Abstract
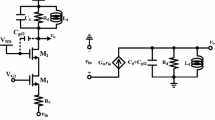
This paper describes the design and implementation of a low-power CMOS class-E Chireix RF outphasing power amplifier (PA) for WLAN applications. The proposed circuit is based on cascode class-E topology with two-stage structure and Chireix power combiner with a floating load. This class-E topology adopts self-biased technique and current-reused technique that avoids using thick-oxide transistors and can enhance the driving ability and power gain. Additionally, the Chireix combiner can reduce the loss of power and improve the efficiency by avoiding the use of isolation resistance. With a 2.5 V power supply, the realized prototype achieved 21.4 dBm of maximum output power and 29.9 % of average power-added efficiency (PAE) at 2.4 GHz. When operated for minimum input levels at 2.5 V, it reached 38.8 dB power gain. For a WLAN OFDM signal with 20 MHz, the error vector magnitude of 3 % is achieved with peak drain efficiency of 62 %. Moreover, the outphasing power amplifier is fully integrated with TSMC 0.18-µm CMOS technology and the chip area including testing pads is 1.07 × 1.17 mm2.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chireix, H. (1935). High power outphasing modulation. Proceedings of the IRE, 23(11), 1370–1392.
Raab, F. H. (1985). Efficiency of outphasing RF power-amplifier systems. IEEE Transactions on Communications, 33(10), 1094–1099.
Doherty, W. H. (1936). A new high efficiency power amplifier for modulated waves. Proceedings of the IRE, 24(9), 1163–1182.
Kahn, L. R. (1952). Single-sideband transmission by envelope elimination and restoration. Proceedings of the IRE, 40(7), 803–806.
Oishi, K., Yoshida, E., Sakai, Y., Takauchi, H., Kawano, Y., Shirai, N., et al. (2014). A 1.95 GHz fully integrated envelope elimination and restoration CMOS power amplifier with envelope/phase generator and timing aligner for WCDMA and LTE. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 49, 2915–2924.
Díaz, D., García, O., Oliver, J. A., Alou, P., Vasic, M., & Cobos, J. A., et al. (2013). High efficiency power amplifier applying the envelope elimination and restoration technique with a single stage envelope amplifier with ripple cancellation network. IEEE energy conversion congress and exposition, pp. 5586–5591.
Kim, W. Y., Son, H. S., Jang, J. Y., Kim, J. H., Oh, I. Y., & Park, C. S. (2014). A fully integrated triple-band CMOS hybrid-EER transmitter for WCDMA/LTE applications. IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium, pp. 1–3.
Kim, B., Kim, J., Kim, D., Son, J., Cho, Y., Kim, J., & Park, B. (2013). Push the envelope: Design concepts for envelope-tracking power amplifiers. IEEE Microwave Magazine, 14(3), 68–81.
Rautio, T., Harju, H., Hietakangas, S., & Rahkonen, T. (2008). Envelope tracking power amplifier with static predistortion linearization. International Journal of Circuit Theory and Applications, 37(2), 365–375.
Kim, J., Kim, D., Cho, Y., Kang, D., Park, B., Moon, K., & Kim, B. (2014). Analysis of envelope-tracking power amplifier using mathematical modeling. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 62(6), 1352–1362.
Woo, J. L., Jeon, M. S., & Kwon, Y. (2014). Dynamic FET stack control for enhanced efficiency in envelope tracking power amplifiers. In: IEEE MTT-S international microwave symposium, pp. 1–4.
Kim, J., Kim, D., Cho, Y., Kang, D., & Kim, B. (2013). Envelope-tracking power amplifier with enhanced back-off efficiency using average switch current control of supply modulator. Asia-Pacific microwave conference proceedings, pp. 435–437.
Kim, J., Kim, D., Cho, Y., Kang, D., Park, B., & Kim, B. (2013). Envelope-tracking two-stage power amplifier with dual-mode supply modulator for LTE applications. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 61(1), 543–552.
Kim, J., Kim, D., Cho, Y., Kang, D., Park, B., Moon, K., & Kim, B. (2013). Supply modulator for envelope-tracking operation of dual-mode handset power amplifier. European microwave conference, pp. 1315–1318.
Hekkala, A., Kotelba, A., Lasanen, M., Järvensivu, P., & Mämmelä, A. (2012). Novel digital compensation approaches for envelope tracking amplifiers. Wireless Personal Communications, 62(1), 55–77.
Zhao, J., Wolf, R., & Ellinger, F. (2013). Fully integrated LTE Doherty power amplifier. In: International semiconductor conference Dresden-Grenoble, pp. 1–3.
Hu, S., Kousai, S., Park, J. S., Chlieh, O. L., & Wang, H. (2014). A +27.3 dBm transformer-based digital Doherty polar power amplifier fully integrated in bulk CMOS. IEEE radio frequency integrated circuits symposium, pp. 235–238.
Chen, W., Zhang, S., Lin, Y., Liu, Y., & Ghannouchi, F. M. (2014). A concurrent dual-band uneven Doherty power amplifier with frequency-dependent input power division. IEEE Transaction on Circuits and System I, 61(2), 552–561.
Zhao, C., Park, B., Cho, Y., & Kim, B. (2013). Analysis and design of CMOS Doherty power amplifier using voltage combining method. In: IEEE international wireless symposium, pp. 1–4.
Akbarpour, M., Helaoui, M., & Ghannouchi, F. M. (2013). Broadband Doherty power amplifiers. IEEE topical conference power amplifier wireless radio application, pp. 1–3.
Boumaiza, S., Golestaneh, H., Ali Abadi, M. N., Mohamed, A. M. M., & Wu, D. Y. (2014). Broadband Doherty power amplifiers: Advances and challenges. IEEE 15th annual wireless microwave technology conference, pp. 1–6.
Zhao, C., Park, B., & Kim, B. (2014). Complementary metal-oxide semiconductor doherty power amplifier based on voltage combining method. Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, IET, 8(3), 131–136.
Xia, J., Zhu, X., Zhang, L., Zhai, J., & Sun, Y. (2013). High-efficiency GaN Doherty power amplifier for 100-MHz LTE-advanced application based on modified load modulation network. IEEE Transactions on Microwave Theory and Techniques, 61(8), 2911–2921.
Lee, M. W., Kam, S. H., Lee, Y. S., & Jeong, Y. H. (2010). A highly efficient three-stage Doherty power amplifier with flat gain for WCDMA applications. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 24, 17–18.
Fritzin, J., Jung, Y., Landin, P. N., Händel, P., Enqvist, M., & Alvandpour, A. (2011). Phase Predistortion of a Class-D outphasing RF amplifier in 90 nm CMOS. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 58(10), 642–646.
Fritzin, J., Svensson, C., & Alvandpour, A. (2011). A +32 dBm 1.85 GHz class-D outphasing RF PA in 130 nm CMOS for WCDMA/LTE. Proceedings of the ESSCIRC, pp. 127–130.
Tai, W., Xu, H., Ravi, A., Lakdawala, H., Bochobza-Degani, O., Richard Carley, L., & Palaskas, Y. (2012). A transformer-combined 31. 5 dBm outphasing power amplifier in 45 nm LP CMOS with dynamic power control for back-off power efficiency enhancement. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 47(7), 1646–1658.
Jung, Y., Fritzin, J., Enqvist, M., & Alvandpour, A. (2013). Least-squares phase predistortion of a +30 dBm class-D outphasing RF PA in 65 nm CMOS. Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, IEEE Transactions on, 60(7), 1915–1928.
Ding, L., Hur, J., Hezar, R., & Haroun, B. (2014). A 25 dBm outphasing power amplifier with novel non-isolated combining network. IEEE radio frequency integrated circuits symposium, pp. 231–234.
Banerjee, A., Hezar, R., Ding, L., Schemm, N., & Haroun, B. (2014). A 29.5 dBm Class-E outphasing RF power amplifier with performance enhancement circuits in 45 nm CMOS. European solid state circuits conference 40th, pp. 467–470.
Godoy, P. A., Chung, S., Barton, T. W., Perreault, D. J., & Dawson, J. L. (2012). A 2.4-GHz, 27-dBm asymmetric multilevel outphasing power amplifier in 65-nm CMOS. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 47(10), 2372–2384.
Vander Heijden, M. P., & Acar, M. (2014). A radio-frequency reconfigurable CMOS-GaN class-E chireix power amplifier. In: IEEE MTT-S International microwave symposium, pp 1–4.
Raab, F. H., & Sokal, N. O. (1978). Transistor power losses in the class-E tuned power amplifier. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 13(6), 912–914.
Hayati, M., Floberg, H., & Lotfi, A. (2014). Modeling and analysis of class-E zero-voltage switching amplifier at any grading coefficient and duty ratio. Journal of Electromagnetic Waves and Applications, 28(5), 655–668.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the Open Fund Project of Key Laboratory (No. 12K012) and Young Teachers Program in Hunan Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Du, S., Zhu, X. A Low-Power CMOS Class-E Chireix RF Outphasing Power Amplifier for WLAN Applications. Wireless Pers Commun 90, 1547–1561 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3409-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-016-3409-3