Abstract
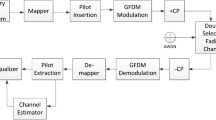
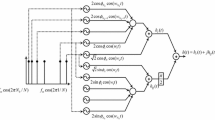
Mobility-induced Doppler spread and multipath propagation introduce the time- and frequency-selectivity (doubly selectivity) in fading channels. Based on the complex exponential basis expansion model (BEM) to approximate the doubly selective channel (DSC), a low-complexity channel estimation scheme for block transmission systems over DSC are developed in this paper. Using the developed scheme, the long data block is divided into a few short data subblocks in terms of the maximum normalized Doppler frequency and block length, and each subblock is performed to respective channel estimation. Thus the total calculation complexity is effectively decreased because the number of the BEM channel coefficients to estimate is greatly reduced for each sub-block. Moreover, by utilizing these channel estimation values to refit the true channel, we can obtain better channel estimation. Besides, the normalized mean square error (NMSE) expressions for the developed scheme and the existing scheme are derived in detail, respectively. Compared to the existing scheme, the proposed scheme has lower calculation complexity and superior performance. The simulation results verify the effectiveness of the developed scheme, and the theory values of the derived NMSE accord with corresponding simulation values.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giannakis G. B., Tepedelenlioglu C. (1998) Basis expansion models and diversity techniques for blind identification and equalization for time-varying channels. Proceedings of IEEE 86(10): 1969–1986
Ma X., Giannakis G. B. (2003) Maximum-diversity transmissions over doubly-selective wireless channels. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 49(7): 1823–1840
Wang Z., Ma X., Giannakis G. B. (2004) OFDM or single-carrier block transmissions?. IEEE Transactions on Communications 52(3): 380–394
Ann, K., Teo, D., & Ohno S. (2005). Optimal MMSE finite parameter model for doubly-selective channels. In Proceedings of IEEE global telecommunications conference (pp. 3503–3507). St. Louis, Missouri.
Rousseaux O., Leus G., Moonen M. (2006) Estimation and equalization of doubly selective channels using known symbol padding. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 54(3): 979–990
Zheng Y. R., Xiao C. (2002) Improved models for the generation of multiple uncorrelated Rayleigh fading waveforms. IEEE Communications Letters 6(6): 256–258
Barbarossa S., Scaglione A., Giannakis G. B. (2002) Performance analysis of a deterministic channel estimator for block transmission systems with null guard intervals. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 50(3): 684–695
Zhu Q., Liu Z. (2006) Optimal pilot superimposition for zero-padded block transmissions. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 5(8): 2194–2201
Barhumi I., Moonen M. (2009) MLSE and MAP equalization for transmission over doubly selective channels. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 58(8): 4120–4128
Hrycak T., Das S., Matz G., Feichtinger H. G. (2010) Low complexity equalization for doubly selective channels modeled by a basis expansion. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 58(11): 5706–5719
Dong M., Tong L., Sadler B. M. (2004) Optimal insertion of pilot symbols for transmissions over time-varying flat-fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 52(5): 1403–1418
Ma X., Giannakis G. B., Ohno S. (2003) Optimal training for block transmissions over doubly selective wireless channels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 51(5): 1351–1366
Zemen T., Mecklenbrauker C. F. (2005) Time-variant channel estimation using discrete prolate spheroidal sequences. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 53(9): 3597–3607
Zhang, Q. T., Zhao, X. Y., Zeng, Y. X., & Song, S. H. (2006). Efficient estimation of fast fading OFDM channels. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on communications (pp. 4601–4605). Istanbul, Turkey.
Kannu A. P., Schniter P. (2008) “Design and analysis of MMSE pilot-aided cyclic-prefixed block transmissions for doubly selective channels”. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 56(3): 1148–1160
Tugnait J. K., He S. (2007) Doubly-selective channel estimation using data-dependent superimposed training and exponential basis models. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 6(11): 3877–3883
Leus, G. (2004). On the estimation of rapidly time-varying channels. In: Proceedings of 2004 European signal processing conference (pp. 2227–2230). Vienna, Austria.
Qu F., Yang L. (2010) On the estimation of doubly-selective fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 9(4): 1261–1265
Whitworth T., Ghogho M., McLernon D. (2009) Optimized training and basis expansion model parameters for doubly-selective channel estimation. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 8(3): 1490–1498
Rabbi M. F., Hou S.-W., Ko C. C. (2010) High mobility orthogonal frequency division multiple access channel estimation using basis expansion model. IET Communications 4(3): 353–367
Ohon S., Giannakis G. B. (2004) Capacity maximizing pilots and precoders for wireless OFDM over rapidly fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 50(9): 2138–2145
Choi Y.-S., Voltz P. J., Cassara F. A. (2001) On channel estimation and detection for multicarrier signals in fast and selective Rayleigh fading channel. IEEE Transactions on Communications 49(8): 1375–1387
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, X., Leung, S.H. & Yin, X. Low-Complexity Channel Estimation for Wireless Block Transmission Systems in Time-and Frequency-Selective Rayleigh Fading Channels. Wireless Pers Commun 67, 367–385 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-011-0388-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-011-0388-2