Abstract
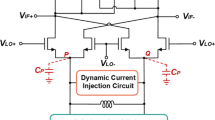
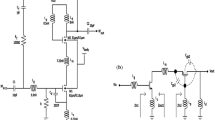
This paper presents a low voltage highly linear up-conversion mixer for 2.4 GHz IEEE 802.11b WLAN transmitter applications based on a Chartered 0.18 μm CMOS technology. In the proposed mixer, the double balanced Gilbert cell topology was adopted and the dual resistive current-reuse and current-bleeding techniques in both the driver and switching stages with a capacitive cross-coupling technique were used. The up-conversion mixer can convert a 10 MHz intermediate frequency signal to a 2.4 GHz radio frequency signal, with a local oscillator power of 0 dBm at 2.39 GHz. A comparison with conventional CMOS mixer shows that this up-conversion mixer has advantages of low voltage, low power consumption and high performance. The post-layout simulation results demonstrate that at 2.4 GHz, the circuit provides 7.1 dB of conversion gain and the input-referred third-order intercept point of 11.3 dBm, while drawing only 5 mA for the mixer core under a supply voltage of 1.2 V. The chip area including testing pads is only 0.65 × 0.75 mm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zolfaghari A., Razavi B. (2003) A low-power 2.4-GHz transmitter/receiver CMOS IC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 38(2): 176–183
Chehrazi S., Mirzaei A., Abidi A. A. (2010) Noise in current-commutating passive FET mixers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers 57(2): 332–344
Khatri H., Gudem P. S., Larson L. E. (2009) Distortion in current commutating passive CMOS downconversion mixers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 57(11): 2671–2681
Verma A., O K. K., Lin J. (2006) A low-power up-conversion CMOS mixer for 22-29-GHz ultra-wideband applications. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 54(8): 3295–3300
Gilbert B. (1968) A precise four-quadrant multiplier with subnanosecond response. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 3(4): 365–373
Vidojkovic V., van der Tang J., Leeuwenburgh A., van Roermund A. H. M. (2005) A low-voltage folded-switching mixer in 0.18-μm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 40(6): 1259–1264
Lin, C.-M., Wei, H.-J., Wang, Y.-T., & Wang, S.-C. (2006). A novel doubly-balanced folded mixer for low supply voltage and direct up-conversion system. In IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology ICSICT 2006 (pp. 1562–1564).
Park J., Lee C. H., Kim B. S., Laskar J. (2006) Design and analysis of low flicker-noise CMOS mixers for direct-conversion receivers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 54(12): 4372–4380
Giuseppina S., Giuseppe P. (2007) A 1.5-V 0.25-μm CMOS up-converter for 3–5 GHz low-power WPANs. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters 49(9): 2209–2212
Chen C. H., Chiang P. Y., Jou C. F. (2009) A low voltage mixer with improved noise figure. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters 19(2): 92–94
Zhuo W., Li X., Shekhar S., Embabi S. (2005) A capacitor cross-coupled common-gate low-noise amplifier. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs 52(12): 875–879
Xiaohua F., Heng Z., Sanchez-Sinencio E. (2008) A noise reduction and linearity improvement technique for a differential cascode LNA. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 43(3): 588–599
Tu, S. H.-L., & Chen, S. C.-H. (2008). A 5.26-GHz CMOS up-conversion mixer for IEEE 802.11a WLAN. In IEEE International Conference on Circuits and Systems for Communications, ICCSC 2008 (pp. 820–823).
Jehyung Y., Huijung K., Changjoon P., Jinho Y. (2008) A new RF CMOS Gilbert mixer with improved noise figure and linearity. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 56(3): 626–631
Kim J. H., An H. W., Yun T. Y. (2009) A low-noise WLAN mixer using switched biasing technique. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters 19(10): 650–652
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wan, Q., Wang, C. & Sun, J. Design of a Low Voltage Highly Linear 2.4 GHz Up-Conversion Mixer in 0.18 μm CMOS Technology. Wireless Pers Commun 70, 57–68 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0678-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0678-3