Abstract
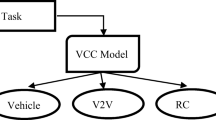
In vehicular cloud computing (VCC) systems, the vehicle cloud (VC) consists of computing resources for multiple vehicles to assist the remote cloud (RC) in making real-time decisions on driving vehicles, to improve road safety and driving comfort. The acquisition of additional cloud facilities to increase the capacity of VCC systems when processing intensive requests for cloud resources is costly. A recent approach uses multiple remote microclouds (RMCs) to assist RCs in processing requests because they are smaller and less costly than RCs. Therefore, this paper presents a VCC system with multiple RCs and RMCs, in which an algorithm for allocating request resources among VCs, RMCs, and RCs. Subsequently, this paper proposes an improved simulated annealing algorithm (ImSA) based on density of vehicles in a geographical area to deploy RCs and RMCs with the minimal deployment cost and response cost. For real applications, the accuracy and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm are evaluated on the basis of the real traffic data from three different areas (i.e., urban area, outskirts, and suburban area) in one week.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vahdat-Nejad, H., Ramazani, A., Mohammadi, T., & Mansoor, W. (2016). A survey on context-aware vehicular network applications. Vehicular Communications, 3, 43–57.
Santos, F., Aquino, A. L., Madeira, E. R., & Cabral, R. S. (2021). Temporal complex networks modeling applied to vehicular ad-hoc networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 192, 103168.
Wang, J., Cho, J., Lee, S., & Ma, T. (2011). Real time services for future cloud computing enabled vehicle networks. In Proceedings of the 2011 international conference on wireless communications and signal processing (WCSP), pp. 1–5.
Lin, C.-C., Chin, H.-H., & Chen, W.-B. (2018). Balancing latency and cost in software-defined vehicular networks using genetic algorithm. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 116, 35–41.
Huang, X., Yu, R., Kang, J., He, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Exploring mobile edge computing for 5G-enabled software defined vehicular networks. IEEE Wireless Communications, 24(6), 55–63.
Ning, Z., Huang, J., & Wang, X. (2019). Vehicular fog computing: Enabling real-time traffic management for smart cities. IEEE Wireless Communications, 26(1), 87–93.
Wang, K., Yin, H., Quan, W., & Min, G. (2018). Enabling collaborative edge computing for software defined vehicular networks. IEEE Network, 32(5), 112–117.
Gerla, M. (2012). Vehicular cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2012 the 11th annual Mediterranean ad hoc networking workshop (med-hoc-net), pp. 152–155.
Lee, E., Lee, E.-K., Gerla, M., & Oh, S. Y. (2014). Vehicular cloud networking: Architecture and design principles. IEEE Communications Magazine, 52(2), 148–155.
Mekki, T., Jabri, I., Rachedi, A., & ben Jemaa, M. (2017). Vehicular cloud networks: Challenges, architectures, and future directions. Vehicular Communications, 9, 268–280.
Jang, I., Choo, S., Kim, M., Pack, S., & Dan, G. (2017). The software-defined vehicular cloud: A new level of sharing the road. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 12(2), 78–88.
Liu, J., Wan, J., Zeng, B., Wang, Q., Song, H., & Qiu, M. (2017). A scalable and quick-response software defined vehicular network assisted by mobile edge computing. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(7), 94–100.
Sharma, S., & Kaul, A. (2018). A survey on Intrusion Detection Systems and Honeypot based proactive security mechanisms in VANETs and VANET Cloud. Vehicular Communications, 12, 138–164.
Nkenyereye, L., Islam, S. M. R., Bilal, M., Abdullah-Al-Wadud, M., Alamri, A., & Nayyar, A. (2021). Secure crowd-sensing protocol for fog-based vehicular cloud. Future Generation Computer Systems, 120, 61–75.
Liu, P., Zhang, Y., Fu, T., & Hu, J. (2021). Intelligent mobile edge caching for popular contents in vehicular cloud toward 6G. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 70(6), 5265–5274.
Zhang, K., Mao, Y., Leng, S., Maharjan, S., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Optimal delay constrained offloading for vehicular edge computing networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), pp. 1–6.
Zhang, K., Mao, Y., Leng, S., He, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2017). Mobile-edge computing for vehicular networks: A promising network paradigm with predictive off-loading. IEEE Vehicular Technology Magazine, 12(2), 36–44.
Aujla, G. S., Chaudhary, R., Kumar, N., Rodrigues, J. J. P. C., & Vinel, A. (2017). Data offloading in 5G-enabled software-defined vehicular networks: A stackelberg-game-based approach. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(8), 100–108.
Zhang, W., Zhang, Z., & Chao, H.-C. (2017). Cooperative fog computing for dealing with big data in the internet of vehicles: Architecture and hierarchical resource management. IEEE Communications Magazine, 55(12), 60–67.
Mustafa, A.M., Abubakr, O.M., Ahmadien, O., Ahmedin, A., & Mokhtar, B. (2017). Mobility prediction for efficient resources management in vehicular cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2017 5th IEEE international conference on mobile cloud computing, services, and engineering (MobileCloud), pp. 53–59.
Li, X., Ma, L., Shankaran, R., Xu, Y., & Orgun, M. A. (2019). Joint power control and resource allocation mode selection for safety-related v2x communication. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 68(8), 7970–7986.
Meneguette, R. I., & Boukerche, A. (2017). Servites: An efficient search and allocation resource protocol based on V2V communication for vehicular cloud. Computer Networks, 123, 104–118.
Feng, J., Liu, Z., Wu, C., & Ji, Y. (2017). Ave: Autonomous vehicular edge computing framework with ACO-based scheduling. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 66(12), 10660–10675.
Rui, L., Yang, S., Gao, Z., Li, W., Qiu, X., & Meng, L. (2022). Smart network maintenance in edge cloud computing environment: An allocation mechanism based on comprehensive reputation and regional prediction model. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 198, 103298.
Liang, H., Cai, L. X., Huang, D., Shen, X., & Peng, D. (2012). An SMDP-based service model for interdomain resource allocation in mobile cloud networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 61(5), 2222–2232.
Zheng, K., Meng, H., Chatzimisios, P., Lei, L., & Shen, X. (2015). An SMDP-based resource allocation in vehicular cloud computing systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 62(12), 7920–7928.
Yu, R., Zhang, Y., Gjessing, S., Xia, W., & Yang, K. (2013). Toward cloud-based vehicular networks with efficient resource management. IEEE Network, 27(5), 48–55.
Zhang, H., Wang, Z., & Liu, K. (2020). V2X offloading and resource allocation in SDN-assisted MEC-based vehicular networks. China Communications, 17(5), 266–283.
Shakarami, A., Shahidinejad, A., & Ghobaei-Arani, M. (2021). An autonomous computation offloading strategy in mobile edge computing: A deep learning-based hybrid approach. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 178, 102974.
Peng, F., & Cui, G. (2015). Efficient simultaneous synthesis for heat exchanger network with simulated annealing algorithm. Applied Thermal Engineering, 78, 136–149.
Lyden, S., & Haque, M. E. (2016). A simulated annealing global maximum power point tracking approach for PV modules under partial shading conditions. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 31(6), 4171–4181.
Chen, F., Gao, Z., Liu, Z., Huang, L., & Tang, Y. (2021). Code-based computation offloading in vehicular fog networks. In Proceedings of the 2021 international conference on communications, computing, cybersecurity, and informatics (CCCI), pp. 1–5.
Fang, J., Li, K., Hu, J., Xu, X., Teng, Z., & Xiang, W. (2021). SAP: An IoT application module placement strategy based on simulated annealing algorithm in edge-cloud computing. Journal of Sensors, 2021, 1–12.
Attiya, I., Abd Elaziz, M., & Xiong, S. (2020). Job scheduling in cloud computing using a modified Harris hawks optimization and simulated annealing algorithm. Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience 2020.
Zhang, Y.-W., Zhang, W.-M., Peng, K., Yan, D.-C., & Wu, Q.-L. (2021). A novel edge server selection method based on combined genetic algorithm and simulated annealing algorithm. Automatika: časopis za automatiku, mjerenje, elektroniku, računarstvo i komunikacije, 62(1), 32–43.
Yuan, H., & Zhou, M. (2021). Profit-maximized collaborative computation offloading and resource allocation in distributed cloud and edge computing systems. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 18(3), 1277–1287.
Bi, J., Yuan, H., Duanmu, S., Zhou, M., & Abusorrah, A. (2021). Energy-optimized partial computation offloading in mobile-edge computing with genetic simulated-annealing-based particle swarm optimization. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 8(5), 3774–3785.
Leyva-Pupo, I., & Cervell’o-Pastor, C. (2022). Efficient solutions to the placement and chaining problem of User Plane Functions in 5G networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 197, 103269.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bi, C., Li, J., Feng, Q. et al. Optimal deployment of vehicular cloud computing systems with remote microclouds. Wireless Netw 30, 5305–5317 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03268-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03268-x