Abstract
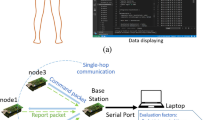
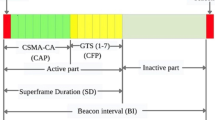
This paper investigates reliability of wireless body area networks based on the IEEE 802.15.6 standard, for the scheduled access mode in an error prone channel. In scheduled access mode, during a time slot that is allocated for communication between a sensor node and the hub, the frame transmission fails if the link is in the deep fade state. To improve reliability of the network, we propose an efficient scheme for packet retransmission. The proposed scheme relies on allocation of spare slots for packet retransmissions in each superframe. We then present analytical models to find the energy efficiency and reliability of the network under the proposed retransmission scheme. Through analytical and simulation results, we establish that the proposed retransmission scheme can significantly improve the reliability of the network in the scheduled access mode, without causing degradation of energy efficiency.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cao, H., Leung, V., Chow, C., & Chan, H. (2009). Enabling technologies for wireless body area networks: A survey and outlook. Communications Magazine, IEEE, 47(12), 84–93.
Boulis, A., Smith, D., Miniutti, D., Libman, L., & Tselishchev, Y. (2012). Challenges in body area networks for healthcare: The MAC. Communications Magazine, IEEE, 50(5), 100–106.
IEEE Standard for Local and metropolitan area networks Part 15.6: Wireless Body Area Networks, 29 Feb. 2012.
Miniutti, D., Smith, D., Hanlen, L., Zhang, A., Boulis, A., Rodda, D., & Gilbert, B. (2010) Sleeping channel measurements for body area networks, IEEE 802.15-09-0778-01-0006.
Kailas, A. (2011). Power allocation strategies to minimize energy consumption in wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp. 2204–2207.
Huang, X., Shan, H., Shen, X. (2011). On energy efficiency of cooperative communications in wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on wireless communications and networking conference, pp. 1097–1101.
Domingo, M. C. (2011). Packet size optimization for improving the energy efficiency in body sensor networks. ETRI Journal, 33(3), 299–309.
Li, Y., Qi, X., Ren, Z., Zhou, G., Xiao, D., & Deng, S. (2011). Energy modeling and optimization through joint packet size analysis of BSN and WiFi networks. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on performance computing and communications, pp. 1–8.
Deepak, K.S., & Babu, A.V. (2012). Packet size optimization for energy efficient cooperative wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of IEEE India conference (INDICON), pp. 736–741.
Omeni, O., Wong, A., Burdett, A. J., & Toumazou, C. (2008). Energy efficient medium access protocol for wireless medical body area sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems, 2(4), 251–259.
Fang, G., & Dutkiewicz, E. (2009). BodyMAC: Energy efficient TDMA-based MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on Communications and Information Technology, ISCIT, pp. 1455–1459.
Li, H., & Tan, J. (2010). Heartbeat-driven medium-access control for body sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 14(1), 44–51.
Marinkovic, S., Spagnol, C., & Popovici, E. (2009). Energy efficient TDMA-based MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. In Proc. of IEEE conference on sensor technologies and applications, pp. 604–609.
Wang, B., Wang, L., Huang, B.Y., Wu, D., Lin, S.J., Gu, J., Zhang, Y.T., & Chen, W. (2009). A low-complexity medium access control framework for body sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on engineering in medicine and biology society, pp. 2446–2449.
Al Ameen, M., Ullah, N., Sanaullah Chowdhury, M., Riazul Islam, S. M., & Kwak, Kyungsup. (2012). A power efficient MAC protocol for wireless body area networks. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2012(1), 1–17.
Ullah, S., Chen, M., & Sup Kwak, K. (2012). Throughput and delay analysis of IEEE 802.15.6-based CSMA/CA protocol. Journal of Medical Systems, 36(6), 3875–3891.
Rashwand, S., Misic, J., & Khazaei, H. (2011). Performance analysis of IEEE 802.15. 6 under saturation condition and error prone channel. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on wireless communications and networking conference, pp. 1167–1172.
Jung, B.H., Akbar, R.U., & Sung, D.K. (2012). Throughput, energy consumption, and energy efficiency of IEEE 802.15. 6 body area network (BAN) MAC protocol. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on personal indoor and mobile radio communications, pp. 584–589.
Sarkar, S., Misra, S., Bandyopadhyay, B., Chakraborty, C., & Obaidat, M. (2015). Performance analysis of IEEE 802.15. 6 MAC protocol under non-ideal channel conditions and saturated traffic regime. In IEEE Transactions on computers, vol. 64, no. 10, pp. 2912–2925.
Tachtatzis, C., Di Franco, F., Tracey, D.C., Timmons, N.F., & Morrison, J. (2010). An energy analysis of IEEE 802.15. 6 scheduled access modes. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on GLOBECOM workshops, pp. 1270–1275.
Prabh, K., & Hauer, J.H. (2011). Opportunistic packet scheduling in body area networks. In Proceedings of European conference on wireless sensor networks (EWSN), Bonn, Germany.
Arrobo, G.E., & Gitlin, R. D. (2011). Improving the reliability of wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, pp. 2192–2195.
Arrobo, G.E., Haas, Z.J., & Gitlin, R.D. (2012). Temporal diversity coding for improving the performance of wireless body area networks. In Proceedings of ICST (Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications Engineering) 7th international conference on body area networks, pp. 187–190.
Liang, T., & Smith, D. B. (2014). Energy-efficient, reliable wireless body area networks: Cooperative diversity switched combining with transmit power control. IET Electronic Letters, 50(22), 1641–1643.
Liu, B., You, Y., & Chen, C.W. (2015). CS-based reliable transmission strategy for Wireless Body Area Networks. In Signal and information processing (ChinaSIP), IEEE China summit and international conference on, pp. 448–452.
Ntouni, G. D., Lioumpas, A. S., & Nikita, K. S. (2014). Reliable and energy-efficient communications for wireless biomedical implant systems. Biomedical and Health Informatics, IEEE Journal of, 18(6), 1848–1856.
Zhang, R., Moungla, H., & Mehaoua, A. (2015). A reliable and energy-efficient leader election algorithm for wireless body area networks. In Communications (ICC), 2015 IEEE international conference on, pp. 530–535.
Tselishchev, Y., Libman, L., & Boulis, A. (2011). Reducing transmission losses in body area networks using variable TDMA scheduling. In Proceedings of 12th IEEE international symposium world of wireless mobile and multimedia networks, Lucca, Italy.
Tselishchev, Y., Libman, L., & Boulis, A. (2011). Energy efficient retransmission strategies under variable TDMA scheduling in body area networks. In Proceedings of 36th IEEE conference on local computer networks, Bonn, Germany.
Torabi, N., & Leung, V. (2014). Cross-layer design for prompt and reliable transmissions over body area networks. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 18(4), 1303–1316.
Mouzehkesh, N., Zia, T., Shafigh, S., & Zheng, L. (2015). Dynamic backoff scheduling of low data rate applications in wireless body area networks. In Wireless Networks, Springer, pp. 1–22. doi:10.1007/s11276-015-0929-9.
Zhang, Q., Chaturvedi, M., & Jacobsen, R.H. (2014). Performance study of the enhancement schemes for Baseline MAC of Body Area networks. In Medical information and communication technology (ISMICT), IEEE international symposium on, pp.1–5.
Nordic nRF24L01+. http://www.nordicsemi.com/.
Zarlink ZL70101. http://www.zarlink.com/zarlink/.
Yazdandoost, K. (2010). Task group 6 channel model. https://mentor.ieee.org/802.15/dcn/08/15-08-0780-10-0006-tg6-channel-model.
Reusens, E., Joseph, W., Latré, B., Braem, B., Vermeeren, G., Tanghe, E., et al. (2009). Characterization of on-body communication channel and energy efficient topology design for wireless body area networks. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 13(6), 933–945.
Fort, A., Ryckaert, J., Desset, C., De Doncker, P., Wambacq, P., & Van Biesen, L. (2006). Ultra-wideband channel model for communication around the human body. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 24(4), 927–933.
Goldsmith, A. (2005). Wireless communications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Zhen, B., Patel, M., Lee, S., Won, E., & Astrin, A. (2008). IEEE 802.15 TG6 technical requirements document (TRD). https://mentor.ieee.org/802.15/documents?isdcn=644&isgroup=0006.
Sankarasubramaniam, Y., Akyildiz, I.F., & McLaughlin, S.W. (2003). Energy efficiency based packet size optimization in wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE conference on sensor network protocols and applications, pp. 1–8.
Soykan, O. (2002). Power sources for implantable medical devices. Medical Device Manufacturing and Technology, pp.76–79.
Castalia Simulator, http://castalia.npc.nicta.com.au.
Hanlen, L., & Rodda, D. (2010). Public dataset for BAN radio channel models. http://nicta.com.au/research/projects/humanperformanceimprovement/researchoutcomes/wireless.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deepak, K.S., Babu, A.V. Enhancing Reliability of IEEE 802.15.6 Wireless Body Area Networks in Scheduled Access Mode and Error Prone Channels. Wireless Pers Commun 89, 93–118 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3254-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3254-4