Abstract
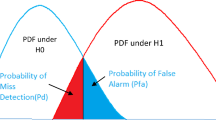
In this paper, we propose entropy-based spectrum sensing schemes to detect the existence of a primary user in Cognitive Radio (CR). To support this proposal, we have studied four types of entropies [Approximate Entropy (ApEn), Bispectral Entropy (BispEn), Sample Entropy (SamEn) and Rényi Entropy (RenyiEn)] and their applications for spectrum sensing. The reason for investigating these entropies comes from the fact that different types of entropies have different characteristics which make them more or less suitable for specific applications. Monte Carlo simulations were executed to find out how suitable these measures are for CR. Averaged value curves, boxplots and Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) tests document the performance of these types of entropies. The results show that BispEn outperformed the other three entropy measures. The ANOVA test shows that BispEn can sense modulated signals when the (SNR) is as low as −15 dB. This is at least a 5 dB improvement compared to the other entropies studied in this paper.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AWGN:
-
Additive White Gaussian Noise
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of Variance
- ApEn:
-
Approximate Entropy
- ASK:
-
Amplitude-shift keying
- BispEn:
-
Bispectral Entropy
- CR:
-
Cognitive Radio
- EEG:
-
Electroencephalography
- FCC:
-
Federal Communications Commission
- HRV:
-
Heart Rate Variability
- RenyiEn:
-
Rényi Entropy
- RRC:
-
Root-raised Cosine
- SamEn:
-
Sample Entropy
- SNR:
-
Signal to Noise Ratio
- OFDM:
-
Orthogonal Frequency-division Multiplexing
References
Haykin S. (2005) Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications. Selected Areas in Communications, IEEE Journal on 23(2): 201–220
Sridhara K., Chandra A., Tripathi P. (2008) Spectrum challenges and solutions by cognitive radio: An overview. Wireless Personal Communications 45: 281–291
Federal Communications Commission. (2005). Notice of proposed rule making and order: Facilitating opportunities for flexible, efficient, and reliable spectrum use employing cognitive radio technologies. ET Docket No. 03-108
Gavrilovska L., Atanasovski V. (2011) Spectrum sensing framework for cognitive radio networks. Wireless Personal Communications 59: 447–469
Budiarjo I., Lakshmanan M., Nikookar H. (2008) Cognitive radio dynamic access techniques. Wireless Personal Communications 45: 293–324
Yucek T., Arslan H. (2009) A survey of spectrum sensing algorithms for cognitive radio applications. Communications Surveys Tutorials IEEE 11(1): 116–130
Nagaraj S. V. (2009) Entropy-based spectrum sensing in cognitive radio. Signal Processing 89(2): 174–180
Zhang Y., Zhang Q., Wu S. (2010) Entropy-based robust spectrum sensing in cognitive radio. Communications, IET 4(4): 428–436
Zhang Y. L., Zhang Q. Y., Melodia T. (2010) A frequency-domain entropy-based detector for robust spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. Communications Letters, IEEE 14(6): 533–535
Proakis J. G., Salehi M. (2008) Digital communications, 5th edn. McGraw Hill, NY
Harris R. J. (1994) ANOVA: An analysis of variance primer. F E Peacock Pub, Itasca
The MathWorks Inc. (2007). MATLAB version 7.4.0 (R2007a).
Fishman G. S. (1995) Monte Carlo: Concepts, algorithms, and applications. Springer, New York
Pincus S. M. (1995) Approximate entropy (ApEn) as a complexity measure. Chaos 5(1): 110–117
Bein B. (2006) Entropy. Best Practice and Research Clinical Anaesthesiology 20(1): 101–109
Faust O., Acharya U.R., Molinari F., Chattopadhyay S., Tamura T. (2012) Linear and non-linear analysis of cardiac health in diabetic subjects. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control 7(3): 295–302
Richman J. S., Moorman J. R. (2000) Physiological time-series analysis using approximate entropy and sample entropy. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology 278(6): H2039–2049
Al-Angari H. M., Sahakian A. V. (2007) Use of sample entropy approach to study heart rate variability in obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Biomedical Engineering, IEEE Transactions on 54(10): 1900–1904
Rényi, A. (1960). On Measures Of Entropy And Information. In Proceedings of the 4th Berkeley symposium on mathematics, statistics and probability, (pp. 547–561).
Tabatabaei, T. S., Krishnan, S., & Anpalagan, A. (2010). SVM-based classification of digital modulation signals. Systems man and cybernetics (SMC), 2010 IEEE international conference on (pp. 277–280).
Nikias C. L., Raghuveer M. R. (1987) Bispectrum estimation: A digital signal processing framework. Proceedings of the IEEE 75(7): 869–891
Mohebbi M., Ghassemian H. (2012) Prediction of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation based on non-linear analysis and spectrum and bispectrum features of the heart rate variability signal. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine 105(1): 40–49
Bao M., Zheng C., Li X., Yang J., Tian J. (2009) Acoustical vehicle detection based on bispectral entropy. Signal Processing Letters, IEEE 16(5): 378–381
Tukey J. W. (1977) Exploratory data analysis. Addison-Wesley, New York
Fisher R. A. (1918) The correlation between relatives on the supposition of mendelian inheritance. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh 52: 399–433
Shannon, C. E. (1948). A mathematical theory of communication. Bell System Technical Journal, 27, 379–423; 623–656.
Renevey, P., & Drygajlo, A. (2001). Entropy based voice activity detection in very noisy conditions. In Proceedings of 7th European conference on speech communication and technology, EUROSPEECH’2001, (pp. 1887–1890).
Zhang Q. T. (1989) An entropy-based receiver for the detection of random signals and its application to radar. Signal Processing 18(4): 387–396
Rehm, C. R., Temple, M. A., Raines, R. A., & Mills, R. F. (2006). Entropy-based spectral processing on the ieee 802.11A OFDM waveform. In Military communications conference, 2006. MILCOM 2006. IEEE, (pp. 1–5).
Chen, X., & Nagaraj, S. (2008). Entropy based spectrum sensing in cognitive radio. In Wireless telecommunications symposium, 2008. WTS 2008, (pp. 57–61).
Gu, J., Liu, W. Jang, S. J., & Kim, J. M. (2010). Cross entropy based spectrum sensing. In Communication technology (ICCT), 2010 12th IEEE international conference on, (pp. 373–376).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, W., Ma, J. & Faust, O. A Comparative Study of Different Entropies for Spectrum Sensing Techniques. Wireless Pers Commun 69, 1719–1733 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0659-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0659-6