Abstract
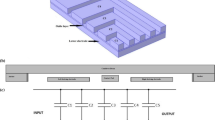
A new electro-thermally driven high Q tunable RF MEMS capacitor is proposed in this paper. The tuning mechanism of the varactor is chosen to obtain tuning; hence the capacitor has linear tuning range. In order to satisfy the low voltage operation of the varactor electro-thermal actuators were chosen as the drive and latching mechanism. However, those actuators consume lots of power, accordingly, in order to suppress that shortcoming a true mechanically latching mechanism is proposed which considerably decreases the total power consumption of the varactor. In order to investigate important operational aspects of the proposed varactor, different FEM simulations are carried out. The results are as follow; the Q-factor is 43.39 at 1 GHz for a 0.46 pF capacitance value. The tuning ratio is 1.17:1 and self-resonant frequency is 16.61 GHz. The propose varactor works by applying an actuation voltage of 3.1 V and consumes a power of 180 mW for about 2.7 ms for each tuning steps. The proposed varavtor of this paper can be a promising choice for low lass and low power RF tunable networks.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pirmoradi, E., Mirzajani, H., & Ghavifekr, H. B. (2014). Design and simulation of a novel electro-thermally actuated lateral RF MEMS latching switch for low power applications. Microsystem Technologies, pp. 1–11. doi:10.1007/s00542-014-2084-0.
Kaur, R., Tripathi, C. C., & Kumar, D. (2014). Low voltage Rf Mems capacitive shunt switches. Wireless Personal Communications, pp. 1–11. doi:10.1007/s11277-014-1823-y.
Mahmoodnia, H., & Ganji, B. A. (2013). A novel high tuning ratio MEMS cantilever variable capacitor. Microsystem Technologies, pp. 1–6.
Baghelani, M., & Ghavifekr, H. B. (2010). Ring shape anchored RF MEMS contour mode disk resonator for UHF communication applications. Microsystem Technologies, 16(12), 2123–2130.
Mirzajani, H., Nasiri, M., Ghavifekr, H. B. (2012) A novel MEMS-based wideband frequency tunable microstrip patch antenna. In: 20th Iranian conference on electrical engineering, Tehran, pp. 1383–1387. doi:10.1109/IranianCEE.2012.6292574.
Mirzajani, H., Ghavifekr, H. B., Aghdam, E. N., Demaghsi, H., & Vafaie, R. H. (2014). Enhancement of mechanical resonant modes by miniaturization of frequency tunable MEMS-enabled microstrip patch antenna. Microsystem Technologies, pp. 1–11. doi:10.1007/s00542-014-2126-7.
Nasiri, M., Mirzajani, H., Atashzaban, E., & Ghavifekr, H. B. (2013). Design and simulation of a novel micromachined frequency reconfigurable microstrip patch antenna. Wireless Personal Communications, 72(1), 259–282. doi:10.1007/s11277-013-1012-4.
Rebeiz, G. M. (2004). RF MEMS: Theory, design, and technology. Hoboken: Wiley.
Shim, Y., Wu, Z., & Rais-Zadeh, M. A. (2012). Multimetal surface micromachining process for tunable RF MEMS passives of microelectromechanical systems, Vol. 21, No. 4.
Borwick R. L., III, Stupara, P. A., DeNatalea, J., Andersona, R., Tsaia, C., Garretta, K., & Erlandson, R. (2012) A high Q, large tuning range MEMS capacitor for RF filter systems.
Yoon, J.-B., & Nguyen, C. T.-C. (2000). A high-Q tunable micromechanical capacitor with movable dielectric for RF applications. In: Technical digest, IEEE international electron devices meeting, San Francisco, California, pp. 489–492.
Rebeiz, G. M., & Muldavin, J. B. (2001). RF MEMS switches and switch circuits. Microwave Magazine IEEE, 2(4), 59–71.
Daneshmand, M., Fouladi, S., Mansour, R. R., Lisi, M., & Stajcer, T. (2009). Thermally actuated latching RF MEMS switch and its characteristics. IEEE Microwave Theory and Techniques Transactions, 57(12), 3229–3238.
Xiang, H. J., & Shi, Z. F. (2009). Static analysis for functionally graded piezoelectric actuators or sensors under a combined electro-thermal load. European Journal of Mechanics A, Solids, 28(2), 338–346.
Maloney, J. M. (2001). Fabrication and thermal actuation of 3-D micro electro mechanical systems, Master’s thesis, University of Maryland, College Park. pp. 33–41.
Leblond, H., Blondy, P., Baillargeat, D. (2006). In: Proceedings of the 36th European microwave conference, pp. 44–47.
Monajemi, P. (2006) In: Topical meeting on silicon monolithic integrated circuits in RF systems, pp. 222–225.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barzegar, S., Mirzajani, H. & Ghavifekr, H.B. A New Linearly Tunable RF MEMS Varactor with Latching Mechanism for Low Voltage and Low Power Reconfigurable Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 83, 2249–2265 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2514-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2514-z