Abstract
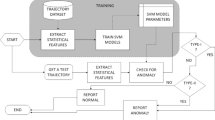
Smart spaces represent an emerging new paradigm that encompasses diverse active research areas such as ubiquitous, grid and cloud computing. Hence, there are a wide variety of interesting issues and applications for smart spaces, and surveillance is one issue that has long received much attention. In many cases, human motion is one of the most important clues used in assessing a situation for surveillance purposes. In this paper, we propose a new human abnormality detection scheme for surveillance purposes. More specifically, we first present a motion sequence matching algorithm called Dynamic View Warping to represent specific motion characteristics. Secondly, we propose a matching speed-up technique called Dynamic Group Warping that establishes boundaries in Dynamic View Warping. Thirdly, we propose an indexing scheme for motion sequences and present K-NN search algorithm to efficiently and effectively find similar motion sequences. Our extensive experiments show that our proposed methods achieve outstanding performance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shen S., Tong M., Deng H., Liu Y., Wu X., Wakabayashi K., Koike H. (2008) Model based human motion tracking using probability evolutionary algorithm. Pattern Recognition Letters 29(13): 1877–1886
Balan, A. O., & Black, M. J. (2006). An adaptive appearance model approach for model based articulated objecttracking. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 758–765).
Yamato, J., Ohya, J., & Ishii, K. (1992). Recognizing human action in time-sequential images using hidden markov models. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. 379–385).
Paragios N., Deriche R. (2000) Geodesic active contours and level sets for the detection and tracking of moving objects. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Inelligence 22(7): 266–280
Wren C., Azarbayejani A., Darrell T., Pentland A. (1997) Pfinder: Real-time tracking of the human body. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Inelligence 19(7): 780–785
Hogg D. (1983) Model-based vision: A program to see a walking person. Image and Vision Computing 1(1): 5–20
Zhao, T., & Nevatia, R. (2003). Bayesian human segmentation in crowded situations. In IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (pp. II459–II466).
Breit H., Rigoll G. (2003) A flexible multimodal object tracking system. IEEE Conference on Image Processing 3: 133–136
Viola, P., Jones, M. J., & Snow, D. (2003). Detecting pedestrians using patterns of motion and appearance. In IEEE conference on computer vision (pp. 734–741).
Kasai, D., Aizawa, K., & Yamasaki, T. (2009). Retrieval of time-varying mesh and motion capture data using 2D video queries based on silhouette shape descriptors. In IEEE conference on multimedia and expo (pp. 854–857).
Yi, B., Jagadish, H., & Faloutsos, C. (1998). Efficient retrieval of similar time sequences under time warping. In International conference on data engineering (pp. 23–27).
Schuldt, C., Laptev, I., & Caputo, B. (2004). Recognizing human actions: A local svm approach. In International conference on pattern recognition (pp. 32–36).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tak, YS., Rho, S. & Hwang, E. Motion Sequence-Based Human Abnormality Detection Scheme for Smart Spaces. Wireless Pers Commun 60, 507–519 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-011-0305-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-011-0305-8