Abstract
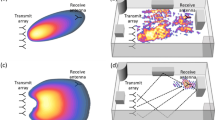
The purpose of this paper is to investigate the performance of Time Reversal (TR) for short-range Multiple-Input Single-Output (MISO) systems in the Industrial, Scientific, and Medical (ISM) 5 GHz band using actual channel measurements. Such a scenario is considered for low cost user equipment applications, where low-complexity schemes like TR will be an potential candidate. The experiment is conducted with 8 transmit antennas and 1 receive antenna per user. The antennas are arranged in compact and distributed configurations, and the channel is measured in both Line-of-Sight (LOS) and Non-Line-of-Sight (NLOS) dominated scenarios. We investigate the performance of TR in terms of time compression, spatial focusing, and diversity gain, by analyzing the delay spread, the spatial Peak-to-Average-Leakage power ratio and the diversity gain, respectively. The conclusions that can be drawn from the experiment are: TR with multiple transmit antennas shows better performance compared to the single antenna link in terms of time compres- sion, spatial focusing, and diversity gain, even in realistic short-range communications. Second, a distributed 8 Tx antenna configuration achieves lower delay spread and higher diversity gain than a compact antenna array with the same number of elements. In the situation where practical impairments are taken into consideration, the system delay involving propagation and processing time is found to be a crucial parameter degrading the performance of TR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, J.B., Jensen, J., Jensen, S.H., & Frederiksen, F. (1999). Prediction of future fading based on past measurement. In Proceedings of the fall vehicular technology conference, Delft, The Netherlands, Vol. 1, pp. 151–155.
Duel-Hallen A., Hu S., Hallen H. (2000). Long-range prediction of fading signals. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine 17(3): 62–75
Emami, M., Vu, M., Hansen, J., Paulraj, A.J., Papanicolaou G. (2004). Matched filtering with rate back-off for low-complexity communications in very large delay spread channels. In Proceedings of the Conference record of the 38 asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers, Vol. 1, pp. 218–222.
Fink M. (1992). Time reversal of ultrasonic fields. I. Basic principles. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics and Frequency Control 39(5): 555–556
Fink, M. (1999). Time-reversed acoustics. Scientific American, pp. 67–73.
Goldsmith A., Jafar S.A., Jindal, N., Vishwanath S. (2003). Capacity limits of MIMO channels. IEEE J. on Select. Areas in Communications 21: 684–702
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Analog-to-digital_converter, Wikipedia, access time:18.10.2006. http://para.maxim-ic.com/index.mvp?tree=adconverters, Maxim Integrated Products, Dallas Semiconduction, access time:18.10.2006.
Hyoung-kyu Song. (1999). A channel estimation using sliding window approach and tuning algorithm for MLSE. IEEE Communications Letters, 3(7).
Jakes, W.C. (1974). Microwave mobile communications. IEEE Press. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, New York: ISBN 0-7803-1069-1, p. 39.
Kyritsi P., Cox D.C., Valenzuela R.A., Wolniansky P.W. (2003). Correlation analysis based on MIMO channel measurements in an indoor environment. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 21(5): 713–720
Kyritsi P., Papanicolaou G., Eggers P.C.F., Oprea A. (2004). MISO time reversal and delay spread compression for FWA channeles at 5GHz. Antennas and wireless propagation letters 3: 96–99
Lerosey, G., Rosny, J., Tourin, A., Derode, A., Montaldo, G., & Fink, M. (2004). Time reversal of electromagnetic waves. Physical Review Letters 92 (19), id. 193904-1.
Llorente, J.M., Adenet, A., Lemasson, Ch., & Zhou, X. (2005). Time reversal for WLAN application. Master Thesis, Aalborg University, Denmark.
Maxim Integrated Products. How quantization and thermal noise determine an ADC’s effective noise figure. Application Note 1197.
Nguyen, H.T., Andersen, J.B., & Pedersen, G.F. (2005). The potential use of time reversal techniques in multiple element antenna systems. IEEE Communications Letters, 9 (1).
Sans, M.B. (2003). MIMO channel characterization of an urban/suburban environment at 5-6 GHz, Master Thesis, Aalborg University, Danmark.
Shen, Z., Andrews, J.G., & Evans, B.L. (2003). Short range wireless channel prediction using local information. In conference record of the 37 proceedings of the asilomar conference on signals, systems and computers, Vol. 1, pp. 1147–1151.
Strohmer, T., Emami, M., Hansen, J., Papanicolaou, G., & Paulraj, A.J. (2004). Application of Time-Reversal with MMSE Equalizer to UWB communications. In Proceeding of the global telecommunications conference, 2005, GLOBECOM’04, IEEE, Vol. 5, pp. 3123–3127.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Kyritsi, P., Martinez, J. et al. Assessment of MISO time reversal for short-range communications in the 5 GHz ISM band. Wireless Pers Commun 43, 759–776 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-007-9280-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-007-9280-5