Abstract
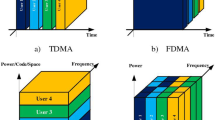
In orthogonal frequency division with multiple access (OFDMA) systems dynamic radio resource allocation improves overall performance by exploiting the multiuser diversity gains. A key issue in OFDMA is the allocation of the OFDM subcarriers and power among users sharing the channel. This paper proposes a new rate adaptive resource allocation scheme in the OFDMA downlink transmission system. Our proposed algorithm is based on the users’ sensitivity to the subcarrier allocation which means how frequency selective is the channel from the user’s perspective. As a result of frequency selectivity of the channel, different subchannels of the same user experience different levels of fade. However, how different they undergo fading could be measured by difference between maximum and minimum channel gain of that user. Our proposed method is based on difference between maximum channel gain and minimum channel gain for each user and uniform distribution of power among subcarriers. Simulation results show that the proposed algorithm achieves higher capacity over fixed TDMA method, and reported suboptimal methods with acceptable rate proportionality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews G., Ghosh A., Muhamed R. (2002) Fundamentals of WiMAX. Wiley, New York, pp 100–105
Cover T. M., Thomas J. A. (1991) Elements of information theory. Wiley, New York
Goldsmith A. J., Chua S.-G. (1997) Variable-rate variable-power MQAM for fading channels. IEEE Transactions on Communications 45: 1218–1230
Sadr S., Anpalagan A., Raahemifar K. (2009) Radio resource allocation algorithms for the downlink of multiuser OFDM communication systems. IEEE Communion Surveys & Tutorials 11(3): 92–106
Falahati, A., & Ardestani, M.-R. (2008). Adaptive subcarrier assignment and power distribution in multiuser OFDM systems with proportional data rate requirement. Iranian Journal of Electrical & Electronic Engineering, 4(1 & 2), 10–16.
Shen Z., Andrews J. G., Evans B. L. (2005) Adaptive resource allocation for multiuser OFDM with constrained fairness. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications 4(6): 2726–2737
Wong, I., Shen, Z., Evans, B., & Andrews, J. (2004). A low complexity algorithm for proportional resource allocation in OFDMA systems. In Proceedings, IEEE signal processing workshop (pp. 1–6), Austin, TX.
Hui, J., & Zhou, Y. (2006). Enhanced rate adaptive resource allocation scheme in downlink OFDM system. In IEEE 63rd vehicular technology conference.
Chow P. S., Cioffi J. M. (1992) Bandwidth optimization for high speed data transmission over channels with severe intersymbol interference. Proceedings of the IEEE Globecom 1: 59–63
Rhee, W., & Cioffi, J. M. (2000). Increase in capacity of multiuser OFDM system using dynamic subchannel allocation. In Proceedings of the IEEE international vehicular technology conference (Vol. 2, pp. 1085–1089).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashourian, M., Salimian, R. & Nasab, H.M. A Low Complexity Resource Allocation Method for OFDMA System Based on Channel Gain. Wireless Pers Commun 71, 519–529 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0826-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-012-0826-9