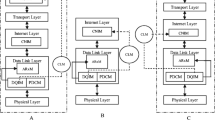
Abstract
During the last few years, bandwidth and traffic control have immerged as issues of great importance in ad-hoc wireless networks, requiring sophisticated managing techniques. Moreover, due to the increasing variety of applications and consequently respective need for bandwidth control, such issues are expected to become even more critical in the near future. Main characteristics of MANETs such as multi-hop communication and supporting dynamically varying topologies rapidly and unpredictably change or remain static over long periods of time augments the complexity of the problem as well as the need to efficiently handle it. In order to circumvent those problems, many researchers turn their attention to cross-layer design which provides the possibility to create lightweight and flexible substrate for the demanding ad-hoc wireless networks. This design approach provides critical features that suit the characteristics of ad-hoc wireless networks. This paper proposes a novel, lightweight and efficient cross-layer architecture for congestion control at wireless ad-hoc networks. The performance of this framework is evaluated considering characteristic ad-hoc routing protocols, such as AODV and DSR, in static as well as mobile network topologies using the well known network simulator NS2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pogkas N., Karastergios G., Antonopoulos C., Koubias S., Papadopoulos G. (2007) Architecture design and implementation of an ad-hoc network for disaster relief operations. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 3(1): 63–72
Chen L., Heinzelman W.B. (2005) QoS-Aware routing based on bandwidth estimation for mobile ad hoc networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 23(3): 561–572
Schwienger, K., & Fettweis, G. (2005). Power and energy consumption for multi-hop protocols: A sensor network point of view. International Workshop on Wireless Ad-hoc Network.
Barrett, C., Drozda, M., Marathe, A., & Marathe, M. V. (2002). Characterizing the interaction between routing and MAC protocols in ad-hoc networks. In MOBIHOC’02, June 9–1, 2002.
Kawadia V., Kumar P.R. (2005) Principles and protocols for power control in wireless ad hoc networks. IEEE Journal On Selected Areas In Communications: Special Issues on Wireless Ad Hoc Networks 23(1): 76–88
Mohapatra P., Li J., Gui C. (2003) QoS in mobile ad hoc networks. IEEE Wireless Communications 10(3): 44–52
Wu J., Dai F. (2004) Mobility control and its applications in mobile ad hoc networks. IEEE Network 18(4): 30–35
Van Dinh, D., Vuong, M. D., Nquyen, H. P., & Nquyen, H. X. (2005). Wireless sensor actor networks and routing performance analysis. International Workshop on Wireless Ad-hoc Networks.
Monks, J. P., Bharghavar, V., & Hwu, W.-M. W. (2001). A power controlled multiple access protocol for wireless packet networks. In IEEE INFOCOM. Anchorage, Alaska.
Gomez J., Campbell A.T. (2003) PARO: Supporting dynamic power controlled routing in wireless ad hoc networks. Wireless Networks 9: 443–460
Singh S., Raghavendra C.S. (1998) PAMAS-Power aware multi-access protocol with signalling for ad hoc networks. ACM SiGCOM 28(3): 5–26
Bandyopadhyay, S., Hasuike, K., Horisawa, S., & Tawara, S. (2001). An adaptive MAC and directional routing protocol for ad hoc wireless network using ESPRA antenna. In MOBIHOC ACM. Long Beach, CA, USA.
Krunz M., Muqattash A., Lee S.-J. (2004) Transmission power control in wireless ad hoc networks: Challenges, solutions, and open issues. IEEE Network 18(5): 8–14
Sichitiu, M. L. (2004). Cross-layer scheduling for power efficiency in wireless sensor networks. In IEEE INFOCOM. Hong Kong, China.
Safwat, A., Hassanein, H., & Mouftah, H. (2003). Optimal cross-layer designs for energy-efficient wireless ad hoc and sensor networks. In IEEE IPCCC 2003.
Jacobson, V. (1988). Congestion avoidance and control. In Symposium Proceedings on Communications Architectures and Protocols (pp. 314–329), Stanford, CA.
Antonopoulos, Ch., Giannoulis, S., Koubias, S., & Lyperopoulos, I. (2005). The effect of power consumption on the real time performance of routing protocols for ad hoc wireless networks. In 10th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation, 19–22 September 2005, Catania, Italy.
Holland G., Vaidya N. (2002) Analysis of TCP performance over mobile ad hoc networks. Wireless Networks 8: 275–288
Jin C. et al (2005) FAST TCP: From theory to experiments. IEEE Network 19(1): 4–11
Peng Fu C., Liew S.C. (2003) TCP Veno: TCP enhancement for transmission over wireless access networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 21(2): 216–228
Lai, Y.-C., & Yao, C.-L. (2000). The performance comparison between TCP reno and TCP vegas. In IEEE 7th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 4–7 July 2000.
Miller, B., Avrachenkov, K., Stepanyan, K., & Miller, G. (2005). Flow control as stochastic optimal control problem with incomplete information. In IEEE INFOCOM, Miami, FL, USA.
Altman, E., Avrachenkov, K. E., & Prabhu, B. J. (2005). Fairness in MIMD congestion control algorithms. In IEEE INFOCOM, Miami, FL, USA.
Altman, E., Avrachenkov, K. E., Kherami, A. A., & Prabhu, B. J. (2005). Performance analysis and stochastic stability of congestion control protocol. In IEEE INFOCOM, Miami, USA.
Caponetto, R., Lo Bello, L., & Mirabella, O. (2002). Fuzzy traffic smoothing: Another step towards statistical real-time communication over ethernet networks. 1st RTLIA, June 2002, Vienna, Austria.
Chen, L., Low, S. H., & Doyle, J. C. (2005). Joint congestion control and media access control design for ad hoc wireless networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Infocom.
Siris, V. A., & Triantafyllidou, D. (2004). Seamless congestion control over wired and wireless IEEE 802.11 networks. In IFIP NETWORKING, Athens.
Shakkottai S., Rappaport T.S., Karlsson P.C. (2003) Cross-layer design for wireless networks. In IEEE Communications Magazine 41(10): 74–80
Yu Y., Krishnamachari B., Prasanna V.K. (2004) Issues in designing middleware for wireless sensor networks. IEEE Network 18(1): 15–21
Blair G., Campbell A.T., Schmidt D.C. (2004) Middleware technologies for future communication networks. IEEE Network 18(1): 4–5
Conti M., Maselli G., Turi G., Giordano S. (2004) Cross-layering in mobile ad hoc network design. IEEE Computer 37(2): 48–51
Kliazovich D., Granelli F. (2006) Cross-layer congestion control in ad hoc wireless networks. Ad-Hoc Networks 4: 687–708
Anjum, F., & Tassiulas, L. On the behavior of different TCP algorithms over a wireless channel with correlated packet losses. In ACM SIGMETRICS ‘99 5/99, Atlanta Georgia, USA.
Antonopoulos, Ch., Athanasopoulos, A., & Koubias, S. (2006). A simulation study on dropping tendencies of an ad-hoc wireless network. In 11th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), September 20–22, 2006, Prague, Czech Republic.
Bonaventure O. (2004) Software tools for networking. IEEE Network 18(6): 4–5
Perkins, C. E., Royer, E. M., & Das, S. R. (2003). Ad hoc on-demand distance vector (AODV) routing. Internet Draft, MANET Working Group, draft-ietf-manet-aodv-04.txt, October 2003.
Johnson, D. B., Maltz, D. A., & Hu, Y.-C. (2004). The dynamic source routing protocol for mobile ad hoc networks. Internet Draft, MANET Working Group, draft-ietf-manet-dsr-10.txt, July 2004.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonopoulos, C., Koubias, S. Congestion Control Framework for Ad-Hoc Wireless Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 52, 753–775 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-009-9660-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-009-9660-0