Abstract
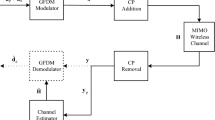
A frequency-domain channel expanding technique (FD-CET) is proposed for channel estimation in an iterative receiver of a low-density parity-check coded orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system. The FD-CET can expand a subset of the frequency-domain channel gains to all of them in a short-point FFT/IFFT format. This technique is applied to estimate the channel gains utilizing the pilots and information from the decoder in an iterative manner. It is a novel low complexity channel estimation method. Numerical results demonstrate that the proposed channel estimator approaches a maximum-likelihood performance within only a few iterations under multi-path channels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gallager R. G. (1963) Low-density parity check codes. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Richardson T., Urbanke R. (2001) The capacity of low-density parity-check codes under message-passing decoding. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory 47(2): 599–618
Sason I. (2009) On universal properties of capacity-approaching LDPC code ensembles. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory 55(7): 2956–2990
ETSI EN 302 307 (2004). Second generation framing structure, channel coding and modulation system for broadcasting, interactive services, news gathering and other broadband satellite applications. ETSI.
IEEE Std. 802.16e (2006). IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks part 16: Air interface for fixed and mobile broadband wireless access systems, amendment 2: Physical and medium access control layer for combined fixed and mobile operation in licensed bands. IEEE.
Bennatan A., Burshtein D. (2006) Design and analysis of nonbinary LDPC codes for arbitrary discrete-memoryless channels. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory 52(2): 549–583
Wachsmann U., Fischer R. F. H., Huber J. B. (1999) Multilevel codes: Theoretical concepts and practical design rules. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory 45(7): 1361–1391
Caire G., Taricco G., Biglieri E. (1998) Bit interleaved coded modulation. IEEE Transaction on Information Theory 44(5): 927–946
Guan, W., & Xiang, H. (2009). Decoding and design of LDPC codes for high-order modulations. Wireless Personal Communications. doi:10.1007/s11277-009-9830-0.
Hwang T., Yang C., Wu G., Li S., Li Y. (2009) OFDM and its wireless applications: A survey. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 58(4): 1673–1694
Wang, Y., Cao, Y., Li, X., & Yang, S. (2009). A novel transmission scheme for irregular LDPC coded OFDM system. ICIEA 2009, pp. 1351–1355
Yang, C., & Ku, M. (2008). LDPC coded OFDM modulation for high spectral efficiency transmission. ECCSC 2008, pp. 280–284.
Park S. Y., Kim Y. G., Kang C. G. (2004) Iterative receiver for joint detection and channel estimation in OFDM systems under mobile radio channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 53(2): 450–460
Niu, H., & Ritcey, J. A. (2003). Iterative channel estimation and decoding of pilot symbol assisted LDPC coded QAM over flat fading channels. In: Proceeding of 37th Asilomar Conference (Vol. 2, pp. 2265–2269).
Oh M. K., Kwon H. M., Park D. J., Lee Y. H. (2008) Iterative channel estimation and LDPC decoding with encoded pilots. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 57(1): 273–285
Tuchler M., Singer A. C., Koetter R. (2003) Minimum mean squared error equalization using a priori information. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 50(3): 673–683
Lipschutz, S. (1991) Schaum’s outline of theory and problems of linear algebra (2nd ed. pp. 44–45). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Brigham E. O. (2002) The fast fourier transform. Prentice-Hall, New York
Ptzold M. (2002) Mobile fading channels. Wiley, Chichester, UK
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, W., Xiang, H. Low-Complexity Channel Estimation Using Short-Point FFT/IFFT for an Iterative Receiver in an LDPC-Coded OFDM System. Wireless Pers Commun 64, 739–747 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-010-0216-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-010-0216-0