Abstract
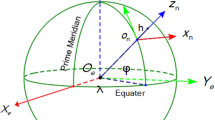
In this paper, the Doppler shift due to satellite vehicle motion in Global Positioning System (GPS) is investigated via a computational geometric analysis for a stationary GPS receiver, which resides on the surface of the earth. For an in-plane stationary receiver, the Doppler shift is derived as a function of the satellite vehicle’s central angle. For an off-plane stationary receiver, the visible region is calculated as a function of the elevation angle and the Doppler shift is derived as a function of the central angle and of the elevation angle. Also, the difference between the Doppler shift corresponding to an off-plane stationary receiver and the Doppler shift corresponding to an in-plane stationary receiver is calculated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Misra P. (2006) Global positioning system: Signals, measurements, and performance (2nd ed.). Ganga-Jamuna Press, Lincoln, MA
Yu K., Ian S., Guo Y. (2009) Ground-based wireless positioning. Wiley-IEEE Press, West Sussex
Wang D. (2011) Wireless location: Raning, positioning and sytstems using multi-carrier transmission. LAMBERT Academic Publishing, Germany
Zhao G., Wang D., Fattouche M. (2011) Time sum of arrival based BLUE for mobile target positioning. Advanced Scienced Letters 4(1): 165–167
Wang D., Fattouche M. (2010) OFDM transmission for time-based range estimation. IEEE Signal Processing Letters 17(6): 571–574
Wang D., Fattouche M. (2010) Multipath mitigation for LOS TBRE using NDB OFDM transmission and phase correlation. IET Electronics Letters 46(21): 1467–1468
Zhao, G., Wang, D., Fattouche, M., & Jin, M. (2011). Novel wireless positioning system for OFDM-based cellular networks. IEEE Systems Journal (accepted).
Dai L., Wang Z., Wang J., Yang Z. (2010) Positioning with OFDM signals for the next-generation GNSS. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics 56(2): 374–379
Leick A. (2004) GPS satellite surveying (3rd ed.). Wiley, Hoboken, NJ
WIKIPEDIA: GPS signals. (2011). http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPS-signals.
GPS NAVSTAR. (1995). Global positioning system standard positioning service signal specification. http://www.navcen.uscg.gov/pubs/gps/sigspec/gpssps1.pdf.
Manadhar, D., Suh, Y., & Shibasak, R. (2004) GPS signal acquisition and tracking—an approach towards development of software-based GPS receiver. Technical report of IEICE ITS 2004-16.
Hyun, C. S., Hyun, K. J., & Shin, C. S., et al. (2008). Acquisition and tracking schemes for a GPS L5 receiver. In Proceedings of international conference of control, automation and systems (pp. 2214–2217).
Bao J., Tsui Y. (2005) Fundamentals of global positioning system receivers: A software approach (2nd ed.). Willey, London
Borre K., Akos D. M., Bertelsen N., Rinder P., Jensen S. H. (2007) A software-defined GPS and Galileo receiver. Birkhauser, Boston
Normark, P.-L., & Stahlberg, C., (2005). Hybrid GPS/Galileo real time software receiver. In Proceedings of ION GNSS (pp. 1–8).
Ando, H. (1993). GPS Satellite signal tracking system for GPS receivers. US Patent 5177490.
He S., Doroslovacki M., Guo Z., Zhang Y. (2003) Attitude rate estimation by GPS Doppler signal processing. Journal of Electronics 20: 13–19
Wolf, M. (1991). Receiver for Bandspread signals, particularly GPS receiver. US Patent 5016257.
Featherstone S. (2004) Outdoor guide to using your GPS. Creative Publishing, Minneapolis
El-Rabbany A. (2007) Introduction to GPS: The global positioning system. Artech House, Norwood, MA
Sweet R. J. (2003) GPS for mariners. McGraw-Hill, New York
Bossler, J. D., Jensen, J. R., McMaster, R. B., & Rizos, C. (2002). Manual of geospatial science and technology. (pp. 96–96). Boa Raton: CRC Press
Kaplan E. D., Hegarty C. J. (2006) Understanding GPS: Principles and applications (2nd ed.). Artech House, London
Wang, D., Leung, H., Fattouche, M., & Ghannouchi, F. M. (2011). Efficient spectrum allocation and TOA-based localization in cognitive networks. Wireless Personal Communications, Springer. doi:10.1007/s11277-011-0365-9.
Zhao, G., Wang, D., Fattouche, M., & Jin, M. (2011). A novel OFDM-based wireless positioning protocol for cellular networks. ICIC Express Letters, 5(4B), 1207–1212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Fattouche, M. & Ghannouchi, F. Geometry-Based Doppler Analysis for GPS Receivers. Wireless Pers Commun 68, 1–13 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-011-0435-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-011-0435-z