Abstract
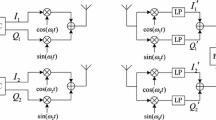
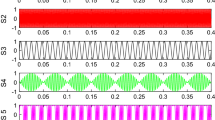
As an important factor in the fast fixed-point algorithm of independent component analysis (ICA), robustness has a significant influence on the separate performance of ICA. However, the traditional objective functions used in fast fixed-point algorithm of ICA will be invalid in separating the original signals when the outliers mix in signals. In this paper, we introduce a new robust objective function based on the Negentropy maximization. With second order approximation with Maclaurin expansion, the proposed function enables the estimation of individual independent components. In addition, it guarantees the separate performance of ICA that the original signals whether mix with outliers. Furthermore, combined with the proposed objective function, the fast fixed-point algorithm of ICA is reliable in the scenario of the signals mix with outliers. Simulation results show that the separate performance of proposed objection function is superior to the traditional objective functions as the outliers appear in the original signals.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breuer, L., Dammers, J., Roberts, T. P. L., & Shah, N. J. (2014). A constrained ICA approach for real-time cardiac artifact rejection in magnetoencephalography. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 61(2), 405–414.
Li, X.-L., & Adalı, T. (2013). Noncircular complex ICA by generalized householder reflections. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 61(24), 6423–6430.
Nafta, A., Johannisson, P., & Shtaif, M. (2013). Blind equalization in optical communications using independent component analysis. Journal of Lightwave Technology, 31(12), 2043–2049.
Ma, X., Zhang, H., Zhao, X., Yao, L., & Long, Z. (2013). Semi-blind independent component analysis of fMRI based on real-time fMRI system. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 21(3), 416–426.
Mehrabian, H., Chopra, R., & Martel, A. L. (2013). Calculation of intravascular signal in dynamic contrast enhanced-MRI using adaptive complex independent component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 32(4), 699–710.
Hyvärinen, A. (1999). Fast and robust fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 10(3), 626–634.
Hyvärinen, A., & Oja, E. (2000). Independent component analysis: Algorithms and applications. Neural Networks, 13(4–5), 411–430.
Hyvärinen, A., & OJA, E. (1997). A fast fixed-point algorithm for independent component analysis [J]. Neural Computation, 9(7), 1483–1492.
Hyvärinen, A., Karhunen, J., & Oja, E. (2001). independent component analysis. New York: Wiley.
Cook, D., Buja, A., & Cabrera, J. (1993). Projection pursuit indexes based on orthonormal function expansions. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2(3), 225–250.
Hyvärinen, A. (1998). New approximations of differential entropy for independent component analysis and projection pursuit. In Advances in neural information processing systems (Vol. 10, pp. 273–279). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Jones, M. C., & sibson, R. (1987). What is projection pursuit? Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series A, 150, 1–36.
Hyvärinen, A. (1999). Fast independent component analysis with noise data using Gaussian moments. In Proceedings of the international symposium on circuits and systems (pp. V57–V61).
Hyvärinen, A. (1999). Gaussian moments for noisy independent component analysis. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 6(6), 145–147.
Bingham, E., & Hyvärinen, A. (2000). A fast fixed-point algorithm for independent component analysis of complex valued signals. International Journal of Neural Systems, 10, 1–8.
Hyvärinen, A. (1999). Fast and robust fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 10(3), 626–634.
Hyvärinen, A. (1997). One unit contrast functions for independent component analysis: A statistical analysis. In Neural networks for signal processing VII (pp. 388–397), Amelia Island, FL.
Huber, P. J. (1981). Robust statistics. New York: Wiley.
Amari, S., Cichocki, A., & Yang, H. H. (1996). A new learning algorithm for blind signal separation. In Advances in neural information processing systems (pp. 757–763). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, P., Li, L. & Zhang, H. A New Robust Objective Function Based on Maximum Negentropy Approximation in Independent Component Analysis. Wireless Pers Commun 79, 877–890 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1892-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-1892-y