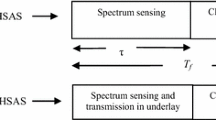
Abstract
Cognitive radios are promising solutions to the problem of overcrowded spectrum. The cognitive capability is the key technology that enables the secondary users to use licensed spectrum in a dynamic manner that the spectrum of the primary users are as unaffected as possible. But the metrics for composite cognitive capability are required in time in order to capture the temporal, spectral, and spatial variations (“spectrum holes”) simultaneously with cognitive signal strength under sophisticated cognitive radio environments. In this paper, in order to evaluate the spectrum awareness effectively, a novel analytical modeling of composite cognitive capability with an overlay sensing approach is proposed. A cognitive scenario with elliptically spatial variations is assumed, which consists of primary units and cognitive radio units (CRUs) with concurrent temporal and spectral scanning schemes. Moreover, a metric of spectrum holes ratio (SHR) is defined to evaluate the composite cognitive capability. Furthermore, CRUs can also detect transmission signals strength and “assist” receiving signal through a tone-assisted relaying signal to enhance system performance and reach lower symbol error probability with a specific tone-to-signal ratio above signal-to-noise ratio decision thresholds under a constant elliptic SHR locus.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ntia, U.S. frequency allocations. http://www.ntia.doc.gov/osmhome/allochrt.pdf.
Spectrum policy task force report. (2002, November). Federal communications commission, Tech. Rep. 02-155.
Mitola, J. III. & Maguire, G. Q. Jr. (1999). Cognitive radio: Making software radios more personal. IEEE Personal Communications, 6, 13–18.
Mitola, J., III. (2000, May 8). Cognitive radio: An integrated agent architecture for software defined radio, Ph. D. diss., Royal Institute of Technology, Sweden.
Haykin, S. (2005). Cognitive radio: Brain-empowered wireless communications. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 23(2), 201–220.
Akyildiz, F., Lee, W. Y., Vuran, M. C., & Mohanty, S. (2006). NeXt generation/dynamic spectrum access/cognitive radio wireless networks: A survey, computer network. www.elsevier.com/locate/comnet.
Srinivasa, S., & Jafar, S. A. (2007). The throughput potential of cognitive radio: A theoretical perspective. IEEE Communications Magazine, 45, 73–79.
Amanna, A., & Reed, J. H. (2010). Survey of cognitive radio architectures. Paper presented at the IEEE SoutheastCon 2010 (SoutheastCon) (pp. 292–297).
Wang, B., & Ray, K. J. R. (2011). Advances in cognitive radio networks: A survey. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 5(1), 5–23.
Fragkiadakis, A. G., Tragos, E. Z., & Askoxylakis, I. G. (2013). A survey on security threats and detection techniques in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 58, 428–445.
Zhao, Y., Mao, S., Neel, J. O., et al. (2009 April). Performance evaluation of cognitive radios: Metrics, utility functions, and methodology. In Proceedings of the IEEE, 97 (pp. 642–659).
Cordeiro, C., Challapali, K., Birru, D., et al. (2005, November 8–11). IEEE 802.22: The first worldwide wireless standard based on cognitive radios. In Paper presented at the First IEEE international symposium on new frontiers in dynamic spectrum access networks, DySPAN 2005 (pp. 328–337).
Cordeiro, C., Challapali, K., & Birru, D. (2006). IEEE 802.22: An introduction to the first wireless standard based on cognitive radios. Journal of Communications, 1(1), 328–337.
Leu, A. E., Mark, B. L., & McHenry, M. A. (2009, April). A framework for cognitive WiMAX with frequency agility. Proceedings of the IEEE, 97(4), 755–773.
Kim, H., & Shin, K. G. (2010). In-band spectrum sensing in IEEE 802.22 WRANs for incumbent protection. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 9, 1766–1779.
Burda, K. (2004). The performance of the follower jammer with a wideband scanning receiver. Journal of Electrical Engineering, 55, 36–38.
Liao, C. H., & Woo, T. K. (2012). Chapter 5: Adaptation from transmission security (TRANSEC) to cognitive radio communication. In C.-X. Wang, & J. Mitola III. (Eds.), Advances in cognitive radio system (pp. 81–104). http://www.intechopen.com.
Chen, H. (2010). Relay selection for cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio networks. In Paper presented at the 2010 international conference on communications and mobile computing (CMC) (vol. 2, pp. 188–192).
Ganesan, G., & Li, Y. (2007). Cooperative spectrum sensing in cognitive radio, part I: Two user networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 6, 2204–2213.
Huang, S., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., & Zhao, F. (2012). Energy-efficient cooperative spectrum sensing with amplify-and-forward relaying. IEEE Communications Letters, 16, 450–453.
Zou, Y., Yao, Y.-D., & Zheng, B. (2012). Cooperative relay techniques for cognitive radio systems: Spectrum sensing and secondary user transmissions. IEEE Communications Magazine, 50, 98–103.
Pei, Y., Liang, Y.-C., Teh, K. C., & Li, K. H. (2009). How much time is needed for wideband spectrum sensing? IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8, 5466–5471.
Fragkiadakis, A. G., Tragos, E. Z., & Askoxylakis, I. G. (2008). Distance- and traffic-aware channel assignment in cognitive radio networks. In Paper presented at the 5th annual IEEE communications society conference on sensor, mesh and ad hoc communications and networks, SECON ’08 (pp. 10–18).
Luo, L., & Roy, S. (2012). Modelling and analysis of detection time trade-offs for channel searching in cognitive radio networks. IET Communications, 6, 819–827.
Torrieri, D. (1985). Principles of secure communication systems (pp. 160–165). Artech House.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, CH., Woo, TK. A Novel Analytical Modeling of Composite Cognitive Capability with an Overlay Sensing Approach. Wireless Pers Commun 78, 831–849 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1786-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1786-z