Abstract
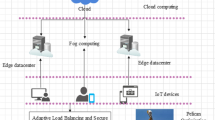
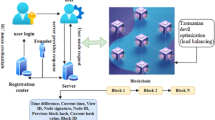
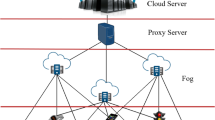
Fog computing has provided answers to several issues in recent years, including the accuracy and caliber of the data gathered. Due to its inherent distributed architecture, security and load-balancing techniques present difficulties. This study proposes blockchain-based user authentication for fog computing and enhanced subtraction-average-based optimizer (ESABA)-based load balancing. Fog computing has integrated blockchain technology into its user authentication procedure. Subtraction Average Based Optimizer (SABO) and Oppositional Based Learning (OBL) functions are then combined to form the ESABA. The oppositional function in the SABO is employed to improve the initial population through their solutions. This procedure yields the best results for load balancing and user authentication. The suggested approach is put into practice in Python, and several performance metrics like waiting time, processing time, memory consumption for user verification, and authentication are assessed. The performance compared with the existing algorithm. The results demonstrate superior performance in both security and load balancing, highlighting the method’s potential for practical applications in fog computing. The proposed method takes a minimum response time of 0.5 s for twenty-five task scheduling.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing does not apply to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
CISCO, (2015). “Cisco Fog Computing Solutions: Unleash the Power of the Internet of Things,”p. 6, [Online]. Available: https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en us/solutions/trends/iot/docs/computing-solutions.pdf.
Dastjerdi, H., Gupta, R., Calheiros, S., Ghosh, and Buyya, R. (2016). Fog Computing: principles,architectures, and applications,” in Internet of Things. Elsevier, pp. 61–75.[Online].Available:http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780128053959000046.
Tordera, E. M., Masip-Bruin, X., Garc´ıa-Almi˜nana, J., Jukan, A., Ren, G.-J., and Zhu, J. (2017). Do we all really know what a fog node is? current trends towards.an open definition,” Computer Communications. [Online]. Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0140366416307113?via=ihub.
Xu, X., Fu, S., Cai, Q., Tian, W., Liu, W., Dou, W., Sun, X., & Liu, A. X. (2018). Dynamic resource allocation for load balancing in fog environment. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2018, 6421607.
Al-fuqaha, A., Guizani, M., Mohammadi, M., Aledhari, M., & Ayyash, M. (2015). Internet of things : A survey on enabling internet of things : A survey on enabling technologies, protocols, and applications. IEEE communications surveys & tutorials, 17(4), 2347–2376.
Puthal, D., Obaidat, M. S., Nanda, P., Prasad, M., Mohanty, S. P., & Zomaya, A. Y. (2018). Secure and sustainable load balancing of edge data centers in fog computing. IEEE Communications Magazine, 56(5), 60–65.
Verma, M., Bhardwaj, N., & Yadav, A. K. (2016). Real time efficient scheduling algorithm for load balancing in fog computing environment. International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science, 8(4), 1–10.
Puthal, D., Ranjan, R., Nanda, A., Nanda, P., Jayaraman, P. P., & Zomaya, A. Y. (2019). Secure authentication and load balancing of distributed edge datacenters. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 124, 60–69.
Talaat, F. M., Ali, S. H., Saleh, A. I., & Ali, H. A. (2019). Effective load balancing strategy (ELBS) for real-time fog computing environment using fuzzy and probabilistic neural networks. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 27, 883–929.
Mazumdar, N., Nag, A., & Singh, J. P. (2021). Trust-based load-offloading protocol to reduce service delays in fog-computing-empowered IoT. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 93, 107223.
Srinivas, KV., and Krishna, BG., fog computing for secure and sustainable load balancing of edge data centers.
He, X., Ren, Z., Shi, C., & Fang, J. (2016). A novel load balancing strategy of software-defined cloud/fog networking in the Internet of Vehicles. China Communications, 13(Supplement2), 140–149.
Kashyap, V., Ahuja, R., & Kumar, A. (2024). A hybrid approach for fault-tolerance aware load balancing in fog computing. Cluster Computing. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3315754/v1
Premkumar, N., & Santhosh, R. (2024). Secure authentication scheme with Archimedes optimization algorithm for load balancing technique in fog computing. International Journal of Information Technology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41870-024-01861-7
Mahapatra, A., SK, Majhi., K, Mishra., R, Pradhan., DC, Rao., and SK, Panda. (2024). An energy-aware task offloading and load balancing for latency-sensitive IoT applications in the Fog-Cloud continuum. IEEE Access.
Hasan, M. K., Sundararajan, E., Islam, S., Ahmed, F. R., Babiker, N. B., Alzahrani, A. I., Alalwan, N., & Khan, M. A. (2024). A novel segmented random search based batch scheduling algorithm in fog computing. Computers in Human Behavior, 158, 108269.
Trojovský, P., & Dehghani, M. (2023). Subtraction-average-based optimizer: A new swarm-inspired metaheuristic algorithm for solving optimization problems. Biomimetics, 8(2), 149.
Smaili, I. H., Almalawi, D. R., Shaheen, A. M., & Mansour, H. S. (2024). Optimizing PV sources and shunt capacitors for energy efficiency improvement in distribution systems using subtraction-average algorithm. Mathematics, 12(5), 625.
Pradhan, M., Roy, P. K., & Pal, T. (2018). Oppositional based grey wolf optimization algorithm for economic dispatch problem of power system. Ain Shams Engineering Journal, 9(4), 2015–2025.
Alzubi, J. A., Alzubi, O. A., Singh, A., & Mahmod, A. T. (2023). A blockchain-enabled security management framework for mobile edge computing. International Journal of Network Management, 33(5), e2240.
Alzubi, A. J. (2021). Blockchain-based lamport merkle digital signature: Authentication tool in IoT healthcare. Computer Communications. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comcom.2021.02.002
Funding
The authors declare that they do not have competing interests and funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Premkumar, N., Sridharan, S., Viswanathan, R.V. et al. Enhanced subtraction-average-based optimizer and blockchain for security and load balancing in fog computing. Wireless Netw 31, 2243–2255 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-024-03869-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11276-024-03869-0