Abstract
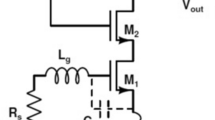
A low voltage 2.4 GHz CMOS power amplifier for wireless personal area network (WPAN) applications is presented in TSMC 0.13 \(\upmu \)m CMOS process. It consists of driver and power amplifier stages which are connected in current reuse structure. The driver amplifier has push pull inverter configuration. The power amplifier is the common source amplifier. These two stages are biased in class AB mode. For optimizing out-of-band emissions, the proposed power amplifier is linearized by RF predistortion technique. For efficient power amplifier, the design parameters are needed to be optimized using particle swarm optimization technique. The optimized power amplifier achieves 0 dBm output power, 34.06 % PAE, 18 dB power gain at 2.4 GHz frequency. It consumes 2.95 mW power at a supply voltage of 1.2 V.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soomro, A., & Cavalcanti, D. (2007). Opportunities and challenges in using WPAN and WLAN technologies in medical environments. IEEE Communications Magazine, 45(2), 114–122.
Zolfaghari, A., & Razavi, B. (2003). A low-power 2.4-GHz transmitter/receiver CMOS IC. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(2), 176–183.
Choi, P., Park, H. C., Kim, S., Park, S., Nam, I., Kim, T. W., et al. (2003). An experimental coin-size radio for extremely low-power WPAN (IEEE 802.15.4) application at 2.4 GHz. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 38(12), 2258–2268.
Lin, K. E., Weng, R. M., Hsiao, C. L., & Wei, H. C. (2004). A 1V 2.4 GHz CMOS power amplifier with integrated diode linearizer. In Proceedings of the IEEE Asia-Pacific conference on circuits and systems (pp. 109–111).
Ho, K. W., & Luong, H. C. (2003). A 1V CMOS power amplifier for bluetooth applications. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-II: Analog and Digital Signal Processing, 50(8), 445–449.
Chee, Y. H., Rabaey, J., & Niknejad, A. M. (2004). A Class A/B low power amplifier for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the international symposium on circuits and systems (ISCAS’ 04) (pp. 409–412).
Liu, G., King Liu, T. J., & Niknejad, A. M. (2006). A 1.2V, 2.4GHz fully integrated linear CMOS power amplifier with efficiency enhancement. In Proceedings of the IEEE custom intergrated circuits conference (CICC’ 06) (pp. 141–144).
Haldi, P., Chowdhury, D., Reynaert, P., Liu, G., & Niknejad, A. M. (2008). A 5.8 GHz 1 V linear power amplifier using a novel on-chip transformer power combiner in standard 90 nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 43(5), 1054–1063.
Le, V. H., Han, S. K., & Lee, S. G. (2011). A low power driver amplifier for unlicensed 2.4 GHz band. IEICE Transactions on Electronics, 94(1), 120–123.
Jia, H., Chi, B., Kuang, L., & Wang, Z. (2012). A 1 V, 69–73 GHz CMOS power amplifier based on improved Wilkinson power combiner. Microelectronics Journal, 43(6), 370–376.
Chenjian, W., Zhiqun, L., Nan, Y., Meng, Z., & Liang, C. (2013). \(0.18\upmu \)m CMOS low voltage power amplifier for WSN application. Telkomnika, 11(8), 4470–4476.
Elmala, M., Paramesh, J., & Soumyanath, K. (2006). A 90-nm CMOS Doherty power amplifier with minimum AM-PM distortion. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 41(6), 1323–1332.
Son, K. Y., Koo, B., & Hong, S. (2012). A CMOS power amplifier with a built-in RF predistorter for handset applications. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 60(8), 2571–2580.
Onizuka, K., Ishihara, H., Hosoya, M., Saigusa, S., Watanabe, O., & Otaka, S. (2012). A 1.9 GHz CMOS power amplifier with embedded linearizer to compensate AM-PM distortion. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 47(8), 1820–1827.
Chu, M., & Allstot, D. J. (2005). Elitist nondominated sorting genetic algorithm based RF IC optimizer. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems-I: Regular Papers, 52(3), 535–545.
Yeung, S. H., Chan, W. S., Ng, K. T., & Man, K. F. (2012). Computational optimization algorithms for antennas and RF/microwave circuit designs: An overview. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 8(2), 216–227.
Le, K. T. (2004). Designing a ZigBee-ready IEEE 802.15.4 compliant radio transceiver. http://web.eecs.umich.edu/~prabal/teaching/eecs598-w10/readings/Le04.pdf.
Allen, P. E., & Holberg, D. R. (2002). CMOS analog circuit design (2nd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Kazimierczuk, M. K. (2008). RF power amplifiers. New York: Wiley.
Ruiz, H. S., & Pérez, R. B. (2014). Linear CMOS RF power amplifiers: A complete design workflow. New York: Springer Science+Business Media.
AGILENT: Agilent ADS presentation on RF predistortion of power amplifiers. http://cp.literature.agilent.com/litweb/pdf/5989-9107EN.pdf.
Kennedy, J., Eberhart, R. C., & Shi, Y. (2001). Swarm intelligence. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann. http://www.swarmintelligence.org/SIBook/SI.php.
Hassan, R., Cohanim, B., & Weck, O. D. (2004). A comparison of particle swarm optimization and genetic algorithm. http://web.mit.edu/deweck/www/PDF_archive/3%20Refereed%20Conference/3_50_AIAA-2005-1897.pdf.
Robinson, J., & Rahmat-Samii, Y. (2004). Particle swarm optimization in electromagnetics. IEEE Transactions On Antennas And Propagation, 52(2), 397–407.
Coelho, L. S., & Sierakowski, C. A. (2008). A software tool for teaching of particle swarm optimization fundamentals. Advances in Engineering Software, 39, 877–887.
Nguyen, T. K., Krizhanovskii, V., Lee, J., Han, S. K., Lee, S. G., Kim, N. S., et al. (2006). A low-power RF direct-conversion receiver/transmitter for 2.4-GHz-band IEEE 802.15.4 standard in \(0.18\upmu \)m CMOS technology. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 54(12), 4062–4071.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manjula, S., Selvathi, D. Optimal Design of Low Power CMOS Power Amplifier Using Particle Swarm Optimization Technique. Wireless Pers Commun 82, 2275–2289 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2346-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2346-x