Abstract
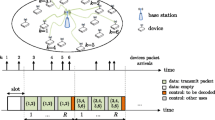
Framed Slotted Aloha (FSA) protocols are widely used in various communication systems. This paper investigates the performance of FSA systems that employ diversity transmission (DT) techniques over erasable wireless channels. Two DT schemes, DT-SWIR and DT-SWOR, differentiated by the underlying channel sampling procedures, i.e., sampling with/without replacement (SWIR/SWOR), are proposed. Modified versions, MDT-SWIR and MDT-SWOR, in which new and backlogged users use different diversity factors are also presented. To further exploit the advantages of using DT, we introduce a new PMDT-SWIR scheme in which the transmitting power of a packet can be varied. Using a probabilistic retransmission model, we develop exact combinatorial analyses to evaluate the throughput and activity factor. Characteristics of all schemes are comprehensively studied through numerical examples. For a dynamically controlled system, the optimal retransmission probabilities that result in maximal throughput for the MDT-SWIR, MDT-SWOR, and PMDT-SWIR are determined. All mathematical analyses are validated via computer simulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roberts L. (1975) ALOHA packet system with and without slot and capture. Computer Communication Review 5(2): 28–42
Carleial A., Hellman M. (1975) Bistable behavior of ALOHA-type systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications 23(4): 401–410
Abramson N. (1977) The throughput of packet broadcasting channels. IEEE Transactions on Communications 25(1): 117–128
Wang D., Comaniciu C., Tureli U. (2007) Cooperation and fairness for slotted Aloha. Wireless Personal Communications 43(5): 13–27
Yu Y., Cai X., Giannakis G. (2006) On the instability of slotted aloha with capture. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 5(2): 257–261
Altman, E., Barman, D., Benslimane, A., & Azouzi, R. (2005). Slotted Aloha with priorities and random power. InLecture notes in computer science (Vol. 3462, pp. 610–622).
Pahlavan K., Levesque A. H. (1995) Wireless information networks. Wiley, New York
Abramson N. (1993) Multiple access communication: Foundations for emerging technologies. IEEE Press, New York
Tobagi F. A., Binder R., Leiner B. (1984) Packet radio and satellite networks. IEEE Communications Magazine 22(11): 24–40
Brand A., Aghvami H. (2002) Multiple access protocols for mobile communications: GPRS, UMTS and beyond. Wiley, New York
Namislo C. (1989) Analysis of mobile radio slotted Aloha networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications 2(4): 583–588
Fakhouri S., Yongacoglu A. (1992) Performance evaluation of multiple access techniques in land mobile satellite networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 41(3): 226–230
Klair D., Chin K. W., Raad R. (2009) On the energy consumption of Pure and Slotted Aloha based RFID anti-collision protocols. Computer Communications 32(1): 961–973
Chung, I.-H., & Tsai, C.-A. (1994). Performance analysis of framed aloha systems with diversity transmission and erasure. In Proceedings of IEEE global telecommunications conference (GLOBECOM’94) (pp. 176–180). San Francisco.
Schoute F. C. (1983) Dynamic frame length ALOHA. IEEE Transactions on Communications 31(4): 565–568
Wieselthier J. E., Ephremides A., Michaels L. A. (1989) An exact analysis and performance evaluation of framed ALOHA with capture. IEEE Transactions on Communications 37(2): 125–137
Ma X., Refai H. H. (2009) Analysis of sliding frame R-ALOHA protocol for real-time distributed wireless networks. Wireless Networks 15(8): 1102–1112
Lam S. S. (1980) Packet broadcast networks—a performance analysis of the R-ALOHA protocol. IEEE Transactions on Computers 29(7): 596–603
Chung I.-H., Rappaport S. S. (1992) Diversity reservation ALOHA. International Journal of Satellite Communications 10(2): 47–60
Ren, W., Liu, E., Ward, J., Hodgart, S., & Sweeting, M. (2005). A control-centralized framed-Aloha with capture for LEO satellite communications. In Proceedings of second IFIP international conference on wireless and optical communications networks (pp. 1–5). Dubai.
Okada, H., Nakanishi, Y., & Igarashi, Y. (1978). Analysis of framed Aloha channel in satellite packet switching networks. In Proceedings of international conference on computer communications (pp. 617–622).
Goodman D. J., Valenzuela R. A., Gayliard K. T., Ramamurthi B. (1989) Packet reservation multiple access for local wireless communication. IEEE Transactions on Communications 37(8): 885–890
Benelli G., Cau G. R., Radaelli A. (1994) A performance evaluation of slotted Aloha multiple access algorithms with fixed and variable frames for radiomobile networks. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 43(2): 181–193
Ma X. (2007) Transient solution of sliding frame R-Aloha for real-time Ad Hoc wireless networks in a fading environment. IEEE Communications Letters 11(4): 354–356
Poupyrev, P., Davis, P., Miroyuki, H., & Aoyama, T. (2006). A media access protocol for proactive information discovery in ubiquitous networks. In Proceedings of IEEE wireless and mobile computing, networking and communications (WiMob’2006) (pp. 276–283). Montréal.
EPCglobal (2008). EPC radio-frequency identity protocols class-1 generation-2 UHF RFID protocol for communications at 860–960 MHz.
Floerkemeier, C., & Wille, M. (2006). Comparison of transmission schemes for framed Aloha based RFID protocols. In Proceedings of international symposium on applications and the internet workshops (pp. 1–4). Phoenix.
Peng, Q., Zhang, M., & Wu, W. (2007). Variant enhanced dynamic frame slotted Aloha algorithm for fast object identification in RFID system. In Proceedings of IEEE international workshop on anti-counterfeiting, security, identification (pp. 88–91). Xiamen.
Zhen B., Kobayashi M., Shimizu M. (2005) Framed Aloha for multiple RFID objects identification. IEICE Transactions on Communications E88-B(3): 991–999
Park J., Chung M. Y., Lee T. J. (2007) Identification of RFID tags in framed-slotted ALOHA with robust estimation and binary selection. IEEE Communications Letters 11(5): 452–454
Floerkemeier, C. (2006). Transmission control scheme for fast RFID object identification. In Proceedings of fourth annual IEEE international conference on pervasive computing and communications (PerCom 2006) (pp. 1–6). Pisa.
Lee, S. R., & Lee, C. W. (2006). An enhanced dynamic framed slotted Aloha anti-collision algorithm. In Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 4097, pp. 403–412).
Huang, X., & Le, S. (2007). Efficient dynamic framed slotted Aloha for RFID passive tags. In Proceedings of the 9th international conference on advanced communication technology (ICACT) (pp. 94–97). Phoenix Park.
Klair, D. K., Chin, K. W., & Raad, R. (2007) On the suitability of framed slotted Aloha based RFID anti-collision protocols for use in RFID-enhanced WSNs. In Proceedings of 17th international conference on computer communications and networks (ICCCN 2007) (pp. 583–590). Honolulu.
Wu H., Zeng Y. (2010) Bayesian tag estimate and optimal frame length for anti-collision aloha RFID systems. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 7(4): 963–969
Chen W. T. (2009) An accurate tag estimate method for improving the performance of an RFID anticollision algorithm based on dynamic frame length Aloha. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 6(1): 9–15
Bueno-Delgado, M. V., Vales-Alonso, J., & Gonzalez-Castano, F. J. (2009). Analysis of DFSA anticollision protocols in passive RFID environments. In Proceedings of 35th annual conference of IEEE industrial electronics (pp. 2610–2617). Porto.
Prodanoff Z. G. (2010) Optimal frame size analysis for framed slotted aloha based RFID networks. Computer Communications 33(5): 648–653
Yoon W. J., Chung S. H., Lee S. J. (2008) Implementation and performance evaluation of an active RFID system for fast tag collection. Computer Communications 31(17): 4107–4116
Cho, H., Lee, W., & Baek, Y. (2007). LDFSA: A learning-based dynamic framed slotted Aloha for collision arbitration in active RFID systems. In Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 4459, pp. 655–665)
Shin J. D., Yeo, S. S., Kim, T. H., & Kim, S. K. (2007). Hybrid tag anti-collision algorithms in RFID systems. In Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 4490, pp. 693–700).
Eom J. B., Lee T. J. (2010) Accurate tag estimation for dynamic framed-slotted Aloha in RFID systems. IEEE Communications Letters 14(1): 60–62
Knerr B., Holzer M., Angerer C., Rupp M. (2010) Slot-wise maximum likelihood estimation of the tag population size in FSA protocols. IEEE Transactions on Communications 58(2): 578–585
Su W., Alchazidis N. V., Ha T. T. (2010) Multiple RFID tags access algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing 9(2): 74–187
Wasikon, S. M., & Deris, H. M. (2009). Hasten dynamic frame slotted Aloha algorithm for fast identification in RFID systems. In Lecture notes of the institute for computer sciences, social informatics and telecommunications engineering (Vol. 18, pp. 162–174).
Tong, Q., Zou, X., & Tong, H. (2009) Dynamic frame slotted Aloha algorithm based on Bayesian estimation in RFID systems. In Proceedings of IEEE world congress on computer science and information engineering (pp. 384–388). Los Angeles.
Onat, I., & Miri, A. (2009) Disel: A distance based slot selection protocol for framed slotted Aloha RFID systems. In Proceedings of IEEE wireless communications and networking conference (WCNC) (pp. 1–6). Budapest.
Yu, C., & Zhou, F. (2009) A new frame size adjusting method for framed slotted Aloha algorithm. In Proceedings of IEEE international conference on e-business (pp. 493–496). Athens.
Sarangan V., Devarapalli M. R., Randhakrishnan S. (2008) A framework for fast RFID tag reading in static and mobile environments. Computer Networks 52(5): 1058–1073
Shwartz A., Sidi M. (1989) Erasure, capture, and noise errors in controlled multiple-access networks. IEEE Transactions on Communications 37(11): 1228–1231
Zorzi M. (1998) Mobile radio slotted Aloha with capture, diversity and retransmission control in the presence of shadowing. Wireless Networks 4(5): 379–388
Kwon, Y. H., Oh, M. K., & Park, D. J. (2004) Throughput enhancements for short packets in the wireless packet network. In Proceedings of 7th international conference on signal processing (ICSP’04) (pp. 1833–1836). Beijing.
Kao B., Garciau-Molina H., Barbars D. (1994) Aggressive transmissions of short messages over redundant paths. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems 5(1): 102–109
Annamalai A., Bhargava V. K. (1998) Analysis and optimization of adaptive multicopy transmission ARQ protocols for time-varying channels. IEEE Transactions on Communications 46(10): 1356–1368
Annamalai A., Bhargava V. K. (2000) Simple and efficient techniques to implement a self-reconfigurable ARQ system in a slowly varying mobile radio environment. Wireless Personal Communications 13(1–2): 97–117
Willig A. (2005) Redundancy concepts to increase transmission reliability in wireless industrial LANs. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics 1(3): 173–182
de Moraes, R. M., Sadjadpour, H. R., & Garcia-Luna-Aceves, J. J. (2004) Throughput-delay analysis of mobile ad-hoc networks with a multi-copy relaying strategy. In Proceedings of first annual IEEE communications society conference on sensor and ad hoc communications and networks (IEEE SECON) (pp. 200–209). Santa Clara.
Shea J. M., Wong T. F., Wong W. H. (2007) Cooperative-diversity slotted Aloha. Wireless Networks 13(3): 361–369
Wang E. W., Yum T. S. (1994) The optimal multicopy aloha. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control 39(6): 1233–1236
Leung Y. W. (1995) Generalized multicopy Aloha. IEE Electronics Letters 31(2): 82–83
Feller W. (1968) An introduction to probability theory and its application. Wiley, New York
Chung, I.-H., & Yen, M.-C. (2006). Performance analysis of a framed ALOHA system with diversity frequency hopping. In Lecture notes in computer science (Vol. 4138, pp. 561–571).
Zhang X., Gao Q., Zhang J., Wang G. (2008) Impact of transmit power on throughput performance in wireless ad hoc networks with variable rate control. Computer Communications 31(15): 3638–3642
LaMaire R. Q., Krishna A., Zorzi M. (1998) On the randomization of transmitter power levels to increase throughput in multiple access radio systems. Wireless Networks 4(3): 263–277
del Angel G., Fine T. L. (2004) Optimal power and retransmission control policies for random access systems. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking 12(6): 1156–1166
Habaebi M. H., Ali M. B. (2001) Improving the performance of the FPBA algorithm using random transmitter power levels. IEE Proceedings-Communications 148(4): 212–216
Chung, I.-H. (1993). An exact performance analysis of framed-aloha protocols with diversity over noisy channels. Technical Report, NSC 82-0404-E-216-012. Taiwan, R.O.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, IH., Yen, MC. An Exact Combinatorial Analysis for the Performance Evaluation of Framed Slotted Aloha Systems with Diversity Transmission Over Erasable Wireless Channels. Wireless Pers Commun 69, 1689–1718 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0658-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0658-7