Abstract
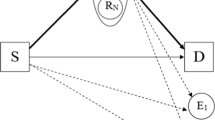
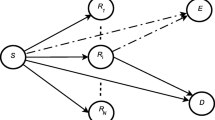
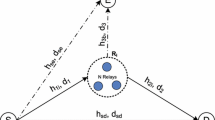
This work presents theoretical analysis on security performance for relay selections based on either statistical or instantaneous channel state information (CSI) of the eavesdropper (CSI-E) channels in a decode-and-forward relaying network. By considering security constraints, we have derived exact expressions for the average secrecy rate and the secrecy outage probability. Moreover, analytical expressions of the false secrecy probability are derived for the suboptimal relay selection based on statistical CSI-E, which are used as the constrained functions of new selection metrics. Furthermore, our work achieves a better tradeoff between the outage probability and the false secrecy probability. The accuracy of our performance analysis is verified by simulation results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wyner A. D. (1975) The wire-tap channel. Bell System Technical Journal 54: 1355–1367
Leung-Yan-Cheong S. K., Hellman M. E. (1978) The Gaussian wire-tap channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 24: 451–456
Csiszár I., Körner J. (1978) Broadcast channels with confidential messages. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 24: 339–348
Bloch M., Barros J., Rodrigues M. R. D., McLaughlin S. W. (2008) Wireless information-theoretic security. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 54: 2515–2534
Gopala P. K., Lai L., Gamal H. E. (2008) On the secrecy capacity of fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 54: 4687–4698
Goel S., Negi R. (2008) Guaranteeing secrecy using artificial noise. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 7: 2180–2189
Khisti A., Wornell G. W. (2010) Secure transmission with multiple antennas I: The MISOME wiretap channel. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 56: 3088–3104
Zhou X., McKay M. R. (2010) Secure transmission with artificial noise over fading channels: Achievable rate and optimal power allocation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology 59: 3831–3842
He F., Man H., Wang W. (2011) Maximal ratio diversity combining enhanced security. IEEE Communications Letters 15: 509–511
Sun, X., Wang, J., Xu, W., & Zhao, C. (2012). Performance of secure communications over correlated fading channels. IEEE Signal Signal Processing Letters (to appear).
Pabst R., Walke B. H., Schultz D. C. et al (2004) Relay-based deployment concepts for wireless and mobile broadband radio. IEEE Communications Magazine 42: 80–89
Xu W., Dong X., Lu W. (2011) Joint precoding optimization for multiuser multiantenna relaying downlinks using quadratic programming. IEEE Transactions on Communications 59: 1228–1235
Xu W., Dong X., Lu W. (2010) MIMO relaying broadcast channels with linear precoding and quantized channel state information feedback. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 58: 5233–5245
Xu, W., Dong, X., & Lu, W. (2010). Joint optimization for source and relay precoding under MIMO downlink channels. In Proceedings of IEEE ICC (pp. 1–5).
Oohama, Y. (2007). Capacity theorems for relay channels with confidential messages. In Proceedings of IEEE ISIT (pp. 926–930), Sept 2007.
Lai L., Gamal H. E. (2008) The relay-eavesdropper channel: Cooperation for secrecy. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 54: 4005–4019
He, X., & Yener, A. (2009). Two-hop secure communication using an untrusted relay. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networks.
Krikidis I., Thompson J. S., McLaughlin S. (2009) Relay selection for secure cooperative networks with jamming. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 8: 5003–5011
Krikidis I. (2010) Opportunistic relay selection for cooperative networks with secrecy constraints. IET Communications 4: 1787–1791
Dong L., Han Z., Petropulu A., Poor H. V. (2010) Improving wireless physical layer security via cooperating relays. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing 58: 1875–1888
Proakis J. G. (1995) Digital communications. McGraw-Hill, New York
Gradshteyn I. S., Ryzhik I. M. (2004) Table of integrals, series, and products (6th ed.). Elsevier, Singapore
Chau Y. A., Huang K. Y. (2008) Channel statistics and performance of cooperative selection diversity with dual-hop amplify-and-forward relay over rayleigh fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 7: 1779–1785
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, X., Xu, W., Jiang, M. et al. Opportunistic Selection for Decode-and-Forward Cooperative Networks with Secure Probabilistic Constraints. Wireless Pers Commun 70, 1633–1652 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0771-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0771-7