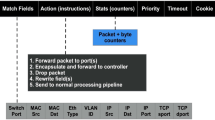
Abstract
Future internet is required to be flexible, scalable, reliable, secure and having other advanced features. Software Defined Networking (SDN) fulfills most of the task to achieve require functioning. OpenFlow technology is the first standard for SDN which executes the protocols based on the required application. It is also capable for controlling multiple hardware or software switches from a single controller. This can be achieved by the separation of data plane and control plane from a network core devices. In this paper, a proposed architecture of an OpenFlow based small campus network is deployed. The performance analysis for a custom designed network model is achieved by executing few networking test on a defined nodes using network control protocols. The performance analysis of bandwidth, throughput and other network parameters between nodes for Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and User Datagram Protocol (UDP) connection is also performed. A custom model has been designed using a prototype network emulator that is Mininet and the code for network topology is executed in Python script.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A standard defined by RFC 826 in 1982.
References
Lo, C.-C., Chin, H.-H., Horng, M.-F., Kuo, Y.-H., & Hsu, J.-P. (2014). a flexible network management framework based on OpenFlow technology. In M. Ali, J. S. Pan, S. M. Chen, & M. F. Horng (Eds.), Modern advances in applied intelligence (pp. 298–307). Switzerland: Springer.
Jammal, M., Singh, T., Shami, A., Asal, R., & Li, Y. (2014). Software-defined networking: State of the art and research challenges. Computer Networks, 72, 74–98.
van der Pol, R. (2011). OpenFlow - Technology Assessment, GigaPort3 RoN 2011 Deliverable D1.2, December 2011. USA. [Online]. https://www.surf.nl/binaries/content/assets/surf/en/2013/RoN-2011-D1.2.pdf.
McKeown, N., Anderson, T., Balakrishnan, H., Parulkar, G., Peterson, L., Rexford, J., et al. (2008). OpenFlow: Enabling Innovation in Campus Networks. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 38(2), 69–74.
Home–Open Networking Foundation. (2013). [Online]. https://www.opennetworking.org/index.php?lang=en
HP. (2012). Realizing the power of SDN with HP Virtual Application Networks. [Online]. http://h17007.www1.hp.com/docs/interopny/4AA4-3871ENW.pdf
Lara, A., Kolasani, A., & Ramamurthy, B. (2014). Network innovation using OpenFlow: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 16(1), 493–512.
OpenFlow Switch Specification, Version 1.1.0 (Wire Protocol 0x02). (2011). [Online]. http://archive.openflow.org/documents/openflow-spec-v1.1.0.pdf
The Network Simulator – NS-2. [Online]. http://www.isi.edu/nsnam/ns/
Network Planning and Simulation (OPNET) | Network Simulation (OPNET Modeler Suite) | Riverbed, Riverbed, [Online]. http://www.riverbed.com/products-solutions/products/network-performance-management/network-planning-simulation/Netwrok-Simulation.html
OMNeT++ Community. OMNeT++ Network Simulation Framework. [Online]. http://www.omnetpp.org/
QualNet | SCALABLE Network Technologies. [Online]. http://web.scalable-networks.com/content/qualnet
Team, T. M. (2012).Mininet: An Instant Virtual Network on Your Laptop (or Other PC). [Online]. http://www.mininet.org
Lantz, B., Heller, B., & McKeown, N. (2010). A network in a laptop: Rapid prototyping for software-defined networks. In: Proceedings of the 9th ACM SIGCOMM Workshop on Hot Topics in Networks. New York, NY, USA.
Jha, R., Kharga, P., Bholebawa, I., Satyarthi, S., Gupta, A., & Kumari, S. (2014). OpenFlow Technology: A Journey of Simulation Tools. International Journal of Computer Network and Information Security(IJCNIS), 6(11), 49–55. doi:10.5815/ijcnis.2014.11.07.
T.E. Dickey. (2013). XTERM—Terminal emulator for the X Window system. [Online]. http://invisible-island.net/xterm/
L. MartinGarcia (2010). [Online]. http://www.tcpdump.org/
Iperf—The TCP/UDP Bandwidth Measurement Tool. [Online]. http://iperf.fr/
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bholebawa, I.Z., Jha, R.K. & Dalal, U.D. Performance Analysis of Proposed OpenFlow-Based Network Architecture Using Mininet. Wireless Pers Commun 86, 943–958 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2963-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-2963-4