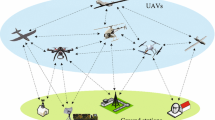
Abstract
In the unmanned ship networking scenario, the position of the unmanned ship changes continuously, leading to the result that the desired transmitters and the interference transmitters may exchange identities at any time. The traditional interference alignment technique cannot solve the interference. To solve this problem, this paper proposes an adaptive interference alignment scheme based on the dynamic selection of the desired transmitters for the unmanned ship network. Firstly, according to the characteristics of the unmanned ship networking scene, a new measurement value the non-directional user signal to interference ratio W is proposed, and the desired user set and connection mode are selected through the calculation of W. Secondly, the corresponding interference alignment scheme is designed. The iterative interference alignment algorithm is used for non-directional users, while partial interference alignment algorithm is used for directional users, and the proof of algorithm convergence is given. Lastly, the scheme can dynamically select and update the desired user set and connection mode when the position of the unmanned ship changes, and the corresponding interference alignment scheme will also perform adaptive updates. Experimental results indicate that the scheme can select the optimal connection mode according to the current position of the unmanned ship and eliminate the interference caused by the undesired transmitter.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weigang, C., Jinsheng, Y., Jianguo, M., & Si, L. (2012). New developments in maritime communications: A comprehensive survey. China Communications, 9(2), 31–42.
Jo, S., & Shim, W. (2019). LTE-Maritime: High-speed maritime wireless communication based on LTE technology. IEEE Access, 7, 53172–53181. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2912392.
Zhang, W., Zou, Z., Wang, J., & Du, L. (2020). Multi-ship following operation in ice-covered waters with consideration of inter-ship communication. Ocean Engineering, 210, 107545.
Jafar, S. A., & Shamai, S. (2008). Degrees of freedom region of the MIMO X channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(1), 151–170.
Cadambe, V., & Jafar, S. A. (2008). Interference alignment and the degrees of freedom of the K user interference channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(8), 3425–3441.
Gou, T., & Jafar, S. (2010). Degrees of freedom of the K user M \(\times\)N MIMO interference channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 56(12), 6040–6057.
Gomadam, K., Cadambe, V. R., & Jafar, S. A. (2011). A distributed numerical approach to interference alignment and applications to wireless interference networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 57(6), 3309–3322.
Chen, J. (2021). Multi-layer interference alignment and GDoF of the K-user asymmetric interference channel[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 67(6), 3986–4000.
Liu, F., Wang, S., Li, C., et al. (2021). Propagation Delay Based Cyclic Interference Alignment for X Channels With Two Transmitters[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 25(6), 1844–1847.
Cadambe, V., & Jafar, S. (2009). Interference alignment and the degrees of freedom of wireless X networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 55(9), 3893–3908.
Suh, C., Ho, M., & Tse, D. (2011). Downlink interference alignment. IEEE Transactions on Communication, 59(9), 2616–2626.
Suh, C. & Tse, D. (2008). Interference alignment for cellular networks, In Proc.46th Annu. Allerton Conf. Commun., Control, Comput., Champaign, IL, USA, pp. 1037–1044.
Li, S., Guo, L., Liu, J., Huang, T., Cui, X., & Zhang, Y. (2020). Partial interference alignment scheme for Three-Tier downlink heterogeneous networks. IEEE Access, 8, 155602–155610.
Xia, H., Zhou, X., & Han, S., et al. (2021). Joint secure transceiver design and power allocation for AN-assisted MIMO networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications.
Li, J., Feng, W., Yu, F. R., et al. (2021). Two new kinds of interference alignment schemes for cellular \(K\)-user MIMO downlink networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 70(11), 11827–11842.
Li, S., Ye, W., Guo, L., Liu, J., Huang, T., Cui, X., & Zhang, Y. (2021). The interference alignment scheme based on subspace differentiation for multicell multiuser multiple-input-multiple-output uplink channels. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 32, e4198.
Schreck, J., & Wunder, G. (2012). Interference alignment over limited dimensions for cellular networks: Feasibility and algorithms, In Proc. IEEE Int. ITG WSA, pp. 352–358.
Schreck, J., & Wunder, G. (2011). “Iterative interference alignment for cellular systems,” in Proc. IEEE Int. ITG WSA, pp. 1–8.
Zhuang, B., Berry, R., & Honig, M. (2011). “Interference alignment in MIMO cellular networks,” in Proc. IEEE ICASSP, pp. 3356–3359.
Jung, B. C., & Shin, W. Y. (2010). Opportunistic interference alignment for interference-limited cellular TDD uplink[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 15(2), 148–150.
Yang, H. J., Shin, W. Y., Jung, B. C., et al. (2017). Opportunistic downlink interference alignment for multi-cell MIMO networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 16(3), 1533–1548.
Huacheng Zeng, Y. Thomas Hou, Yi Shi, Wenjing Lou, Sastry Kompella, & Scott F. Midkiff. (2014). Shark-IA: an interference alignment algorithm for multi-hop underwater acoustic networks with large propagation delays. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Underwater Networks and Systems (WUWNET ’14). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, Article 6, 1–8.
Pandey, P., Hajimirsadeghi, M., & Pompili, D. (2014). Region of Feasibility of Interference Alignment in Underwater Sensor Networks. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 39(1), 189–202.
Min, S., Liu, G., Wang, X., et al. (2017). Interference Alignment and Cancelation for the Uplink of Heterogeneous Networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66(2), 1104–1115.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.61972417,61902431) and the Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2020MF005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Wang, M., Wang, X. et al. An adaptive interference alignment scheme based on the dynamic selection of desired transmitters for unmanned ship network. Wireless Netw 28, 2519–2531 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-022-02964-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-022-02964-4