Abstract
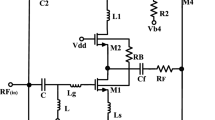
In this paper, a new complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) low-voltage low-power current-reuse up-conversion mixer using Chartered \(0.18\,\upmu \hbox {m}\) CMOS process for radio frequency transmitter applications is presented. A novel self-biasing current-reuse (SBCR) technique is adopted to achieve more ideal conversion gain (CG) and third-order intermodulation intercept point \((\hbox {IIP}_{3})\) in the transconductance stage with minimal additional power consumption, which perfects the mixer than conventional Gilbert mixer. As the new SBCR technique employed in the mixer, the post-layout simulation results demonstrate that the SBCR-mixer features about 13 dB CG with 0 dBm local oscillator (LO) power and port-to-port isolation better than 84 dB, while noise figure is 15.66 dB. The \(\hbox {IIP}_{3}\) and 1 dB compression point of the mixer are 7.78 dBm and \(-\)3.76 dBm at 1.41 mW power consumption from a 1 V supply voltage. The chip area is only \(0.70 \times \,0.72\,\hbox {mm}^{2}\) even including test pads.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kraimia, H., Taris, T., Begueret, J., & Deval, Y. (2011). A 2.4 GHz ultra-low Power current-reuse bleeding mixer with resistive feedback. 18th IEEE international conference on electronics, circuits and systems, Beirut, pp. 488–491.
Murad, S. A. Z., & Mohamad, S. M. (2012). Linearity improvement of 5.2-GHz CMOS up-conversion mixer for wireless applications. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 54, 923–925.
Murad, S. A. Z., Shahimin, M. M., Pokharel, R. K., Kanaya, H., & Yoshida, K. (2011). A fully integrated CMOS Up-conversion mixer with input active Balun for wireless applications. 2011 IEEE Regional symposium on micro and nanoelectronics (RSM), Kota Kinabalu, pp. 112–116.
Murad, S. A. Z., Ahmad, M. F., Mazalan, M., Shahimin, M. M., Rais, S. A. A., Norizan, M. N. (2011). A Design of 5.2 GHz CMOS Up-conversion Mixer with IF Input Active Balun. 2011 IEEE symposium on wireless technology and applications (ISWTA), Langkawi, pp. 1–4.
Fan, X., Zhu, C., Zhang, L. (2009). A 2.4 GHz RF CMOS up-conversion mixer for wireless sensor networks nodes. WCSP 2009. International conference on wireless communications & signal processing, Nanjing, pp. 1–5.
Tsai, T. M., & Lin, Y. S. (2012). 15.1 mW 60 GHz up-conversion mixer with 4.5 dB gain and 57.5 dB LO-RF isolation. Electronics Letters, 48, 844–845.
Sun, X., Huang, F., Tang, X., Zhao, D. (2012). A 1.8-2.6 GHz RF CMOS Up-conversion mixer for wideband applications. 2012 IEEE MTT-S international microwave workshop series on millimeter wave wireless technology and applications(IMWS), Nanjing, pp. 1–4.
Shi, L. X., Chen, C., Wu, J. H., & Zhang, M. (2012). A 1.5-V current mirror double-balanced mixer With 10-dBm IIP3 and 9.5-dB conversion gain. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II: Express Briefs, 59, 204–208.
Liang, K. H., & Chang, H. Y. (2011). 0.5-6GHz low-voltage low-power mixer using a modified cascode topology in 0.18 um CMOS technology. IET Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, 5, 167–174.
Parvizi, M., & Nabavi, A. (2009). Improved derivative superposition scheme for simultaneous second- and third-order distortion cancellation in LNAs. Electronics Letters, 45, 1323–1325.
Parvizi, M., & Nabavi, A. (2010). Low-power highly linear UWB CMOS mixer with simultaneous second- and third-order distortion cancellation. Microelectronics Journal, 41, 1–8.
He, S., & Saavedra, C. E. (2012). An ultra-low-voltage and low-power 2 subharmonic downconverter mixer. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 60, 311–317.
Karanicolas, A. N. (1996). A 2.7-V 900-MHz CMOS LNA and Mixer. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 31, 1939–1944.
Song, C., Lubecke, O. B., & Lo, I. (2013). 0.18 um CMOS wideband passive mixer. Microwave and Optical Technology Letters, 55, 23–27.
Le, V. H., Nguyen, H. N., Lee, I. Y., & Han, S. K. (2011). A passive mixer for a wideband TV tuner. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 58, 398–401.
Vidojkovic, V., van der Tang, J., Leeuwenburgh, A., & van Roermund, A. H. M. (2005). A low-voltage folded-switching mixer in \(0.18-\mu \)m CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 40, 1259–1264.
Krcmar, M., & Boeck, G. (2010). A broadband folded Gilbert cell CMOS mixer. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 64, 39–44.
Toole, B., Plett, C., & Cloutier, M. (2004). RF circuit implications of moderate inversion enhanced linear region in MOSFETs. IEEE Transactions on Circuitsand Systems I, 51(2), 319–327.
Amirabadi, A., Chehelcheraghi, M., & Kamarei, M. (2011). High IIP3 and low-noise CMOS mixer using non-linear feedback technique. Circuits Systems and Signal Processing, 30, 721–739.
Chen, J. D. (2011). A low-voltage high-linearity ultra-wideband down-conversion mixer in 0.18 um CMOS technology. Microelectronics Journal, 42, 113–126.
Laha, S., & Kaya, S. (2013). Bias optimization of 2.4Ghz double gate MOSFET RF mixer. Analog Integrated Circuits and Signal Processing, 77, 529–537.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, L., Wang, C. A Novel Low Voltage Low Power High Linearity Self-biasing Current-reuse Up-conversion Mixer. Wireless Pers Commun 80, 277–287 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-2008-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-014-2008-4