Abstract
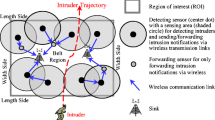
Intrusion detection is one of the most important applications of wireless sensor networks. When mobile objects are entering into the boundary of a sensor field or are moving cross the sensor field, they should be detected by the scattered sensor nodes before they pierce through the field of sensor (barrier coverage). In this paper, we propose an energy efficient scheduling method based on learning automata, in which each node is equipped with a learning automaton, which helps the node to select best node to guarantee barrier coverage, at any given time. To apply our method, we used coverage graph of deployed networks and learning automata of each node operates based on nodes that located in adjacency of current node. Our algorithm tries to select minimum number of required nodes to monitor barriers in deployed network. To investigate the efficiency of the proposed barrier coverage algorithm several computer simulation experiments are conducted. Numerical results show the superiority of the proposed method over the existing methods in term of the network lifetime and our proposed algorithm can operate very close to optimal method.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arora, A., Dutta, P., Bapat, S., Kulathumani, V., Zhang, H., Naik, V., et al. (2004). A line in the sand: A wireless sensor network for target detection, classification, and tracking. Computer Networks, 46(5), 605–634.
Kumar, S., Lai, T. H., & Balogh, J. (2004). On k-coverage in a mostly sleeping sensor network. In ACM MobiCom’04 (pp. 144–158).
Li, X.-Y., Wan, P.-J., & Frieder, O. (2003). Coverage in wireless ad-hoc sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Computers, 52(6), 753–763.
Meguerdichian, S., Koushanfar, F., Potkonjak, M., & Srivastava, M. (2001). Coverage problems in wireless ad-hoc sensor networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE InfoCom (InfoCom’01) (pp. 115–121). Anchorage, AK.
Liu, B., Dousse, O., Wang, J., & Saipulla, A. (2008). Strong barrier coverage of wireless sensor networks. In ACM MobiHoc (pp. 411–419).
Liu, C., & Cao, G. (2011). Spatial-temporal coverage optimization in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transaction on Mobile Computing, 10(4), 465–478.
Ma, H., & Al, E., (2012). Energy efficient k-barrier coverage in limited mobile wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications.
Kumar, S., Lai, T. H., & Arora, A. (2005). Barrier coverage with wireless sensors. In Proceedings of ACM MobiCom (pp. 284–298). Cologne, Germany.
Zhu, C., Zheng, C., Shu, L., & Han, G. (2012). A survey on coverage and connectivity issues in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 35, 619–632.
Gage, D. W. (1992). Command control for many-robot systems. Unmanned Systems Magazine, 22–24.
He, J., & Shi, H. (2012). Constructing sensor barriers with minimum cost in wireless sensor networks. Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, 71, 1654–1663.
Yang, G., & Qiao, D. Barrier information coverage with wireless sensors. (2009). In 28th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications, INFOCOM (pp. 918–926). Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Saipulla, A., Westphal, C., Liu, B., & Wang, J. (2010). Barrier coverage of line-based deployed wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Network, 127–135.
Silvestri, S. (2011). MobiBar: Barrier coverage with mobile sensors. In Proceedings of the the IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM) (pp. 1–6).
Chen, A., Kumar, S., & Lai, T. (2010). Local barrier coverage in wireless sensor networks. IEEE Transaction on Mobile Computing, 9(4), 491–504.
Chen, A., Kumar, S., & Lai, T. H. (2007). Designing localized algorithms for barrier coverage. In Proceedings of the 13th Annual ACM International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking, MobiCom’07, ACM (pp. 63–74). New York, NY, USA.
Ban, D., Yang, W., Jiang, J., Wen, J., & Dou, W. (2010). Energy-efficient algorithms for k-barrier coverage in mobile sensor networks. International Journal of Computers Communications and Control, 5, 616–624.
Ssu, K., Wang, W., Wu, F., & Wu, T. (2009). K-barrier coverage with a directional sensing model. In Proceedings of the International Journal on Smart Sensing and Intelligent Systems (pp. 75–83).
Thathachar, M. A. L., & Sastry, P. S. (2002). Varieties of learning automata: An overview. IEEE Transaction on Systems, Man and Cybernetics-Part B: Cybernetics, 32(6), 711–722.
Narendra, K. S., & Thathachar, M. A. L. (1989). Learning automata: An introduction. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice Hall.
Mostafaei, H., & Meybodi, M. R. (2013). Maximizing lifetime of target coverage in wireless sensor networks using learning automata. Wireless Personal Communications, 71(2), 1461–1477. doi:10.1007/s11277-012-0885-y.
Mostafaei, H., Meybodi, M. R., & Esnaashari, M. (2010). A learning automata based area coverage algorithm for wireless sensor networks. Journal of Electronic Science and Technology, 8(3), 200–205.
Mostafaei, H., Meybodi, M. R., & Esnaashari, M. (2010 ). EEMLA: Energy efficient monitoring of wireless sensor network with learning automata. In International conference on signal acquisition and processing (pp. 107–111). Bangalore, India.
Esnaashari, M., & Meybodi, M. R. (2010). A cellular learning automata-based deployment strategy for mobile wirelesssensor networks. Journal of Parallel and Distribted Computing, 71(7), 988–1001. doi:10.1016/j.jpdc.2010.10.015.
Heinzelman, W., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000 ). Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd Hawaii international conference on system sciences (pp. 1–10). Hawaii, USA.
Kumar, S., Lai, T. H., Posner, M. E., & Sinha, P. (2007). Optimal sleep-wakeup algorithms for barriers of wireless sensors. In Fourth International Conference on Broadband Communications, Networks, and Systems (IEEE BROADNETS) (pp. 327–336). Raleigh, NC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mostafaei, H., Meybodi, M.R. An Energy Efficient Barrier Coverage Algorithm for Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 77, 2099–2115 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1626-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1626-1