Abstract
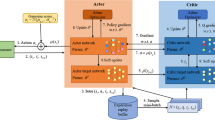
Transferring data in the mobile ad hoc network can be enabled to analyze data transferring and the network that manages the data and route them into the VPN-based routing. Here is the process of maintaining the gateway for the analysis. The main problem here is the routing of the data packets, and the analysis of the nodes in the form of packages is the main issue in this study. To fix this, troubleshooting problems can be enabled for the packets which reach the destinations and the echo response. The primary technique used in this study is energy efficient geographic routing protocol and reward-based intelligent Ad hoc routing is used for the analysis. The energy-efficient geographic routing protocol enables the EGRPM method to reduce the sensor nodes and the WSN. This allows gathering the data and the nodes to maintain the geographic way. Reward-based intelligent Ad hoc routing is used in automatic decision-making, and the analysis of the system to produce the selection action for the research is reinforcement learning. This results from the study of the configuration and the analysis of the data in the ad hoc network. This enables the formation of learning about the routing protocol and facilitates the current data transfer to the research done in the ad hoc networks. This data analysis in the mobile network helps analyze the system and the entire data management.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in the manuscript.
References
Bala, P. C., Eisenreich, B. R., Yoo, S. B. M., et al. (2020). Automated markerless pose estimation in freely moving macaques with OpenMonkeyStudio. Nature Communications, 11, 4560. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18441-5
Xu, L., Yan, W., & Ji, J. (2023). The research of a novel WOG-YOLO algorithm for autonomous driving object detection. Science and Reports, 13, 3699. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-30409-1
Ilyas, N., Ahmad, Z., Lee, B., et al. (2022). An effective modular approach for crowd counting in an image using convolutional neural networks. Science and Reports, 12, 5795. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-09685-w
Al-Ezaly, E., El-Bakry, H. M., Abo-Elfetoh, A., et al. (2023). An innovative traffic light recognition method using vehicular ad-hoc networks. Sci Rep, 13, 4009. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-31107-8
Choi, C., Kim, H., Kang, J. H., et al. (2022). Reconfigurable heterogeneous integration using stackable chips with embedded artificial intelligence. Nat Electron, 5, 386–393. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-022-00778-y
Ramdhany, R., Grace, P., Coulson, G., et al. (2010). Dynamic deployment and reconfiguration of ad-hoc routing protocols. J Internet Serv Appl, 1, 135–152. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13174-010-0010-y
Chen, G. G., Branch, J. W., & Szymanski, B. K. (2006). A self-selection technique for flooding and routing in wireless ad-hoc networks. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 14, 359–380. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10922-006-9036-7
Choudhury, R. R., Paul, K., & Bandyopadhyay, S. (2002). An agent-based connection management protocol for ad hoc wireless networks. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 10, 483–504. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021164222319
Chang, J. M., Lai, C. F., Chao, H. C., et al. (2014). An energy-efficient geographic routing protocol design in vehicular ad-hoc network. Computing, 96, 119–131. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-012-0235-7
Zhang, D., Liu, X., Cui, Y., et al. (2019). A kind of novel RSAR protocol for mobile vehicular ad hoc network. CCF Transactions on Networking, 2, 111–125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42045-019-00019-5
Marwah, G. P. K., & Jain, A. (2022). A hybrid optimization with ensemble learning to ensure VANET network stability based on performance analysis. Science and Reports, 12, 10287. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-14255-1
Mathis, A., Mamidanna, P., Cury, K. M., et al. (2018). DeepLabCut: Markerless pose estimation of user-defined body parts with deep learning. Nature Neuroscience, 21, 1281–1289. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-018-0209-y
Álvarez-Aparicio, C., Guerrero-Higueras, Á. M., González-Santamarta, M. Á., et al. (2022). Biometric recognition through gait analysis. Science and Reports, 12, 14530. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-18806-4
Jiang, X., Hu, H., Qin, Y., et al. (2022). A real-time rural domestic garbage detection algorithm with an improved YOLOv5s network model. Science and Reports, 12, 16802. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-20983-1
Pereira, T. D., Tabris, N., Matsliah, A., et al. (2022). SLEAP: A deep learning system for multi-animal pose tracking. Nature Methods, 19, 486–495. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-022-01426-1
Che, J., He, Y., & Wu, J. (2023). Pedestrian multiple-object tracking based on FairMOT and circle loss. Science and Reports, 13, 4525. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-31806-2
Zhao, Z., Yang, X., Zhou, Y., et al. (2021). Real-time detection of particleboard surface defects based on improved YOLOV5 target detection. Science and Reports, 11, 21777. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01084-x
Zhong, X., Qin, J., Guo, M., et al. (2022). Offset-decoupled deformable convolution for efficient crowd counting. Science and Reports, 12, 12229. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16415-9
Mon, E. E., Ochiai, H., Komolkiti, P., et al. (2022). Real-world sensor dataset for city inbound-outbound critical intersection analysis. Sci Data, 9, 357. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01448-6
Kim, M., Kim, H., Sung, J., et al. (2023). High-resolution processing and sigmoid fusion modules for efficient detection of small objects in an embedded system. Science and Reports, 13, 244. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-27189-5
Pastore, V. P., Moro, M., & Odone, F. (2022). A semi-automatic toolbox for markerless effective semantic feature extraction. Science and Reports, 12, 11899. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16014-8
Cheng, L., Ji, Y., Li, C., et al. (2022). Improved SSD network for fast concealed object detection and recognition in passive terahertz security images. Science and Reports, 12, 12082. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-16208-0
Graczyk, K. M., Pawłowski, J., Majchrowska, S., et al. (2022). Self-normalized density map (SNDM) for counting microbiological objects. Science and Reports, 12, 10583. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-14879-3
Lauer, J., Zhou, M., Ye, S., et al. (2022). Multi-animal pose estimation, identification and tracking with DeepLabCut. Nature Methods, 19, 496–504. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-022-01443-0
Lee, S. M. W., Shaw, A., Simpson, J. L., et al. (2021). Differential cell counts using center-point networks achieves human-level accuracy and efficiency over segmentation. Science and Reports, 11, 16917. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-96067-3
Gao, H., Zhao, W., Zhang, D., et al. (2023). Application of improved transformer based on weakly supervised in crowd localization and crowd counting. Science and Reports, 13, 1144. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-27299-0
Chiriboga, M., Green, C. M., Hastman, D. A., et al. (2022). Rapid DNA origami nanostructure detection and classification using the YOLOv5 deep convolutional neural network. Science and Reports, 12, 3871. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-07759-3
Dehghani, M., Trojovská, E., & Trojovský, P. (2022). A new human-based metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems on the base of simulation of driving training process. Science and Reports, 12, 9924. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-14225-7
Nath, T., Mathis, A., Chen, A. C., et al. (2019). Using DeepLabCut for 3D markerless pose estimation across species and behaviors. Nature Protocols, 14, 2152–2176. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41596-019-0176-0
Korecki, M. (2022). Adaptability and sustainability of machine learning approaches to traffic signal control. Science and Reports, 12, 16681. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-21125-3
Huang, H., Tang, X., Wen, F., et al. (2022). Small object detection method with shallow feature fusion network for chip surface defect detection. Science and Reports, 12, 3914. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-07654-x
Li, W., Liu, K., Zhang, L., et al. (2020). Object detection based on an adaptive attention mechanism. Science and Reports, 10, 11307. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-67529-x
Funding
This research is funded by Ministry of Education and Training under project number B2021.DNA.09.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All author is contributed to the design and methodology of this study, the assessment of the outcomes and the writing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Syed, L., Sathyaprakash, P., Shobanadevi, A. et al. Deep learning-based route reconfigurability for intelligent vehicle networks to improve power-constrained using energy-efficient geographic routing protocol. Wireless Netw 30, 939–960 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03525-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-023-03525-z