Abstract
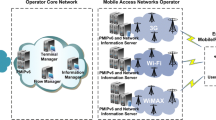
This paper presents a middleware platform for managing devices that operate in heterogeneous environments. The proposed management framework supports terminal-controlled, preference-based access network selection. Two separate problems are identified in this domain: one involving the computation of optimal allocations of services to access networks and quality levels (service configuration), and one concerning the dynamic inference of the user’s preferences, according to the usage context (user profiling). This paper includes an approach to the definition, mathematical formulation and solution of both these problems. Indicative results of the proposed solution methods are presented in the context of a real-life scenario simulating a day in the life of an ordinary user.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Varshney, U. (2000). Recent advances in wireless networking. IEEE Computer, 33(6).
Next generation wireless broadband networks. Special issue in IEEE Network, 14(5).
Gustafsson E., Jonsson A. (2003). Always best connected. IEEE Wireless Communications 10(1): 4955
Varshney, U., & Vetter, R. (2000). Emerging mobile and broadband wireless networks. Communication of the ACM, 43(6).
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee web site, www.ieee802.org.
Third generation mobile systems in Europe. Special issue in IEEE Personal Communication, 5(2).
Wideband CDMA. Feature topic in the IEEE Communication Magazine, 36(9).
Digital Video Broadcasting web site, www.dvb.org.
Management of heterogeneous networks, feature topic in the IEEE Communication Magazine, 36(3).
Fourth generation wireless networks and interconnecting standards. Special issue in the IEEE Personal Communication, 8(5).
Demestichas P., Stavroulaki V., Papadopoulou L., Vasilakos A., Theologou M. (2003). Service configuration and traffic distribution in composite radio environments. IEEE Transaction on Systems, Man and Cybernetics Journal 33(4):69–81
Demestichas, P., Vivier, G., El-Khazen, K., & Theologou, M. (2004). Evolution in wireless systems management concepts: from composite radio to reconfigurability. IEEE Communication Magazine, 42(5).
van Bemmel, J., Teunissen, H., Plas, D.-J., & Peddemors, A. (2002). A Reference Architecture for 4G Services, 7th WWRF meeting, Eindhoven, The Netherlands.
Chantrain, D., Handekyn, K., & Vanderstraeten, H. (2000). The soft terminal: extending service intelligence from the network to the terminal. Alcatel Telecommunications Review.
Busropan, B., van Loon, J., Vervuurt, F., & van Eijk, R. (2003).Access network selection in heterogeneous networks and the role of the operator. 9th WWRF Meeting, Zurich, Switzerland.
Esler, M., Hightower, J., Anderson, T., & Borriello, G. (1999). Next century challenges: Data-centric networking for invisible computing. 5th ACM/IEEE International conference on mobile computing and networking, pp. 256–262.
Weiser, M. (1991). The computer for the 21st century. Scientific American, 265(3), 94–104; reprinted in: IEEE Pervasive Computing, pp. 19–25.
Grimm, R., Anderson, T., Bershad, B., & Wetherall, D. (2000). A system architecture for pervasive computing. 9th ACM SIGOPS European workshop: Beyond the PC: New challenges for the operating system, (pp. 177–182).
Weiser M. (1993). Some computer science issues in ubiquitous computing. Communication of the ACM 36(7): 75–84
Pascoe, J., Ryan, N., & Morse, D. (1999). Issues in developing context-aware computing. First international symposium on handheld and ubiquitous computing. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 1707, pp. 208–221, Springer-Verlag.
Henricksen, K., Indulska, J., & Rakotonirainy, A. (2002). Modeling context information in pervasive computing systems. Pervasive 2002, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 2414, pp. 167-180, Springer-Verlag.
Homayounvala, E., Ghorashi, S.A., & Aghvami, A.H. (2004). A Bayesian approach to modelling user preferences for reconfiguration. E2R workshop on reconfigurable mobile systems and networks beyond 3G, Barcelona, Spain.
Dillinger, M., Madani, K., & Alonistioti, N. (2003). Software defined radio: architectures, systems and functions. John Wiley & Sons.
Irvine, J. (2002). Adam Smith goes mobile: Managing services beyond 3G with the digital marketplace. European Wireless 2002, Florence, Italy.
O’Droma, M. et al., (2003). Always Best Connected Enabled 4G Wireless World. In Proceedings of the 12th IST summit on mobile and wireless communications, (pp.710–716). Aveiro, Portugal, June 2003, ISBN 972-98368-7.
Gazis V., Alonistioti N., Merakos L. (2005). Toward a generic Always Best Connected capability in integrated WLAN/UMTS cellular mobile networks (and beyond). IEEE Wireless Communication Magazine 12(3): 20–29
Lettieri P., Srivastava M.B. (1999). Advances in wireless terminals. IEEE Personal Communications, 6(1): 6–19
Bargh, M., Bijwaard, D., Zandbelt, H., Meeuwissen, E & Peddemors, A. (2003). Mobility management in beyond 3G environments. 9 th WWRF Meeting, Zurich, Switzerland.
Bargh, M., Zandbelt, H., & Peddemors, A. (2003). Managing mobility with federating service platforms. IST-EVOLUTE workshop on beyond 3G evolution of systems and services, Guildford, UK.
Liebsch, M., Singh, A., Chaskar, H., Funato, D., Shim, E. (editors) (2005). The candidate access router discovery protocol. IETF RFC 4066.
Simplicity IST-2004-507558 Project, Deliverable D2302. (2004). Enhanced performance evaluation of system mechanisms.
Judd, G. & Steenkiste, P. (2003). Providing contextual information to ubiquitous computing applications. IEEE International conference on pervasive computing and communications (PerCom 2003). (pp. 133–142).
Perkins, C. (2002). IP Mobility Support for IPv4. IETF RFC 3220.
Johnson, D. B. (2004). Mobility Support in IPv6. IETF RFC 3775.
Koodli, R. (Ed.) (2005). Fast Handovers for Mobile IPv6. IETF RFC 4068.
El Malki, K. (Ed.), (2004). Low latency handoffs in mobile IPv4. IETF draft-ietf-mobileip-lowlatency-handoffs-v4-10.txt, work in progress.
Rosenberg, J., Schulzrinne, H., Camarillo, G., Johnston, A., Peterson, J., Sparks, R., Handley, M., & Schooler, E. (2002). SIP: Session initiation protocol. IETF RFC 3261.
Ahlund, C., & Zaslavsky, A. (2003). Multihoming with Mobile IP (2003). 6 th IEEE international conference on high speed networks and multimedia communications, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2720, 235–243, Springer-Verlag.
Montavont, N. et al. (2005). Analysis of Multihoming in Mobile IPv6. IETF draft-montavont-mobileip-multihoming-pb-statement-04.txt, work in progress.
Ernst, T. (2000). Goals Benefits of Multihoming. IETF draft-ernst-generic-goals-and-benefits-01.txt, work in progress.
Demestichas P., Papadopoulou L., Stavroulaki V., Theologou M., Vivier G., Martinez G., & F. Galliano, Wireless beyond 3G: managing services and network resources. IEEE Computer Magazine., 35(8): 80–82
Demestichas P., Stavroulaki V. (2004). Issues in introducing resource brokerage functionality in B3G composite radio environments. IEEE Wireless Communication Magzine 11(5): 32–40
Carneiro G., Ruela J., Ricardo M. (2004). Cross-layer design in 4G wireless terminals. IEEE Wireless Communication Magazine 11(2): 7–14
Pearl, J. (1988). Probabilistic reasoning in intelligent systems: networks of plausible inference. Morgan Kauffman
Terziyan, V. (2005). A Bayesian Metanetwork, International Journal on Artificial Intelligence Tools, 14(3), 371–384, World Scientific.
Heckerman, D. (1995). A Tutorial on Learning with Bayesian Networks. Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, Tech. Rep. MSR-TR-95-06.
Terziyan, V., & Vitko, O. (2000). Bayesian metanetworks for modelling user preferences in mobile environment. KI 2003: Advances in artificial intelligence, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 2821, pp. 370–384, Springer-Verlag.
Cheng, J., & Greiner, R. (2001). Learning Bayesian belief network classifiers: algorithms and system. 14 th biennial conference of the Canadian society for computational studies of intelligence, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Vol. 2056, pp. 141-151, Springer-Verlag.
Cooper G.F. (1999). Computational complexity of probabilistic inference using Bayesian belief networks. Artificial Intelligence 42 (2-3):393–405
Spirtes, P., Glymour, C., & Scheines, R., Causation, prediction and search. MIT Press.
Cheng, J., Bell, D. A., & Liu, W. (1997). An algorithm for Bayesian belief network construction from data. 6th International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AI & Stats-97), pp. 83–90
Chickering, D. M. (1996). Learning Bayesian networks is NP-complete. In D. Fischer & H.-J. Lenz (Ed.), Learning from Data—Artificial Intelligence and Statistics V, Lecture Notes in Statistics (vol. 112, pp. 121–130). Springer-Verlag.
Chickering, D. M., Geiger, D., & Heckerman, D. (1994). Learning Bayesian networks is NP-hard. Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, Tech. Rep. MSR-TR-94-17.
Buntine W. (1996). A guide to the literature on learning probabilistic networks from data. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 8(2):195–210
Geiger, D., & Heckerman, D. (1955). Likelihoods parameter priors for Bayesian networks. Microsoft Research, Redmond, WA, Tech. Rep. MSR-TR-95-54.
MacKay, D. (1992). Bayesian interpolation. Neural computation, Vol. 4, No. 3, (pp. 415-447), MIT Press.
MacKay, D. (1992). A practical Bayesian framework for backpropagation networks. Neural Computation 4(3), pp. 448–472, MIT Press.
Haykin, S. (1998). Neural networks, a comprehensive foundation. Prentice Hall
Specht, D. (1990). Probabilistic neural networks. In Neural networks, Vol. 3, pp. 109–118, Elsevier.
Bishop, C. M. (1998). Neural networks for pattern recognition. Clarendon Press.
Garson, G. D. (1998). Neural networks, an introductory guide for social scientists. SAGE Publications.
Buntine, W. (1993). Learning classification trees. Artificial intelligence frontiers in statistics: AI and Statistics III, Chapman and Hall.
Friedman, N., & Goldszmidt, M. (1996). Building classifiers using Bayesian networks. Thirteenth national conference on artificial intelligence. (pp. 1277–1284). Portland, OR, AAAI Press.
Pham, D. T., & Karaboga, D. (2000). Intelligent optimisation techniques: Genetic algorithms, simulated annealing and neural networks. Springer-Verlag.
Garey, M., & Johnson, D. (1979). Computers and intractability: A guide to the theory of NP-completeness. W.H. Freeman and Company.
Papadimitriou, C., & Steiglitz, K. (1982). Combinatorial optimization: Algorithms and complexity. Prentice Hall.
Pindyck, R., & Rubinfeld, D. (2004). Microeconomics. Prentice Hall.
Marbukh V. (2004). On aggregate utility maximization based network management: challenges and possible approaches. IEEE International Conference on Communications, 2:1212–1216
Chang C.-S., Liu Z. (2004). A bandwidth-sharing theory for a large number of HTTP-like connections. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 12(5):952–692
Doyle, J. (1983). Methodological simplicity in expert system construction: The case of judgements and reasoned assumptions. Technical Report CMU-CS-83-114, Department of Computer Science, Carnegie-Mellon University.
Forgy, L., & McDermott, J. (1977). OPS: A domain-independent production system. In Proceedings of the 5th international conference on artificial intelligence, (pp. 933–939). William Kaufmann.
Horvitz E., Breese J., Henrion M. (1988). Decision theory in expert systems and artificial intelligence. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning 2, 247–302
Heckerman, D., & Horvitz, E. (1987). On the expressiveness of rule-based systems for reasoning under uncertainty. In Proceedings of the sixth national conference on artificial intelligence. AAAI Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koutsorodi, A.A., Adamopoulou, E.F., Demestichas, K.P. et al. Service configuration and user profiling in 4G terminals. Wireless Pers Commun 43, 1303–1321 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-007-9303-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-007-9303-2