Abstract
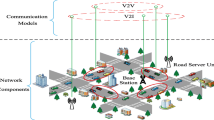
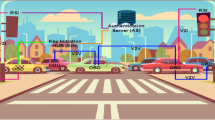
Vehicular ad hoc Networks (VANETs) encompass the Internet of Vehicles, Vehicular Sensor Networks (VSNs), and electronic vehicles and tend to be an essential part of the world. In this network, communications are done through an open channel and are inevitably susceptible to a range of security issues. Their high mobility also adds to this concern. Roaming services are essential for global VANETs and mobility-based networks, which require a robust authentication mechanism to be maintained. Therefore, an effective and secure authentication and session key agreement mechanism in VANET is a challenge yet to be tackled. Recently, different three-party schemes were proposed to use in the handover authentication process, though they have their deficits. The present study showed that the three related schemes (Zhou et al., Patonico et al., and Eftekhari et al.) have security flaws such as insecurity against impersonation attack, key compromise impersonation attack, and man-in-the-middle attack. Also, a secure and robust handover authentication scheme is proposed for roaming service in VSNs, which stamps out the existing schemes' security problems. It considers the intra-network and inter-network roaming authentication models. Our proposed scheme, free from key escrow problems, is highly anonymous and provides forward/backward secrecy. Widely accepted random oracle model, AVISPA tool, and BAN logic used for security analysis. Our scheme outperforms the others in security metrics and improves communication overhead by up to 75%. Also, the simulation results show that our scheme is energy-efficient and imposes a lower end-to-end delay to the network.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muhammad, M., & Safdar, G. A. (2018). Survey on existing authentication issues for cellular-assisted V2X communication. Vehicular Communications, 12, 50–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2018.01.008
Sheikh, M. S., & Liang, J. (2019). A comprehensive survey on VANET security services in traffic management system. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2019, 2423915. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/2423915
Sharma, S., & Kaushik, B. (2019). A survey on internet of vehicles: Applications, security issues and solutions. Vehicular Communications, 20, 100182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2019.100182
Ali, I., Hassan, A., & Li, F. (2019). Authentication and privacy schemes for vehicular ad hoc networks (VANETs): A survey. Vehicular Communications, 16, 45–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2019.02.002
Manvi, S. S., & Tangade, S. (2017). A survey on authentication schemes in VANETs for secured communication. Vehicular Communications, 9, 19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2017.02.001
Tai, W. L., Chang, Y. F., & Chen, Y. C. (2016). A fast-handover-supported authentication protocol for vehicular ad hoc networks. Journal of Information Hiding and Multimedia Signal Processing, 7, 960–969.
Zhou, Y., Long, X., Chen, L., & Yang, Z. (2019). Conditional privacy-preserving authentication and key agreement scheme for roaming services in VANETs. Journal of Information Security and Applications, 47, 295–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jisa.2019.05.018
Patonico, S., Braeken, A., & Steenhaut, K. (2019). Identity-based and anonymous key agreement protocol for fog computing resistant in the Canetti-Krawczyk security model. Wireless Networks. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-019-02084-6
Eftekhari, S. A., Nikooghadam, M., & Rafighi, M. (2020). Security-enhanced three-party pairwise secret key agreement protocol for fog-based vehicular ad-hoc communications. Vehicular Communications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2020.100306
Memon, I. (2015). A secure and efficient communication scheme with authenticated key establishment protocol for road networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 85(3), 1167–1191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2833-0
Liu, Y., Wang, Y., & Chang, G. (2017). Efficient privacy-preserving dual authentication and key agreement scheme for secure V2V communications in an IoV paradigm. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 18(10), 2740–2749. https://doi.org/10.1109/TITS.2017.2657649
Canetti, R., & Krawczyk, H. (2001). Analysis of key-exchange protocols and their use for building secure channels. In International conference on the theory and applications of cryptographic techniques (pp. 453–474). Springer, Berlin. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-44987-6_28.
Muthumeenakshi, R., Reshmi, T. R., & Murugan, K. (2017). Extended 3PAKE authentication scheme for value-added services in VANETs. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 59, 27–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2017.03.011
Wazid, M., Das, A. K., Kumar, N., Odelu, V., Reddy, A. G., Park, K., & Park, Y. (2017). Design of lightweight authentication and key agreement protocol for vehicular ad hoc networks. IEEE Access, 5, 14966–14980. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2723265
Dewanta, F., & Mambo, M. (2019). A mutual authentication scheme for secure fog computing service handover in vehicular network environment. IEEE Access, 7, 103095–103114. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2931217
Xu, G., Liu, J., Lu, Y., Zeng, X., Zhang, Y., & Li, X. (2018). A novel efficient MAKA protocol with desynchronization for anonymous roaming service in global mobility networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 107, 83–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnca.2018.02.003
Ostad-Sharif, A., Babamohammadi, A., Abbasinezhad-Mood, D., & Nikooghadam, M. (2019). Efficient privacy-preserving authentication scheme for roaming consumer in global mobility networks. International Journal of Communication Systems, 32(5), e3904. https://doi.org/10.1002/dac.3904
Lu, Y., Xu, G., Li, L., & Yang, Y. (2019). Robust privacy-preserving mutual authenticated key agreement scheme in roaming service for global mobility networks. IEEE Systems Journal, 13(2), 1454–1465. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2018.2883349
Alzahrani, B. A., Chaudhry, S. A., Barnawi, A., Al-Barakati, A., & Alsharif, M. H. (2020). A privacy preserving authentication scheme for roaming in IoT-based wireless mobile networks. Symmetry, 12(2), 287. https://doi.org/10.3390/sym12020287
Kumar, V., Ahmad, M., Mishra, D., Kumari, S., & Khan, M. K. (2020). RSEAP: RFID based secure and efficient authentication protocol for vehicular cloud computing. Vehicular Communications, 22, 100213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2019.100213
Chen, C. L., Chen, Y. X., Lee, C. F., Deng, Y. Y., & Chen, C. H. (2019). An efficient and secure key agreement protocol for sharing emergency events in VANET systems. IEEE Access, 7, 148472–148484. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2946969
Memon, I., Hussain, I., Akhtar, R., & Chen, G. (2015). Enhanced privacy and authentication: An efficient and secure anonymous communication for location based service using asymmetric cryptography scheme. Wireless Personal Communications, 84(2), 1487–1508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2699-1
Arain, Q., Zhongliang, D., Memon, I., et al. (2017). Privacy preserving dynamic pseudonym-based multiple mix-zones authentication protocol over road networks. Wireless Personal Communications, 95, 505–521. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3906-4
Adhikari, S., Ray, S., Obaidat, M. S., & Biswas, G. P. (2020). Efficient and secure content dissemination architecture for content centric network using ECC-based public key infrastructure. Computer Communications, 157, 187–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2020.04.024
Ogundoyin, S. O. (2020). An autonomous lightweight conditional privacy-preserving authentication scheme with provable security for vehicular ad-hoc networks. International Journal of Computers and Applications, 42(2), 196–211. https://doi.org/10.1080/1206212X.2018.1477320
Hsieh, W. B., & Leu, J. S. (2014). Anonymous authentication protocol based on elliptic curve Diffie–Hellman for wireless access networks. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 14(10), 995–1006. https://doi.org/10.1002/wcm.2252
Cui, J., Liew, L. S., Sabaliauskaite, G., & Zhou, F. (2019). A review on safety failures, security attacks, and available countermeasures for autonomous vehicles. Ad Hoc Networks, 90, 101823. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2018.12.006
Singh, A., & Kad, S. (2016). A review on the various security techniques for VANETs. Procedia Computer Science, 78, 284–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2016.02.055
Sheikh, M. S., Liang, J., & Wang, W. (2020). Security and privacy in vehicular ad hoc network and vehicle cloud computing: A survey. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2020, 5129620. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5129620
Arif, M., Wang, G., Bhuiyan, M. Z. A., Wang, T., & Chen, J. (2019). A survey on security attacks in VANETs: Communication, applications and challenges. Vehicular Communications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2019.100179
Mejri, M. N., Ben-Othman, J., & Hamdi, M. (2014). Survey on VANET security challenges and possible cryptographic solutions. Vehicular Communications, 1(2), 53–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vehcom.2014.05.001
Hajian, R., ZakeriKia, S., Erfani, S. H., & Mirabi, M. (2020). SHAPARAK: Scalable healthcare authentication protocol with attack-resilience and anonymous key-agreement. Computer Networks, 183, 107567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2020.107567
Burrows, M., Abadi, M., & Needham, R. M. (1989). A logic of authentication. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 426(1871), 233–271. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspa.1989.0125
AVISPA, Automated validation of internet security protocols and applications. (2018). http://www.avispa-project.org/.
Hajian, R., & Erfani, S. H. (2021). CHESDA: Continuous hybrid and energy-efficient secure data aggregation for WSN. The Journal of Supercomputing, 77, 5045–5075. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-020-03455-z
Liyanage, K. S. K., Ma, M., & Chong, P. H. J. (2018). Controller placement optimization in hierarchical distributed software defined vehicular networks. Computer Networks, 135, 226–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2018.02.022
Abbasi, I. A., Khan, A. S., & Ali, S. (2018). A reliable path selection and packet forwarding routing protocol for vehicular ad hoc networks. Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2018, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13638-018-1233-z
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
ZakeriKia, S., Hajian, R., Erfani, S.H. et al. Robust and anonymous handover authentication scheme without key escrow problem in vehicular sensor networks. Wireless Netw 27, 4997–5028 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02729-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-021-02729-5