cooperative communication with energy harvesting relays under physical layer security. IET Communications, 9(17), 2131–2139.
Salem, A., Hamdi, K. A., & Rabie, K. M. (2016). Physical layer security with RF energy harvesting in AF multi-antenna relaying networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 64(7), 3025–3038.
Zhang, Y., Zhao, X., & Xie, Y. (2019). Secure communications in SWIPT-enabled two way relay networks. IEEE Access, 7, 111890–111896.
Zhang, J., Tao, X., Wu, H., & Zhang, X. (2018). Secure transmission in SWIPT-powered two-way untrusted relay networks. IEEE Access, 6, 10508–10519.
Jameel, F., Wyne, S., & Ding, Z. (2018). Secure communications in three-step two-way energy harvesting DF relaying. IEEE Communications Letters, 22(2), 308–311.
Jameel, F., Khan, F., Haider, M. A. A., & Haq, A. U. (2017). On physical layer security of two way energy harvesting relays. In Proceedings of international conference on frontiers of information technology (pp. 35–40), Islamabad, Pakistan.
Thakur, C. & Chattopadhyay, S. (2020). Secrecy performance of an improved interference-aided RF energy harvesting scheme in two-way multi-antenna relay network. In Proceedings of IEEE applied signal processing conference (pp. 123–127), Kolkata, India.
Rodriguez, L. J., Tran, N. H., Duong, T. Q., Le-Ngoc, T., Elkashlan, M., & Shetty, S. (2015). Physical layer security in wireless cooperative relay networks: State of the art and beyond. IEEE Communications Magazine, 53(12), 32–39.
Wang, L., Cai, Y., Zou, Y., Yang, W., & Hanzo, L. (2016). Joint relay and jammer selection improves the physical layer security in the face of CSI feedback delays. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 65(8), 6259–6274.
Rajaram, A., Jayakody, D. N. K., Dinis, R., & Beko, M. (2021). Energy efficient secure communication model against cooperative eavesdropper. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1563.
Mamaghani, M. T., Kuhestani, A., & Wong, K.-K. (2018). Secure two-way transmission via wireless-powered untrusted relay and external jammer. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(9), 8451–8465.
Liu, M., & Liu, Y. (2017). Power allocation for secure SWIPT systems with wireless-powered cooperative jamming. IEEE Communications Letters, 21(6), 1353–1356.
Wang, Y., Zhang, T., Yang, W., Yin, H., Shen, Y., & Zhu, H. (2020). Secure communication via multiple RF-EH untrusted relays with finite energy storage. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 7(2), 1476–1487.
Wang, K., Yuan, L., Miyazaki, T., Zeng, D., Guo, S., & Sun, Y. (2017). Strategic antieavesdropping game for physical layer security in wireless cooperative networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66(10), 9448–9457.
Zhang, R., Song, L., Han, Z., & Jiao, B. (2012). Physical layer security for two-way untrusted relaying with friendly jammers. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 61(8), 3693–3704.
Jiang, X., Li, P., Li, B., Zou, Y., & Wang, R. (2021). Security-reliability tradeoff for friendly jammer aided multiuser scheduling in energy harvesting communications. Security and Communication Networks, 2021, 5599334.
Cao, K., Wang, B., Ding, H., & Tian, J. (2019). Adaptive cooperative jamming for secure communication in energy harvesting relay networks. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 8(5), 1316–1319.
Lee, K., Hong, J., Choi, H., & Quek, T. Q. S. (2019). Wireless-powered two-way relaying protocols for optimizing physical layer security. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 14(1), 162–174.
Ha, D.-H., Nguyen, T. N., Tran, M. H. Q., Li, X., Tran, P. T., & Voznak, M. (2020). Security and reliability analysis of a two-way half-duplex wireless relaying network using partial relay selection and hybrid TPSR energy harvesting at relay nodes. IEEE Access, 8, 187165–187181.
Xu, J., Liu, L., & Zhang, R. (2014). Multiuser MISO beamforming for simultaneous wireless information and power transfer. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 62(18), 4798–4810.
Zhang, G., Xu, J., Wu, Q., Cui, M., Li, X., & Lin, F. (2018). Wireless powered cooperative jamming for secure OFDM system. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 67(2), 1331–1346.
Long, H., Xiang, W., & Li, Y. (2017). Precoding and cooperative jamming in multi-antenna two-way relaying wiretap systems without eavesdroppers' channel state information. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 12(6), 1309–1318.
Chen, J., Zhang, R., Song, L., Han, Z., & Jiao, B. (2012). Joint relay and jammer selection for secure two-way relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 7(1), 310–320.
Wang, D., Bai, B., Zhao, W., & Han, Z. (2019). A survey of optimization approaches for wireless physical layer security. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 21(2), 1878–1911.
Boyd, S., Kim, S.-J., Vandenberghe, L., & Hassibi, A. (2007). A tutorial on geometric programming. Optimization Engineering, 8(1), 67–127.
Hayajneh, M., & Gulliver, T. A. (2019). Wireless information and power transfer with optimal transmit antenna selection. IET Communications, 13(19), 3217–3221.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayajneh, M., Gulliver, T.A. Secrecy capacity in two-way energy harvesting relay networks with a friendly jammer. Wireless Netw 27, 4551–4566 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02699-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02699-8