Abstract
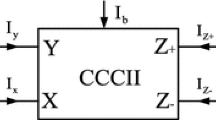
The paper presents a new linearized, of high performance, fully differential transconductor, based on class AB second generation current conveyor (CCII) in CMOS technology. The proposed circuit is composed by two positive CCII cells connected in series and a common mode feedback loop. Unlike other CMOS circuits on the basis of CCII reported in the literature, the proposed transconductor cell allows to obtain a higher transconductance value, an improved linearity and operates at high frequency for a 3.3 V supply voltage. As an application, the new transconductor cell in CMOS technology is used for designing a 4th order differential \(\hbox {G}_\mathrm{m}\)-C low-pass filters in different approximations (Butterworth and Chebyshev) operating up to 300 MHz cut-off frequency. The simulations performed in 130 nm CMOS process confirm the theoretical results.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Toumazou, C., Lidgey, F. J., & Haigh, D. G. (Eds.). (1990). Analogue IC design: The current-mode approach. London: Peter Peregrinus Ltd.
Laker, K. R., & Willy, M. C. (1994). Design of analog integrated circuits and systems. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Sedra, A., & Smith, K. C. (1970). A second-generation current conveyor and its applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuit Theory, 17, 132–134.
Kurashina, T., Ogawa, S., & Watanabe, K. (1998). A high performance class AB current conveyor. In IEEE international conference on electronics, circuits and systems (vol. 3, pp. 143–146). 7–10 September 1998.
Mahattanakul, J., Toumazou, C. & Akbar, A. A. (1997). DC Stable CCII-based instantaneous companding integrator. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems (pp. 821–824). Hong Kong, 9–12 June 1997.
Razavi, B. (2001). Design of analog CMOS integrated circuits. New York: McGraw-Hill Higher Education Inc.
Alzaher, H. A., Elwan, H., & Ismail, M. (2003). A CMOS fully balanced second-generation current conveyor. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 50(6), 278–287.
Fabre, A., & Alami, M. (1997). A precise macromodel for second generation current conveyors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 44(7), 639–642.
Koli, K., & Halonen, K. A. I. (2000). CMRR enhancement techniques for current-mode instrumentation amplifiers. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 47(5), 622–632.
Lindfors, S., Jussila, J., Halonen, K., & Siren, L. (1999). A 3-V continuous-time filter with on-chip tuning for IS-95. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 34(8), 1150–1154.
Acosta, L., Jiménez, M., Carvajal, R. G., Lopez-Martin, A. J., & Ramírez-Angulo, J. (2009). Highly linear tunable CMOS Gm-C low-pass filter. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Regular Papers, 56(10), 2145–2158.
Bozomitu, R. G., & Cehan, V. (2011). A new differential CCII transconductor with increased linearity in bipolar technology. In Proceedings of international symposium on signals, circuits and systems, ISSCS 2011, Article No. 5978692 (pp. 193–196) June 30–July 1.
Chang, Z., Haspeslagh, D., & Verfaille, J. (1997). A highly linear CMOS Gm-C bandpass filter with on-chip frequency tuning. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 32(3) 388–397.
Rijns, J. J. F. (1996). CMOS low-distortion high-frequency variable-gain amplifier. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 31(7), 1029–1034.
Fabre, A., & Alami, M. (1995). Universal current mode biquad implemented from two second generation current conveyors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-1 Fundamental Theory and Applications, 42(7), 383–385.
Fabre, A., Saaid, O., Wiest, F., & Boucheron, C. (1998). High-frequency High-Q BiCMOS current-mode bandpass filter and mobile communication application. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 33(4), 614–625.
Fabre, A., Dayoub, F., Duruisseau, L., & Kamoun, M. (1994). High input impedance insensitive second-order filters implemented from current conveyors. IEEE Transactions Circuits and Systems-I: Fundamental Theories and Applications, 41(12), 918–921.
Liu, S., Tsao, H., & Wu, J. (1991). CCII based continuous-time filters with reduced gain bandwidth sensitivity. IEE Proceedings-G, 138, 210–216.
Shujiang, Z., & Liping, G. (1994). A novel approach For designing continuous-time filters based on CCII. In IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems ISCAS’94 (Vol. 5, pp. 553–556).
Elwan, H. O., & Soliman, A. M. (1996). A novel CMOS current conveyor realization with an electronically tunable current mode filter suitable for VLSI. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 43(9), 663–670.
Karybakas, C. A., & Papazoglou, C. A. (1999). Low-sensitive CCII-based biquadratic filters offering electronic frequency shifting. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 46(4), 527–539.
Lopez-Martin, A. J., Ramirez-Angulo, J., & Carvajal, R. G. (2005). Design of high-performance tunable filters based on current conveyors. In Proceedings of the 2005 European conference on circuit theory and design (vol. 2, pp. II/103–106). 28 August–2 September.
Ben Salem, S., Masmoudi, D. S., Fakhfakh, M., Loulou, M., & Masmoudi, N. (2006). High frequency CCII based oscillators and multifunction filters. In International conference on design and test of integrated systems in nanoscale technology DTIS 2006 (pp. 141–144). 5–7 September 2006.
El Feki, N. B., Ben Samir S., Masmoudi, D. S. & Derbel, N. (2008). Optimization of a rail to rail low voltage CCII for active filter applications. In International conference on design and technology of integrated systems in nanoscale Era, DTIS 2008 (pp. 1–6). 25–27 March 2008.
Biolek, D. (1995). Novel signal flow graphs of current conveyors. In Proceedings of the 38th Midwest symposium: Circuits and systems (Vol. 2, pp. 1058–1061). 13–16 August 1995.
Lin, C.-L. Weng, R.-M., Lee, M.-H., & Kuo, T.-S. (1998). A new current-mode Universal filter using CCII and OTAs. In The 1998 IEEE Asia-Pacific Conference on Circuits and Systems, IEEE APCCAS 1998 (pp. 253–254). 24–27 November 1998.
Thyagarajan, S. V., Pavan, S., & Sankar, P. (2011). Active-RC filters using the Gm-assisted OTA-RC technique. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 46(7), 1522–1533.
Thyagarajan, S. V., Pavan, S., & Sankar, P. (2010). Low distortion active filters using the Gm-assisted OTA-RC technique. In Proceedings of the ESSCIRC (pp. 162–165). 14–16 September 2010.
Zhiqiang, G., Jinxiang, W., Fengchang, L., Mingyan, Y., & Zhongzhao, Zhang. (2009). Wideband reconfigurable CMOS Gm-C filter for wireless applications. In 16th IEEE international conference on electronics, circuits, and systems ICECS 2009 (pp. 179–182). 13–16 December 2009.
Hori, S., Maeda, T., Yano, H., Matsuno, N., Numata, K., Yoshida, N., et al. (2003). A widely tunable CMOS Gm-C filter with a negative source degeneration resistor transconductor. In Proceedings of the 29th European solid-state circuits conference ESSCIRC’03 (pp. 449–452). 16–18 September 2003.
Voorman, H., & Veenstra, H. (2000). Tunable high-frequency Gm-C filters. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 35(8), 1097–1108.
Kuhn, W. B., Nobbe, D., Dylan, K., & Orsborn, A. W. (2003). Dynamic range performance of on-chip RF bandpass filters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 50(10), 685–694.
Frey, D. R. (1996). Exponential state space filters: A generic current mode design strategy. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Fundamental Theory and Applications, 43(1), 34–42.
Koziel, S., & Szczepanski, S. (2002). Design of highly linear tunable CMOS OTA for continuous-time filters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II: Analog and, Digital Signal Processing, 49(2), 110–122.
Tsividis, Y. P., Czarnul, Z., & Fang, S. C. (1986). MOS transconductors and integrators with high linearity. Electronics Letters, 22, 245–246.
Jaikla, W., Silapan, P., Chanapromma, C., & Siripruchyanun, M. (2009). Practical implementation of CCTA based on commercial CCII and OTA. In International symposium on intelligent signal processing and communications systems, ISPACS 2008, pp. 1–4, 8–11 February 2009.
Geiger, R. L., & Sanchez-Sinencio, E. (1985). Active filter design using operational transconductance amplifiers: A tutorial. IEEE Circuits and Devices Magazine, 1, 20–32.
Tsividis, Y. P. (1994). Integrated continuous-time filter design - An overview. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, 29, 166–176.
Chang, C.-M. (1999). New multifunction OTA-C biquads. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II, 46, 820–823.
Chang, C.-M., & Pai, S.-K. (2000). Universal current-mode OTA-C biquad with the minimum components. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I, 47(8), 1235–1238.
Rezaei, F., & Azhari, S. J. (2010). Ultra low-voltage, rail-to-rail input/output stage operational transconductance amplifier (OTA) with high linearity and its application in a Gm-C filter. In The 11th international symposium on quality electronic design (ISQED) (pp. 231–236). 22–24 March 2010.
Bozomitu, R. G., & Cojan, N. (2011). A VLSI implementation of a new low voltage 5(th) order differential G(m)-C low-pass filter with auto-tuning loop in CMOS technology. In Advances in electrical and computer engineering ISSN 1582-7445 (Vol. 11, Issue 1, pp. 23–30).
Huelsman, L. P., & Allen, P. E. (1980). Introduction to the theory and design of active filters. New York: McGraw-Hill Inc.
Sedra, A. S., & Brackett, P. O. (1978). Filter theory and design: Active and passive. London: Pitman Publishing Limited.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bozomitu, R.G. A New Linearized CCII-Based Fully Differential CMOS Transconductor Used for \(\hbox {G}_\mathrm{m}\)-C Active Filters Implementation. Wireless Pers Commun 74, 615–637 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1310-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1310-x