Abstract
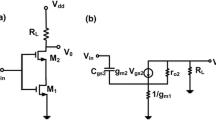
In this paper, a narrowband cascode Low Noise Amplifier (LNA) with shunt feedback is proposed. A typical inductively degenerated cascode LNA can be treated as a Common Source-Common Gate (CS-CG) two stage LNA. The series interstage inductance is connected between CS-CG stages to increase the power gain. An additional inductance which is connected at the gate of CG stage is used to cancel out the parasitic capacitance of CG stage therefore reduces the noise figure of CG stage. The shunt feedback is used to improve the stability and input impedance matching. This configuration provides better input matching, lower noise figure, low power consumption and good reverse isolation. The proposed LNA exhibits the gain of 13 dB, input return loss of −11 dB, noise figure of 2.2 dB and good reverse isolation of −42.8 dB at a frequency of 2.4GHz using TSMC 0.13 μm CMOS technology. It produces gain and noise figure better than conventional cascode LNA. The proposed LNA is biased in moderate inversion region for achieving sufficient gain with low power consumption of 1.5mW at a supply voltage of 1.5V.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kluge W., Poegel F., Roller H., Lange M., Ferchland T., Dathe L., Eggert D. (2006) A fully integrated 2.4-GHz IEEE 802.15.4-compliant transceiver for ZigBeeTM applications. IEEE Journal Of Solid-State Circuits 41(12): 2767–2775
Song T., Oh H. S., Yoon E., Hong S. (2007) A low-power 2.4-GHz current-reused receiver front- end and frequency source for wireless sensor network. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 42(5): 1012–1022
Allstot, D. J., Li, X., & Shekhar, S. (2004). Design considerations for CMOS low noise amplifiers. In Proceedings of IEEE radio frequency integrated circuits (RFIC) symposium (pp. 97–100).
Shaeffer D. K., Lee T. H. (1997) A 1.5-V, 1.5-GHz CMOS low noise amplifier. IEEE Journal Of Solid-State Circuits 32(5): 745–758
Vinu G., Dalmia S., Swaminathan M. (2004) Design of Integrated Low Noise Amplifiers (LNA) Using Embedded Passives in Organic Substrates. IEEE Transactions on Advanced Packaging 27(1): 79–89
Andreani P., Sjöland H. (2001) Noise optimization of an inductively degenerated CMOS low noise amplifier. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems—II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing 48(9): 835–841
Darabi H., Abidi A. A. (2000) A 4.5 mW 900-MHz CMOS receiver for wireless paging. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 35(8): 1085–1096
Zhuo W., Li X., Shekhar S., Embabi S. H. K., Pineda de Gyvez J., Allstot D. J., Sanchez-Sinencio E. (2005) A capacitor cross-coupled common-gate low-noise amplifier. IEEE Transactions On Circuits And Systems—II: Express Briefs 52(12): 875–879
Khurram M., Rezaul Hasan S. M. (2012) 3–5 GHz current-reuse g m boosted CG LNA for ultrawideband in 130 nm CMOS. IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration (Vlsi) Systems 20(3): 400–409
Chang C.-P., Chen J.-H., Wang Y.-H. (2009) A fully integrated 5 GHz low-voltage LNA using forward body bias technology. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters 19(3): 176–178
Li C.-M., Li M.-T., He K.-C., Tarng J.-H. (2010) A low-power self-forward-body-bias CMOS LNA for 3–6.5-GHz UWB receivers. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters 20(2): 100–102
Fu C.-T., Kuo C.-N., Taylor S. S. (2010) Low-noise amplifier design with dual reactive feedback for broadband simultaneous noise and impedance matching. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 58(4): 795–806
Weng R.-M., Liu C.-Y., Lin P.-C. (2010) A low-power full-band low-noise amplifier for ultra-wideband receivers. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 58(8): 2077–2083
Sasilathaa T., Raja J. (2010) A 1 V, 2.4 GHz low power CMOS common source LNA for WSN applications. International Journal of Electronics and Communication (AEU) 64: 940–946
Lo Y.-T., Kiang J.-F. (2011) Design of wideband LNAs using parallel-to-series resonant matching network between common-gate and common-source stages. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 59(9): 2285–2294
Wang S., Huang B.-Z. (2011) A high-gain CMOS LNA For 2.4/5.2-GHz WLAN applications. Progress In Electromagnetics Research C 21: 155–167
Chang P.-Y., Su S.-H., Hsu S. S. H., Cho W.-H., Jin J.-D. (2012) An ultra-low-power transformer-feedback 60 GHz low-noise amplifier in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters 22(4): 197–199
Chen K.-H., Liu S.-I. (2012) Inductorless wideband CMOS low-noise amplifiers using noise-canceling technique. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems—I: Regular Papers 59(2): 305–314
Madan A., McPartlin M. J., Masse C., Vaillancourt W., Cressler J. D. (2012) A 5 GHz 0.95 dB NF highly linear cascode floating-body LNA in 180 nm SOI CMOS technology. IEEE Microwave and Wireless Components Letters 22(4): 200–202
Belostotski L., Haslett J. W. (2006) Noise figure optimization of inductively degenerated CMOS LNAs with integrated gate inductors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems—I: Regular Papers 53(7): 1409–1422
Leroux P., Steyaert M. (2005) LNA-ESD co-design for fully integrated CMOS wireless receivers. Springer, Netherlands
Comer D. J., Comer D. T. (2004) Operation of analog MOS circuits in the weak or moderate inversion region. IEEE Transactions on Education 47(4): 430–435
Toole B., Plett C., Cloutier M. (2004) RF circuit implications of moderate inversion enhanced linear region in MOSFETs. IEEE Transactions on Circuits And Systems—I: Regular Papers 51(2): 319–328
Nguyen T.-K., Kim C.-H., Ihm G.-J., Yang M.-S., Lee S.-G. (2004) CMOS low-noise amplifier design optimization techniques. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques 52(5): 1433–1442
Samavati H., Rategh H. R., Lee T. H. (2000) A 5-GHz CMOS wireless LAN receiver front end. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 35(5): 765–772
Fan X., Zhang H., Sánchez-Sinencio E. (2008) A noise reduction and linearity improvement technique for a differential cascode LNA. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits 43(3): 588–599
Gonzalez G. (1997) Microwave transistor amplifiers: Analysis and design. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Lee T. H. (1998) The design of CMOS radio-frequency integrated circuits. Cambridge University Press, UK
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manjula, S., Selvathi, D. Design of Low Power 2.4GHz CMOS Cascode LNA with Reduced Noise Figure for WSN Applications. Wireless Pers Commun 70, 1965–1976 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0790-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0790-4