Abstract
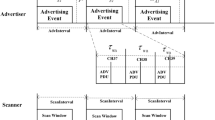
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) evolved from classical Bluetooth technologies for enabling short-range communication in different services and systems. BLE has many advantages over classical Bluetooth technologies, including low-cost deployment and low-power consumption. Recently, a very few number of research studies have been conducted to improve device discovery process of BLE. But, these studies have still some limitations. Prior studies have assumed that advertising PDUs are immediately processed as long as they are received successfully by a scanner. Practically, however, BLE devices may experience lots of collisions due to contention among neighbors, particularly in a crowded environment. With increasing number of BLE devices, delays of both device discovery and connection setup keep exponential growth, which could influence user experience in terms of either time or energy consumption. In this paper, an enhanced mechanism is proposed to enable BLE advertisers and scanners to learn the network contention and adjust their parameters accordingly, so as to achieve fast discovery latency. Through extensive simulations, the proposed mechanism has shown its effectiveness to reduce unexpected long latency in crowded BLE networks.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luigi, A., Iera, A., & Morabito, G. (2010). The internet of things: A survey. Computer Networks, 54(15), 2787–2805.
Giusto, D., Iera, A., Morabito, G., & Atzori, L. (Eds.). (2010). The Internet of Things. Berlin: Springer.
Bluetooth. S. (2010). Bluetooth Core Specification Version 4.0. Specification of the Bluetooth System.
Liu, J., Chen, C., & Ma, Y. (2012). Modeling and performance analysis of device discovery in Bluetooth Low Energy networks. In IEEE Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), 2012 (pp. 1538–1543).
Duflot, M., Kwiatkowska, M., Norman, G., & Parker, D. (2006). A formal analysis of bluetooth device discovery. International Journal on Software Tools for Technology Transfer, 8(6), 621–632.
Basagni, S., Bruno, R., & Petrioli, C. (2006). Device discovery in Bluetooth networks: A scatternet perspective. Lecture notes in computer science (vol. 2345).
Scott, D., Sharp, R., & Upton, E. (2005). Using visual tags to bypass Bluetooth device discovery. ACM SIGMOBILE Mobile Computing and Communications Review (vol. 9, No. 1).
Drula, C., Amza, C., Rousseau, F., & Duda, A. (2007). Adaptive energy conserving algorithms for neighbor discovery in opportunistic Bluetooth networks. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 25(1), 96–107.
Liu, J., & Chen, C. (2012). Energy analysis of neighbor discovery in Bluetooth Low Energy networks. Nokia.(nd).
Liu, J., Chen, C., Ma, Y., & Xu, Y. (2013). Adaptive device discovery in bluetooth low energy networks. In IEEE 77th vehicular technology conference (VTC Spring), 2013 (pp. 1–5).
Liu, J., Chen, C., Ma, Y., & Xu, Y. (2013). Energy analysis of device discovery for bluetooth low energy. In IEEE 78th cehicular technology conference (VTC Fall), 2013 (pp. 1–5).
Cho, K., Park, W., Hong, M., Park, G., Cho, W., Seo, J., & Han, K. (2015). Analysis of Latency Performance of Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) Networks. Sensors, 15(1), 59–78.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the BK21 Plus project (SW Human Resource Development Program for Supporting Smart Life) funded by the Ministry of Education, School of Computer Science and Engineering, Kyungpook National University, Korea (21A20131600005). This work was supported by the IT R&D program of MISP/KEIT. [10041145, Self-Organized Software platform (SoSp) for Welfare Devices]. This research was financially supported by the Ministry of Education (MOE) and National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Human Resource Training Project for Regional Innovation (No. 2014H1C1A1067126). This research is funded by “Technology development for performance enhancement of BLE networks” Project by Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., 2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, G., Park, W., Hong, M. et al. An Adaptive Parameter Setting Algorithm to Enhance Performance in Self-Organizing Bluetooth Low Energy Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 87, 953–969 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2619-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2619-4