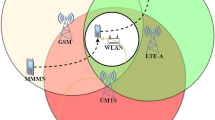
Abstract
Heterogeneous network selection is a popular topic with the rapid development of telecommunication technologies. Literatures employed different ways for solving the issue with drawbacks more or less especially neglecting the user preference and using much subjective configurations. This paper proposes a user preference scheme including realtime or non-realtime pursuit, money and battery consumption concern and non-specific requirement. For front four modes, a technique for order preference by similarity to ideal solution based method with vote which reduces the subjectiveness is introduced. Then, a function-less and totally unsubjective method called directional distance function based data envelopment analysis method faces the non-specific requirement. Several examples test these two methods and the results support them.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ai, X., Zhou, W., Xie, B., & Song, J. (2010). Network selection issue in heterogeneous wireless environment. IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), 18–21 April 2010, Sydney, NSW (pp. 1–6).
Bari, F., & Leung, V. (2007). Automated network selection in a heterogeneous wireless network environment. IEEE Network, 21(1), 34–40.
Chan, H., Fan, P., & Cao, Z. (2005). A utility-based network selection scheme for multiple services in heterogeneous networks. 2005 International Conference on Wireless Networks, Communications and Mobile Computing, Sheraton Maui Resort Maui, HI,2 (pp. 1175–1180).
Chan, P., Sheriff, R., Hu, Y., Conforto, P., & Tocci, C. (2001). Mobility management incorporating fuzzy logic for heterogeneous a IP environment. IEEE Communications Magazine, 39(12), 42–51.
Chen, Q.-B., Zhou, W.-G., Chai, R., & Tang, L. (2011). Game-theoretic approach for pricing strategy and network selection in heterogeneous wireless networks. IET Communications, 5(5), 676–682.
Chung, Y. H., Fare, R., & Grosskopf, S. (1997). Productivity and undesirable outputs: A directional distance function approach. Journal of Environmental Management, 51(3), 229–240.
Cordeiro, C., & Agrawal, D. P. (2006). Ad hoc sensor networks: Theory and applications. Singapore: World Scientific.
Fan, J., Zhang, S., & Zhou, W. (2012). Energy-friendly network selection in heterogeneous wireless networks. Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC Spring), Yokohama, 6–9 May 2012 (pp. 1–6).
Hwang, C. L., & Yoon, K. (1981). Multiple attribute decision making: Mehtods and applications. Berlin: Springer.
Lai, Y. J., & Hwang, C. L. (1994). Fuzzy multiple objective decision making: Methods and applications. Berlin: Springer.
Niyato, D., & Hossain, E. (2009). Dynamics of network selection in heterogeneous wireless networks: An evolutionary game approach. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 58(4), 2008–2017.
Ormond, O., Murphy, J., & Muntean, G. (2006). Utility-based intelligent network selection in beyond 3G systems. IEEE International Conference on Communications (ICC), Istanbul, Turkey,4, (pp. 1831–1836).
Paris, S., Martignon, F., Filippini, I., & Capone, A. (2012). A truthful auction for access point selection in heterogeneous mobile networks communications. ICC, 10–15 June, 2012, Ottawa, ON. (pp. 200–3205).
Pervaiz, H., Ni, Q. (2012). User preferences-adaptive dynamic network selection approach in cooperating wireless networks: A game theoretic perspective. The 11th IEEE TrustCom., 25–27 June, 2012, Liverpool, UK (pp. 1609–1616).
Ray, S. C. (2004). Data envelopment analysis: Theory and techniques for economics and operations research. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Saker, L., Jemaa, S. B., & Elayoubi, S. E. (April, 2009). Q-learning for joint access decision in heterogeneous networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communication and Networking Conference (WCNC), (pp.1–5), Budapest, Hungary.
Song, Q. Y., & Jamalipour, A. (June 2005). Network selection in an integrated wireless LAN and UMTS environment using mathematical modeling and computing techniques. IEEE Transaction on Wireless Communication, 12(3), 42–48.
Stevens-Navarro, E., Lin, Y., & Wong, V. W. S. (February 2008). An MDP-based vertical handoff decision algorithm for heterogeneous wireless networks. IEEE Transaction on Vehicular Technology, 57(2), 1243–1254.
Trestian, R., Ormond, O., & Muntean, G.-M. (2012). Game theory-based network selection: Solutions and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 14(4), 1212–1231.
Wang, Y., Zheng, L., Yuan, J., & Sun, W. (April, 2009). Median based network selection in heterogeneous wireless networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Wireless Communication and Networking Conference (WCNC) (pp.1–5), Budapest, Hungary.
Wang, Y., Zhang, P., Zhou, Y., Yuan, J., Liu, F., & Li, G. (2010). Handover management in enhanced MIH framework for heterogeneous wireless networks environment. Wireless Personal Communications, 52(3), 615–636.
Wang, L., & Kuo, G. (2013). Mathematical modeling for network selection in heterogeneous wireless networks: A tutorial. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 15(1), 271–292.
Zavadskas, E. K., Zakarevicius, A., & Antucheviciene, J. (2006). Evaluation of ranking accuracy in multi-criteria decisions. Informatica, 17(4), 601–618.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Chen, Z., Yang, L.T. et al. User Preference Heterogeneous Network Selection in Less Subjective Ways. Wireless Pers Commun 76, 813–828 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1627-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1627-0