Abstract
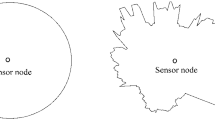
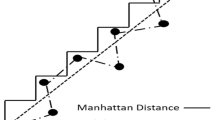
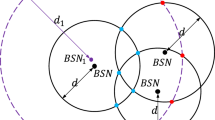
In internet of things (IoT) study, to determine that the location of an event is the key issue, realize that a target location in IoT is one of the research hotspots by using the multihop range-free method. Multihop range-free could obtain relatively reasonable location estimation in the isotropic network, however, during the practical application, it tends to be affected by various anisotropic factors such as the electromagnetic interference, barriers and network attack, which can significantly reduce its performance. In accordance with these problems faced by multihop range-free, this paper proposes a novel IoT localization method: location estimation-kernel partial least squares (LE-KPLS). First of all, this method uses kernel function to define the connectivity information (hop-counts) between nodes, then, the maximum covariance is used to guide and build the inter-node localization model, and then, this model and the hop-counts between the unknown nodes and beacons are used to estimate the coordinate of the unknown nodes. Compared to the existing methods, the LE-KPLS has a high localization precision, great stability and strong generalization performance, without having a high requirement of the number of beacons, and it can well adapt to numerous complicated environments.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atzori, L., Iera, A., & Morabito, G. (2010). The internet of things: A survey. Computer Networks, 54(2010), 2787–2805.
Cordeiro, C. de M., & Agrawal, D. P. (2011). Ad hoc and sensor networks: Theory and applications. Singapore: World Scientific.
Hazas, M., Scott, J., & Krumm, J. (2004). Location-aware computing comes of age. IEEE Computer, 37(2), 95–97.
Chen, Z., et al. (2013). A localization method for the internet of things. The Journal of Supercomputing, 63(3), 657–674.
Liu, Y., & Yang, Z. (2011). Location, localization, and localizability location-awareness technology for wireless networks. Berlin: Springer.
Wu, G., et al. (2012). A novel range-free localization based on regulated neighborhood distance for wireless ad hoc and sensor networks. Computer Networks, 56(2012), 3581–3593.
Xiao, Q., et al. (2010). Multihop range-free localization in anisotropic wireless sensor networks: A pattern-driven scheme. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 9(11), 1592–1607.
Lim, H., & Hou, J. C. (2009). Distributed localization for anisotropic sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 5(2), 1–26.
Niculescu, D., & Nath, B. (2003). DV based positioning in ad hoc networks. Telecommunication Systems, 22(1–4), 267–280.
Zhong, Z., & He, T. (2011). RSD: A metric for achieving range-free localization beyond connectivity. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 22(11), 1943–1951.
Li, M., & Liu, Y. (2010). Rendered path: Range-free localization in anisotropic sensor networks with holes. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 18(1), 320–332.
Tan, G., et al. (2013). Connectivity-based and anchor-free localization in large-scale 2D/3D sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 10(1), 1–21.
Alsheikh, M. A., et al. (2014). Machine learning in wireless sensor networks: Algorithms, strategies, and applications. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 99, 1–24.
Shang, Y., et al. (2003). Localization from mere connectivity. In MobiHoc’03 Proceedings of the 4th ACM international symposium on mobile ad hoc networking and computing. Annapolis, MD.
Shang, Y., & Ruml, W. (2004). Improved MDS-based localization. In INFOCOM 2004.
Hogben, L. (2007). Handbook of linear algebra. UK: CRC Press.
Lee, J., Chung, W., & Kim, E. (2013). A new kernelized approach to wireless sensor network localization. Information Sciences, 243(2013), 20–38.
Lee, J., Choi, B., & Kim, E. (2013). Novel range-free localization based on multidimensional support vector regression trained in the primal space. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 24(7), 1099–1113.
Shawe-Taylor, J., & Cristianini, N. (2004). Kernel methods for pattern analysis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Xu, S., et al. (2011). Multi-output least-squares support vector regression machines. Pattern Recognition Letters, 34(9), 1078–1084.
Rosipal, R., & Trejo, L. J. (2001). Kernel partial least squares regression in reproducing kernel Hilbert space. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2, 97–123.
Baudat, G., & Anouar, F. (2000). Generalized discriminant analysis using a kernel approach. Neural Computation, 12(10), 2385–2404.
Chen, J., et al. (2011). Semi-supervised Laplacian regularized least squares algorithm for localization in wireless sensor networks. Computer Networks, 55(10), 2481–2491.
Cherkassky, V., & Ma, Y. (2004). Practical selection of SVM parameters and noise estimation for SVM regression. Neural Networks, 17(2004), 113–126.
Zhou, G., et al. (2006). Models and solutions for radio irregularity in wireless sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 2(2), 221–262.
Acknowledgments
The paper is sponsored by the NSF of China (61272379), Prospective and Innovative Project of Jiangsu Province (BY2012201); China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M571633), Jiangsu Postdoctoral Science Foundation (1401016B), Natural Science Foundation of the Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions of China (15KJB520009), Project of Modern Educational Technology of Jiangsu Province (2015-R-42440), Jiangsu Province Undergraduate Training Programs for Innovation and Entrepreneurship (201513573005Z) and Doctoral Scientific Research Startup Foundation of Jinling Institute of Technology (JIT-B-201411).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, X., Yang, Z., Song, A. et al. A Novel Multihop Range-Free Localization Based on Kernel Learning Approach for the Internet of Things. Wireless Pers Commun 87, 269–292 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-3042-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-015-3042-6