Abstract
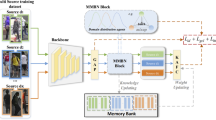
Specific Emitter Identification (SEI) is an important method for secure authentication of devices in wireless networks. However, the lack of empirical identification models for many unknown devices further affects the speed and accuracy of their authentication. This work aims to propose an unsupervised open-set domain adaptation (UOSDA) based method to solve the open-set SEI problem with unknown devices appearing in the test set and few shots in the training set. The basic principle is to learn tensor embedding shared feature space and preserving inter-class substructure, which perform feature space mapping under the joint source and target domain led by mapping error minimize in the source domain. Then, in the shared space, the known and unknown targets are divided by the double clusters method of structure prediction and nearest class prototype. Specifically, this Tensor Embedding Substructure Preserving Open Set Domain Adaptation (TESPOSDA) consists of three parts, tensor substructure based invariant feature learning, unsupervised clustering based on known target intra-class structure prediction and neighbor prediction, UOSDA to refine the predicted labels. Finally, experiments are conducted on the real ADS-B dataset to demonstrate the effectiveness of TESPDA.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, L., Xiang, W., & Tang, X. (2017). An efficient bit-detecting protocol for continuous tag recognition in mobile rfid systems. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 17(3), 503–516.
Zhang, L., Xiang, W., Tang, X., Li, Q., & Yan, Q. (2017). A time-and energy-aware collision tree protocol for efficient large-scale rfid tag identification. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 14(6), 2406–2417.
Liu, S., Huang, S., Wang, S., Muhammad, K., Bellavista, P. & Del Ser, J. (2023) Visual tracking in complex scenes: A location fusion mechanism based on the combination of multiple visual cognition flows. Information Fusion
Liu, S., Gao, P., Li, Y., Fu, W., & Ding, W. (2023). Multi-modal fusion network with complementarity and importance for emotion recognition. Information Sciences, 619, 679–694.
Roy, D., Mukherjee, T., Chatterjee, M., Blasch, E., & Pasiliao, E. (2019). Rfal: Adversarial learning for rf transmitter identification and classification. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 6(2), 783–801.
Tu, Y., Lin, Y., Wang, J., & Kim, J.-U. (2018). Semi-supervised learning with generative adversarial networks on digital signal modulation classification. Comput. Mater. Continua, 55(2), 243–254.
Wu, Q., Feres, C., Kuzmenko, D., Zhi, D., Yu, Z., & Liu, X. (2018). Deep learning based rf fingerprinting for device identification and wireless security. Electronics Letters, 54(24), 1405–1407.
Tu, Y., Lin, Y., Hou, C., & Mao, S. (2020). Complex-valued networks for automatic modulation classification. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 69(9), 10-085–10-089.
Hou, C., Liu, G., Tian, Q., Zhou, Z., Hua, L., & Lin, Y. (2022). Multi-signal modulation classification using sliding window detection and complex convolutional network in frequency domain. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 9(19), 19438–19449.
Liu, C., Wei, Z., Ng, D. W. K., Yuan, J., & Liang, Y.-C. (2020). Deep transfer learning for signal detection in ambient backscatter communications. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 20(3), 1624–1638.
Xiao, Y., Liu, W., & Gao, L. (2020). Radar signal recognition based on transfer learning and feature fusion. Mobile Networks and Applications, 25(4), 1563–1571.
Ujan, S., Navidi, N., & Jr Landry, R. (2020). An efficient radio frequency interference (rfi) recognition and characterization using end-to-end transfer learning. Applied Sciences, 10(19), 6885.
Wang, M., Lin, Y., Tian, Q., & Si, G. (2021). Transfer learning promotes 6g wireless communications: Recent advances and future challenges. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 70(2), 790–807.
Naylor, A. R. (2010). Known knowns, known unknowns and unknown unknowns: A 2010 update on carotid artery disease. The surgeon, 8(2), 79–86.
Mendes Júnior, P. R., De Souza, R. M., Werneck, R. D. O., Stein, B. V., Pazinato, D. V., de Almeida, W. R., Penatti, O. A., Torres, R. D. S., & Rocha, A. (2017). Nearest neighbors distance ratio open-set classifier. Machine Learning, 106(3), 359–386.
Long, H., Xiang, W., Wang, J., Zhang, Y., & Wang, W. (2014). Cooperative jamming and power allocation with untrusty two-way relay nodes. Iet Communications, 8(13), 2290–2297.
Zhang, H., & Patel, V. M. (2016). Sparse representation-based open set recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 39(8), 1690–1696.
Yoshihashi, R., Shao, W., Kawakami, R., You, S., Iida, M. and Naemura, T. (2019). Classification-reconstruction learning for open-set recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (pp. 4016–4025).
Xu, H. and Xu, X. (2021). A transformer based approach for open set specific emitter identification. In 2021 7th International Conference on Computer and Communications (ICCC) (pp. 1420–1425) IEEE.
Lin, Y., Zhu, X., Zheng, Z., Dou, Z., & Zhou, R. (2019). The individual identification method of wireless device based on dimensionality reduction and machine learning. The Journal of Supercomputing, 75(6), 3010–3027.
Lin, Y., Tu, Y., Dou, Z., Chen, L., & Mao, S. (2020). Contour stella image and deep learning for signal recognition in the physical layer. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 7(1), 34–46.
Zhao, Y., Wui, L., Zhang, J. and Li, Y. (2018). Specific emitter identification using geometric features of frequency drift curve. Bulletin of the Polish Academy of Sciences. Technical Sciences, (vol. 66, no. 1) .
Xie, C., Zhang, L., & Zhong, Z. (2022). Meta learning-based open-set identification system for specific emitter identification in non-cooperative scenarios. KSII Transactions on Internet and Information Systems (TIIS), 16(5), 1755–1777.
Panareda Busto, P. and Gall, J. (2017). Open set domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 754–763).
Saito, K., Yamamoto, S., Ushiku, Y. and Harada, T. (2018). Open set domain adaptation by backpropagation. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) (pp. 153–168).
Wang, Z. and Oates, T. (2015). Imaging time-series to improve classification and imputation, In International Conference on Artificial Intelligence
Lu, H., Zhang, L., Cao, Z., Wei, W., Xian, K., Shen, C. and van den Hengel, A. (2017). When unsupervised domain adaptation meets tensor representations. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 599–608).
Wang, Q., & Breckon, T. (2020). Unsupervised domain adaptation via structured prediction based selective pseudo-labeling. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 34(04), 6243–6250.
Fang, Z., Lu, J., Liu, F., Xuan, J., & Zhang, G. (2020). Open set domain adaptation: Theoretical bound and algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 32(10), 4309–4322.
Wang, Q., Bu, P. and Breckon, T. P. (2019). Unifying unsupervised domain adaptation and zero-shot visual recognition. In 2019 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (pp. 1–8) IEEE.
Zhang, Z. and Saligrama, V. (2016). Zero-shot recognition via structured prediction. In European Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 533–548). Springer.
Pickands III, J., (1975). Statistical inference using extreme order statistics the Annals of Statistics (pp. 119–131).
Grimshaw, S. D. (1993). Computing maximum likelihood estimates for the generalized pareto distribution. Technometrics, 35(2), 185–191.
Shafer, G. (1976). A mathematical theory of evidence ( vol. 42). Princeton university press
Ya, T., Yun, L., Haoran, Z., Zhang, J., Yu, w, Guan, G., & Shiwen, M. (2021). Large-scale real-world radio signal recognition with deep learning. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 35(9), 35–48.
Pan, S. J., Tsang, I. W., Kwok, J. T., & Yang, Q. (2010). Domain adaptation via transfer component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 22(2), 199–210.
Long, M., Wang, J., Ding, G., Sun, J., and Yu, P. S. (2013). Transfer feature learning with joint distribution adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 2200–2207).
Wang, J., Feng, W., Chen, Y., Yu, H., Huang, M. and Yu, P. S. (2018). Visual domain adaptation with manifold embedded distribution alignment. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia (pp. 402–410).
Wang, M., Lin, Y., Jiang, H., & Sun, Y. (2022). Tespda-sei: Tensor embedding substructure preserving domain adaptation for specific emitter identification. Physical Communication, 57, 101973.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, No: 62201172). This work is also supported by Key Laboratory of Advanced Marine Communication and Information Technology, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Lin, Y., Liu, C. et al. TESPOSDA-SEI: tensor embedding substructure preserving open set domain adaptation for specific emitter identification. Wireless Netw 29, 2935–2951 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03317-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03317-5